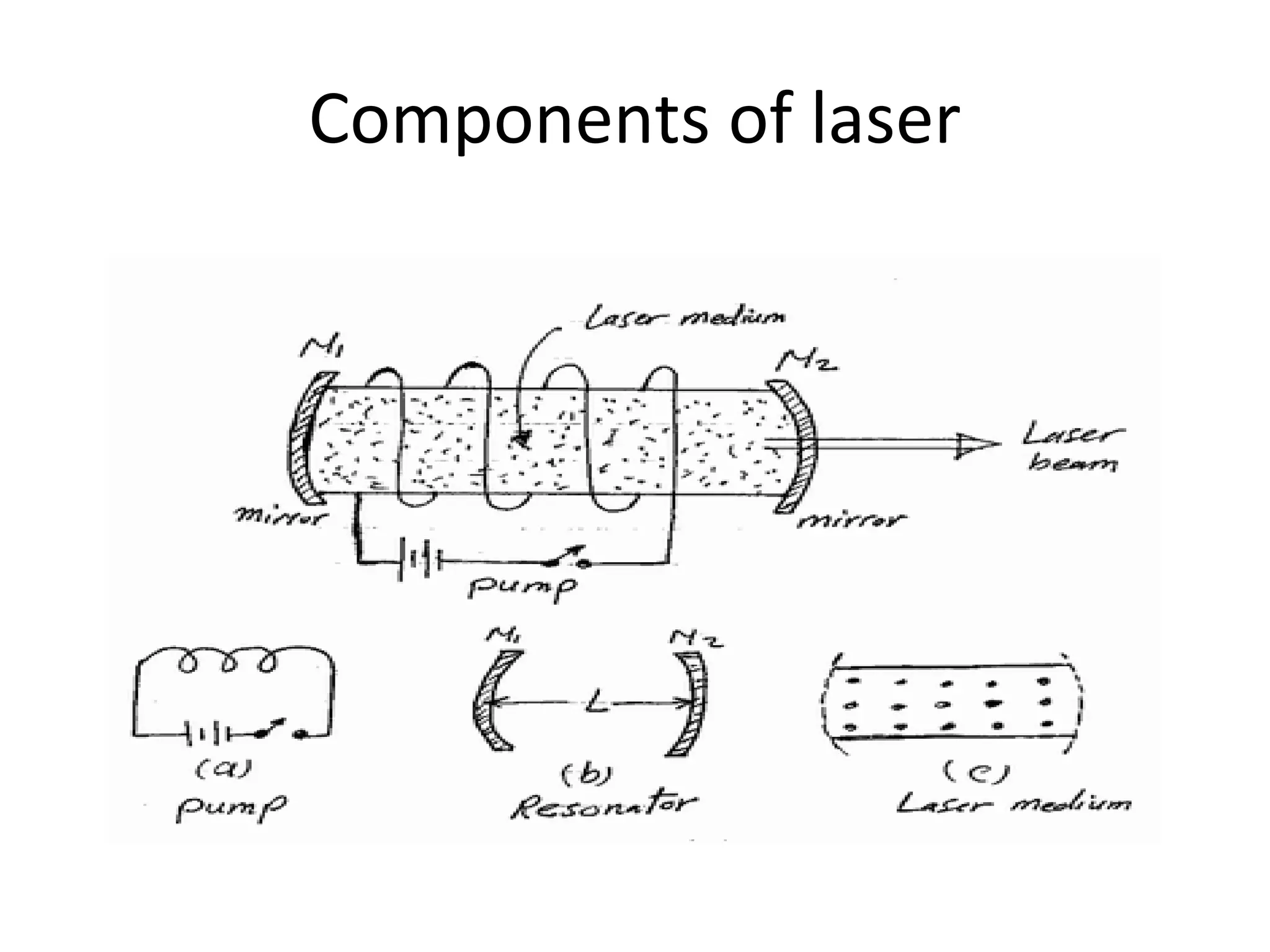
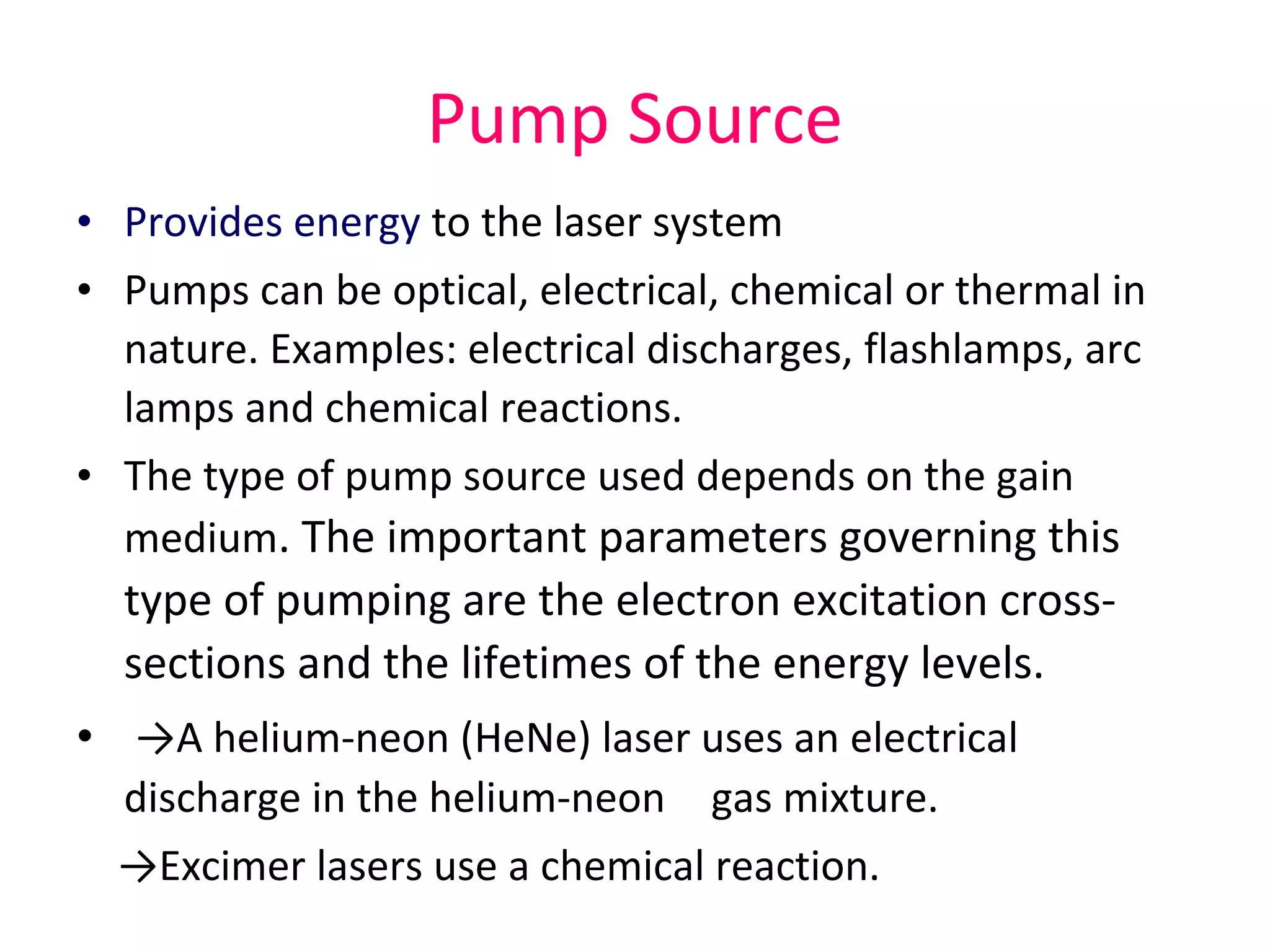
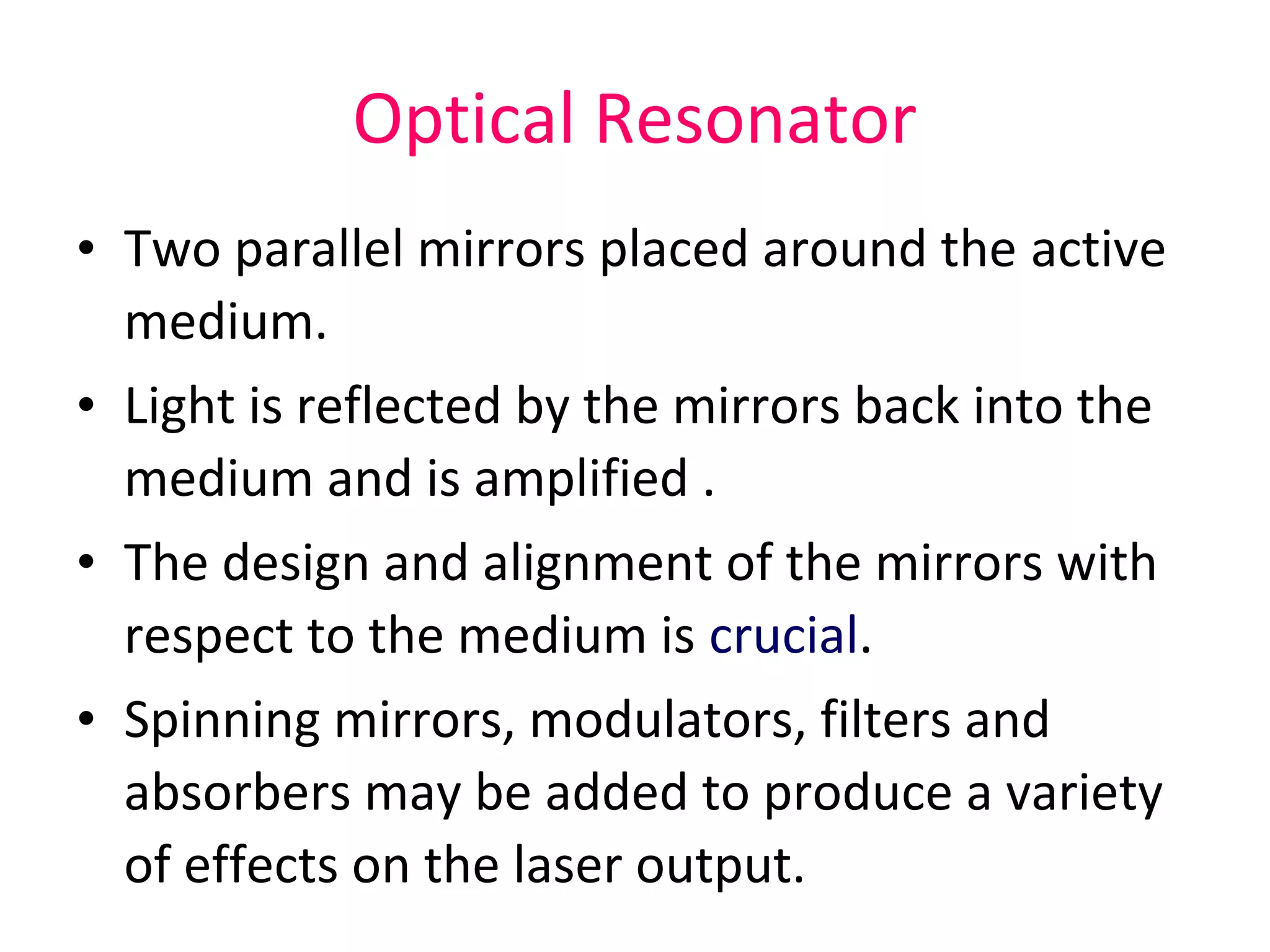
This document provides an introduction to lasers, including their key characteristics and components. It discusses how lasers produce coherent, monochromatic, and directional light through stimulated emission of radiation. The essential components of all lasers are described as the active medium, excitation mechanism, high reflectance mirror, and partially transmissive mirror. Examples of different types of active media and pump sources are given. The document also explains the function of the optical resonator formed by two mirrors around the active medium.