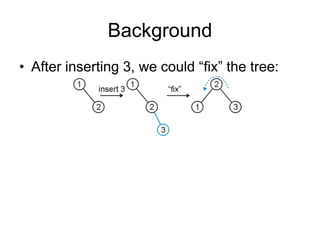
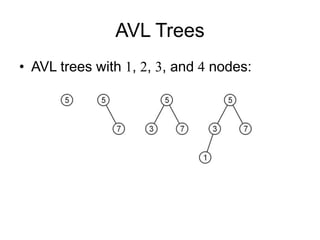
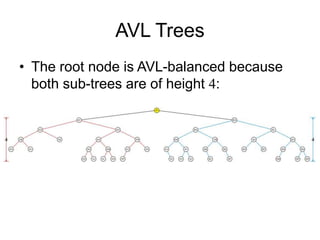
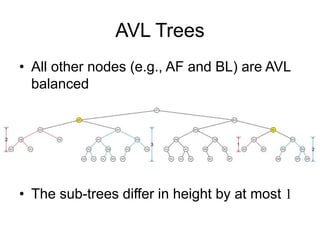
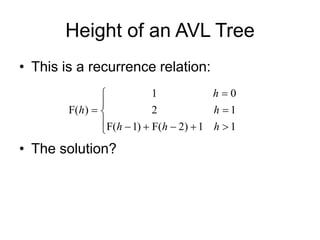
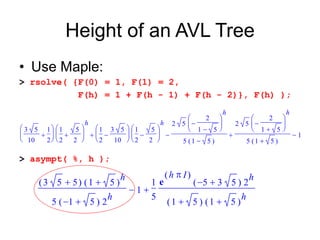
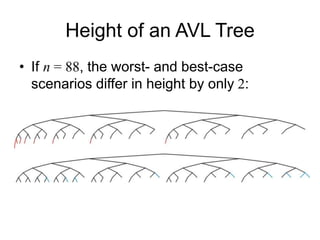
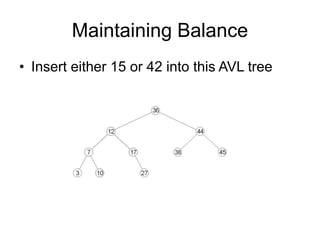
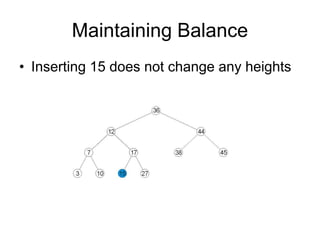
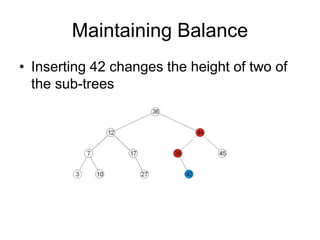
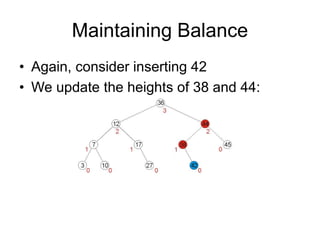
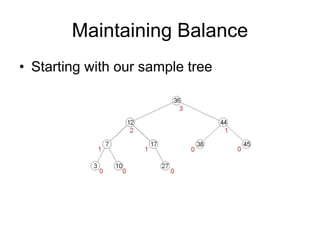
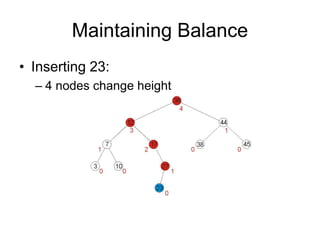
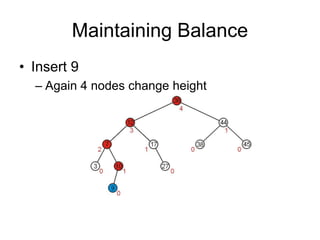
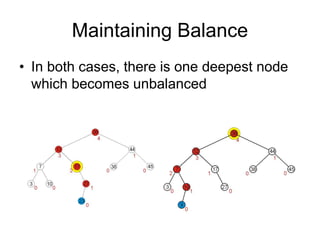
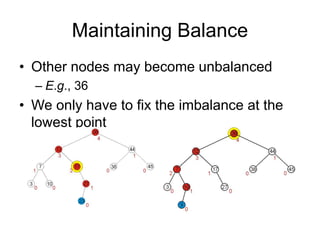
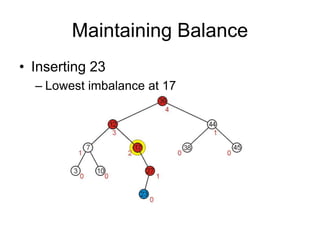
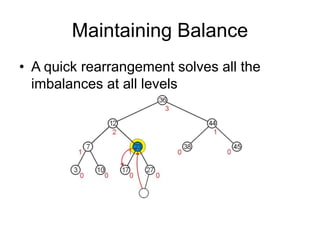
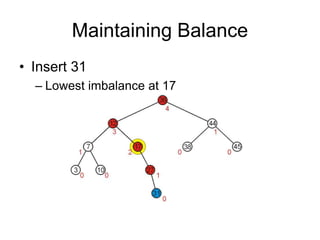
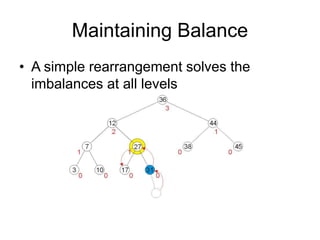
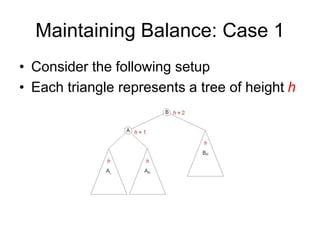
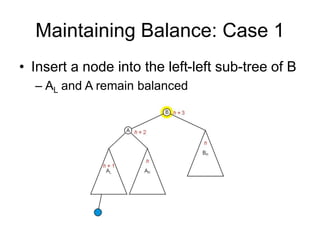
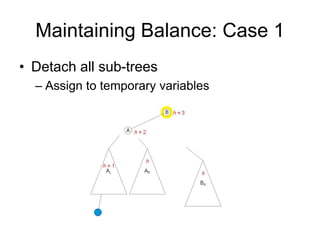
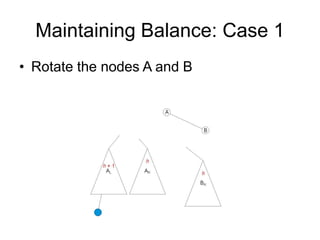
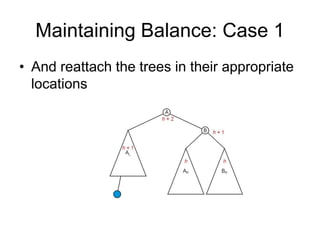
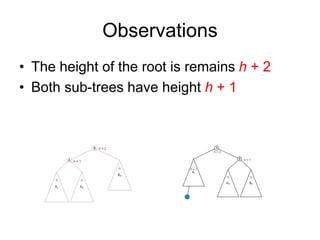
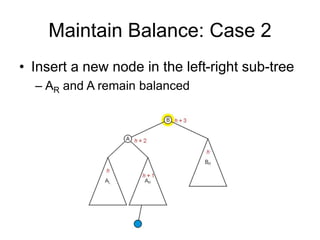
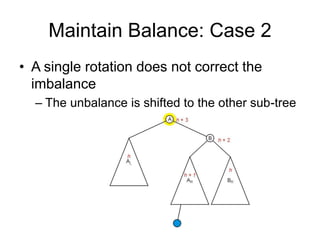
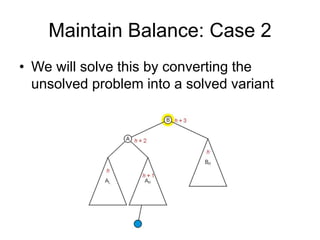
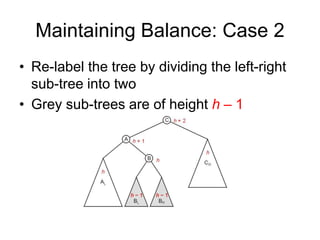
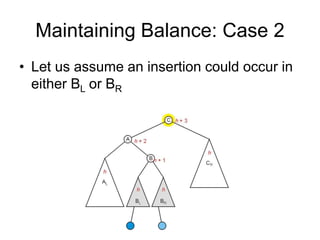
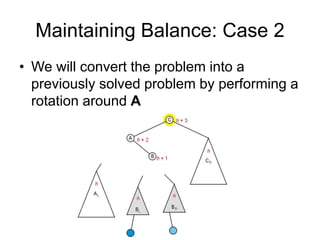
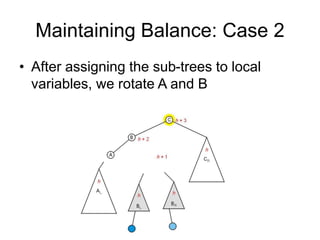
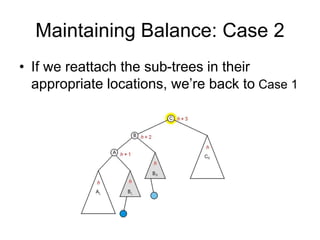
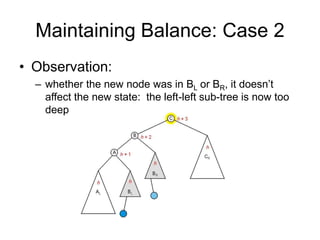
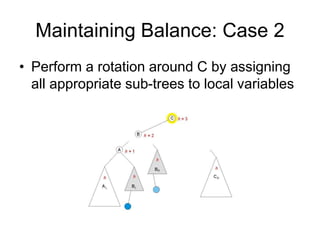
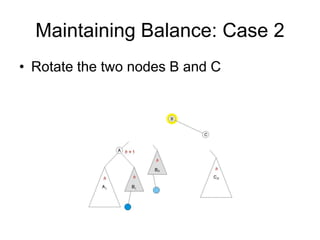
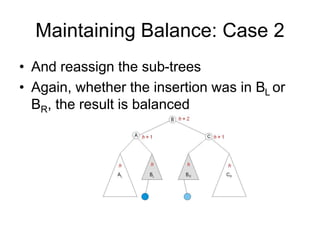
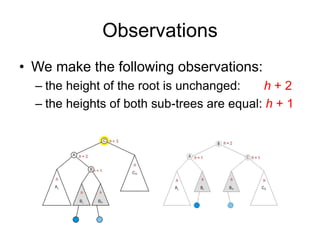
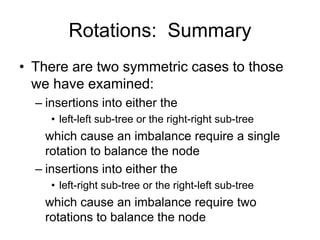
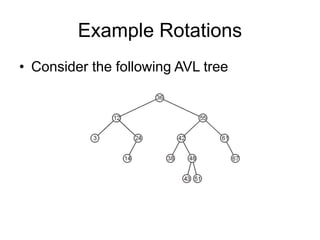
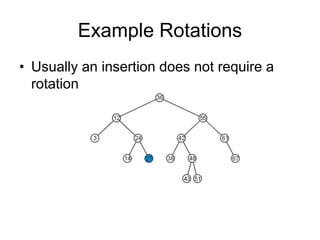
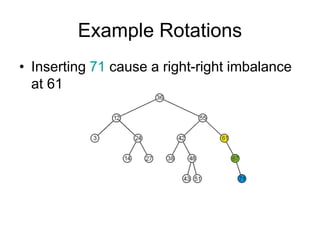
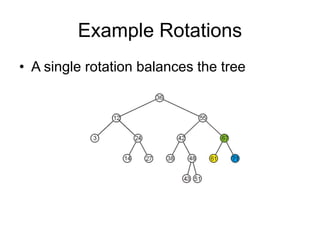
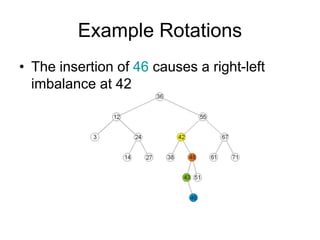
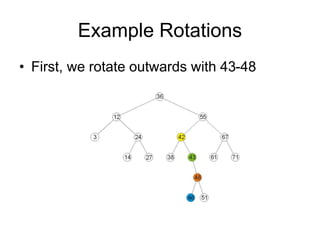
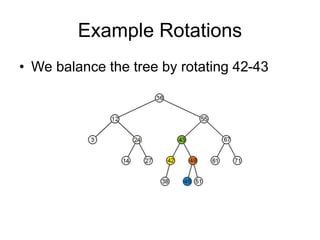
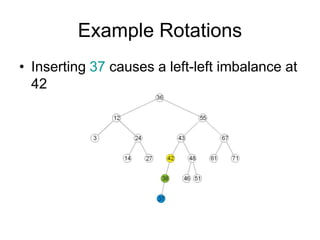
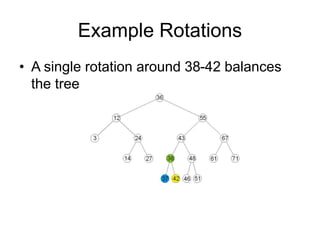
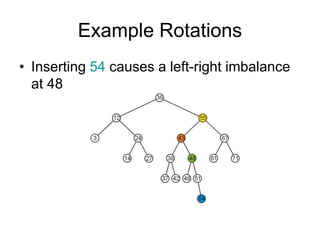
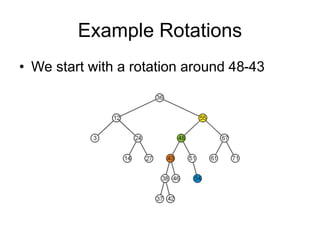
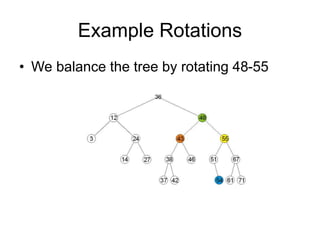
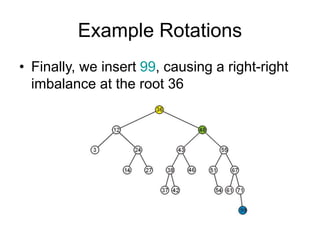
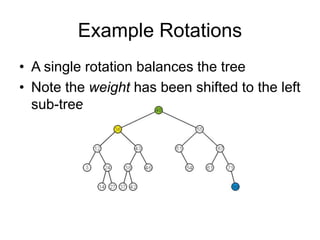
AVL trees are self-balancing binary search trees. They ensure that the heights of the two subtrees of any node differ by at most one. This balance property is maintained during insertions and deletions via rotations. There are two types of rotations needed - a single rotation to balance nodes where the imbalance is on one side, and a double rotation to balance nodes where the imbalance is on both sides. All operations on AVL trees, including rotations, take O(log n) time, making them efficient for search, insertion, and deletion.






















![AVL Trees as Arrays?
• While the polynomial behaviour of n1.44 is
not as bad as exponential behaviour, it is
still reasonably sub-optimal when
compared to the linear
growth associated with
node-based trees
• This plot shows
n n1.44
for n = [0, 1000]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-230506160150-db7bb18c/85/4-10-AVLTrees-1-ppt-78-320.jpg)

