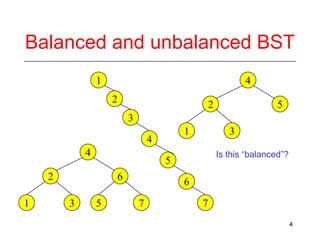
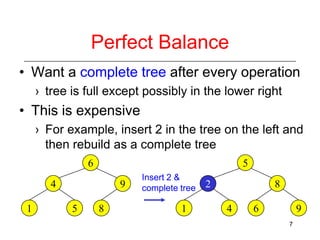
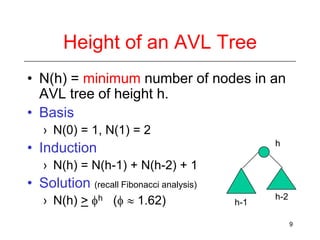
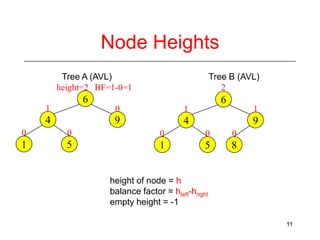
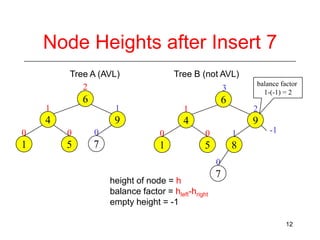
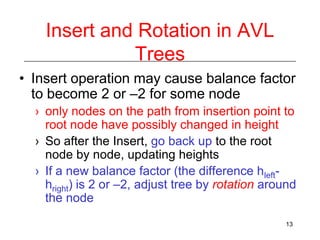
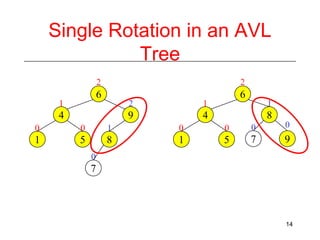
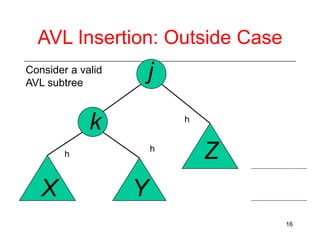
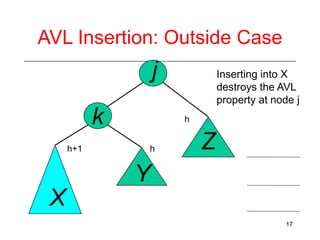
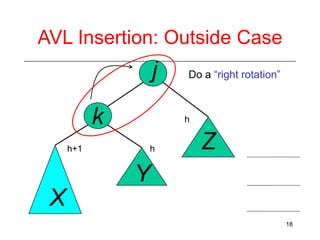
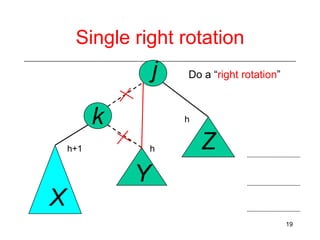
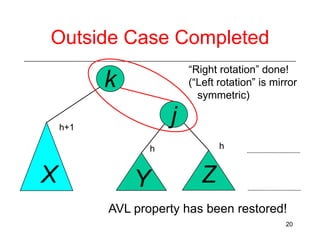
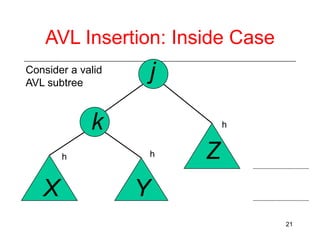
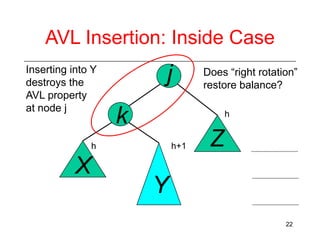
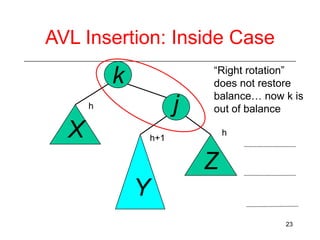
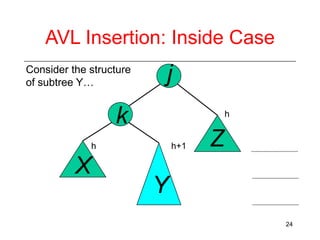
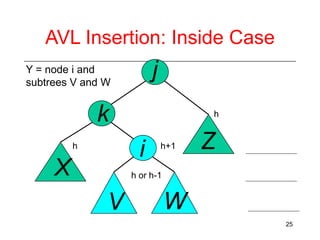
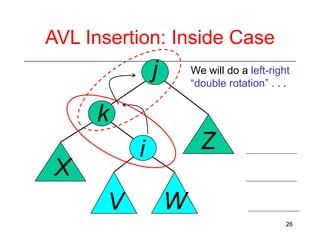
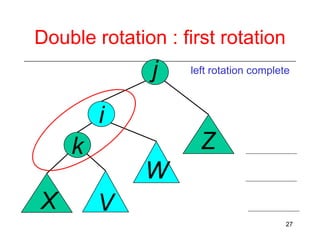
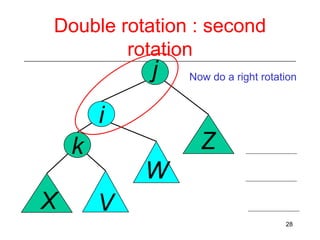
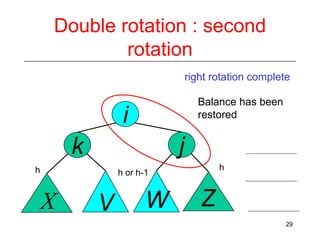
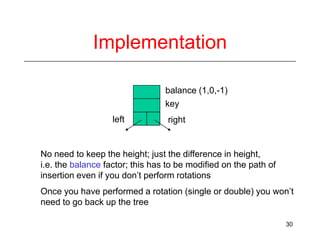
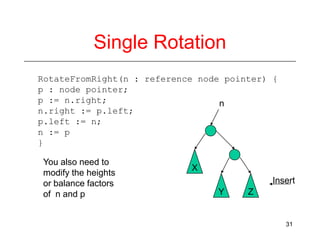
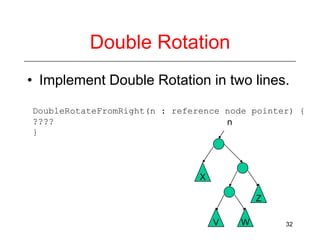
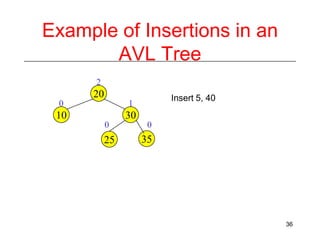
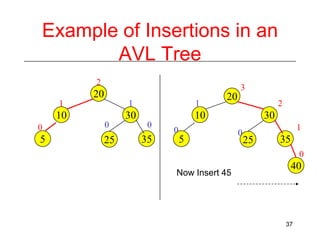
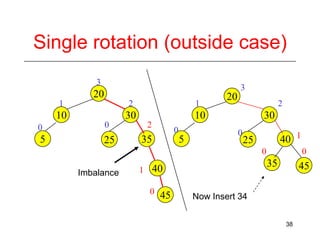
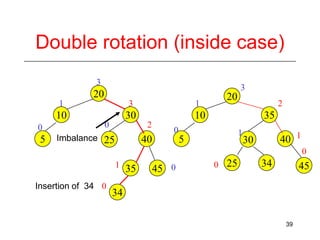
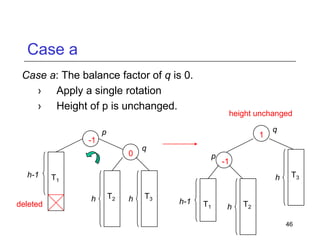
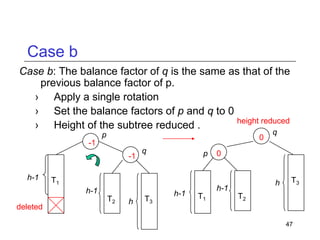
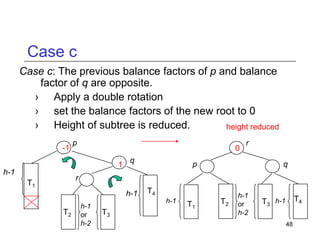
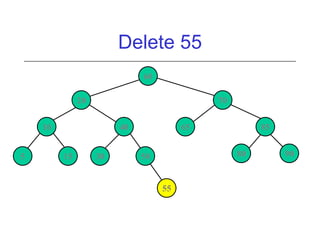
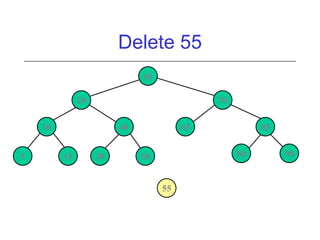
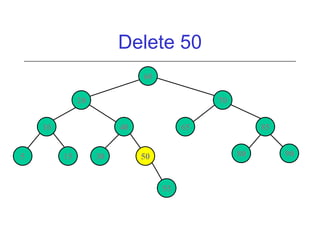
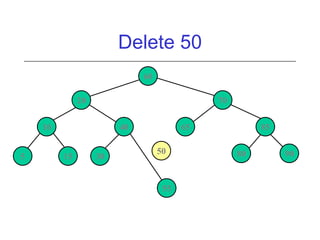
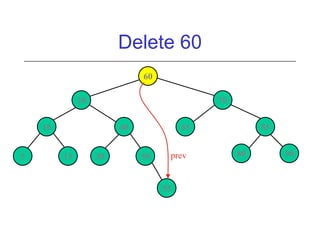
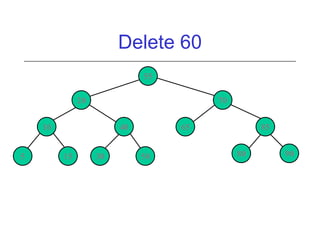
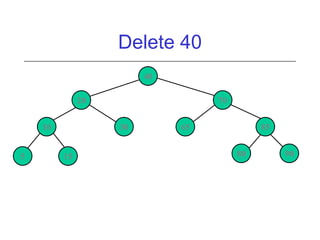
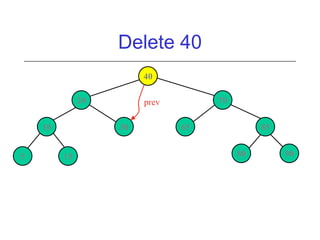
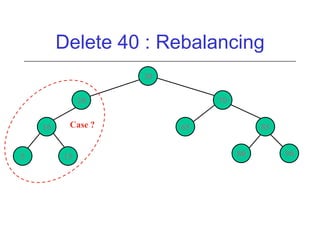
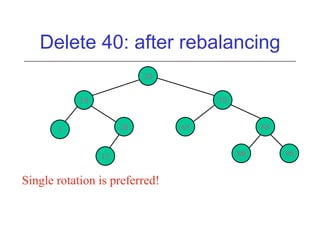
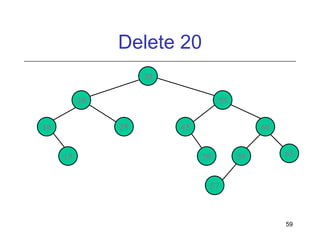
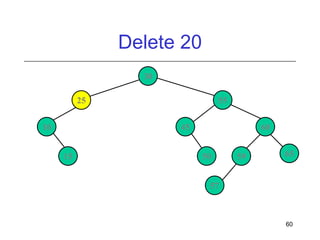
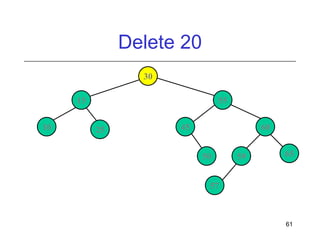
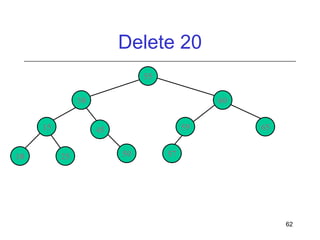
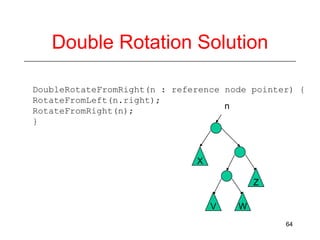
This document discusses AVL trees, which are self-balancing binary search trees. It begins by explaining that binary search trees have O(log N) best case time for operations but can degrade to O(N) in the worst case if the tree becomes unbalanced. The document then introduces AVL trees, which maintain balance by ensuring that the heights of any node's two child subtrees differ by at most one. This guarantees search, insertion, and deletion operations take O(log N) time. The document explains the node height calculation and covers insertion and deletion algorithms in AVL trees through examples, including single and double rotations to rebalance the tree.