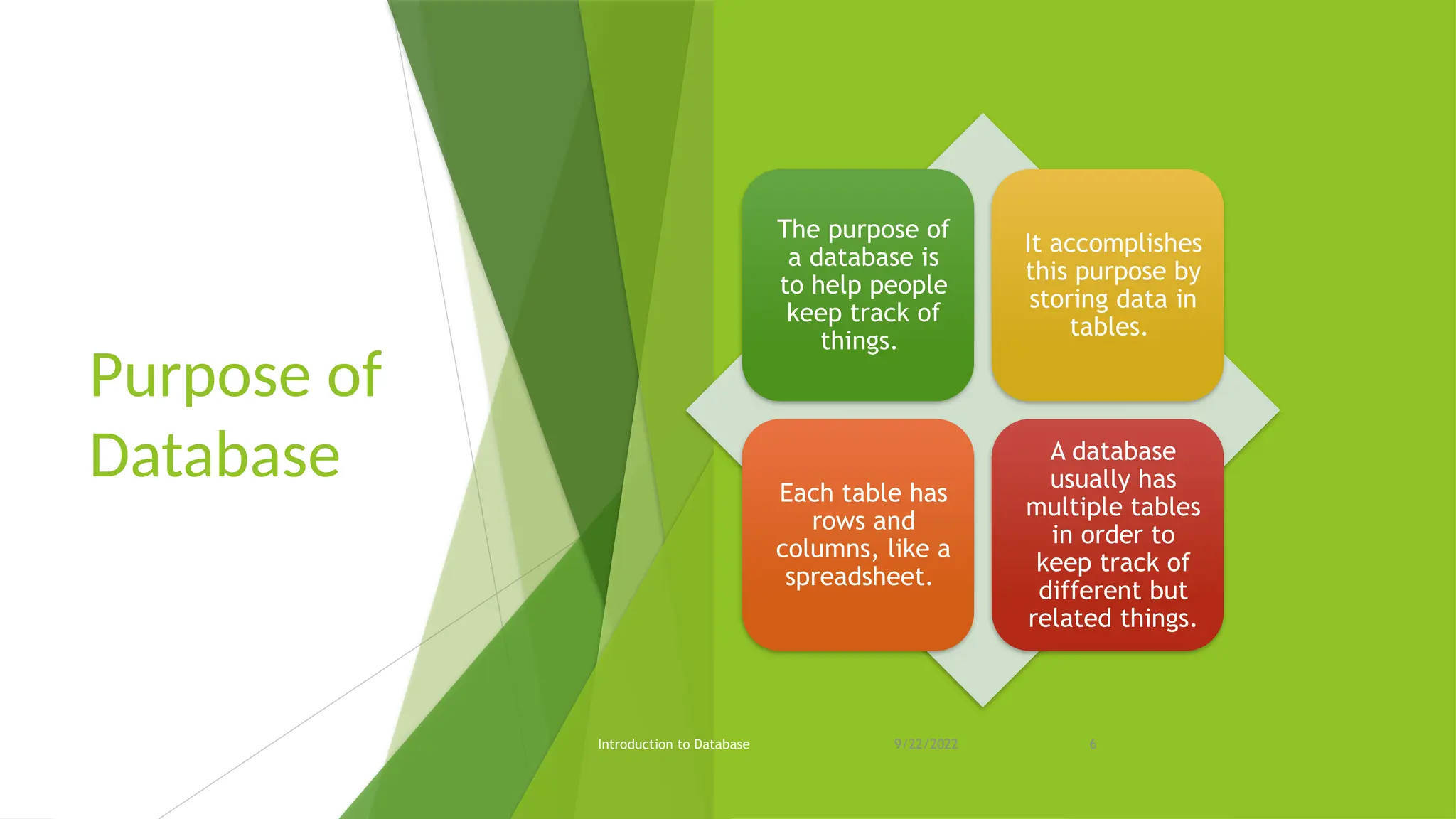
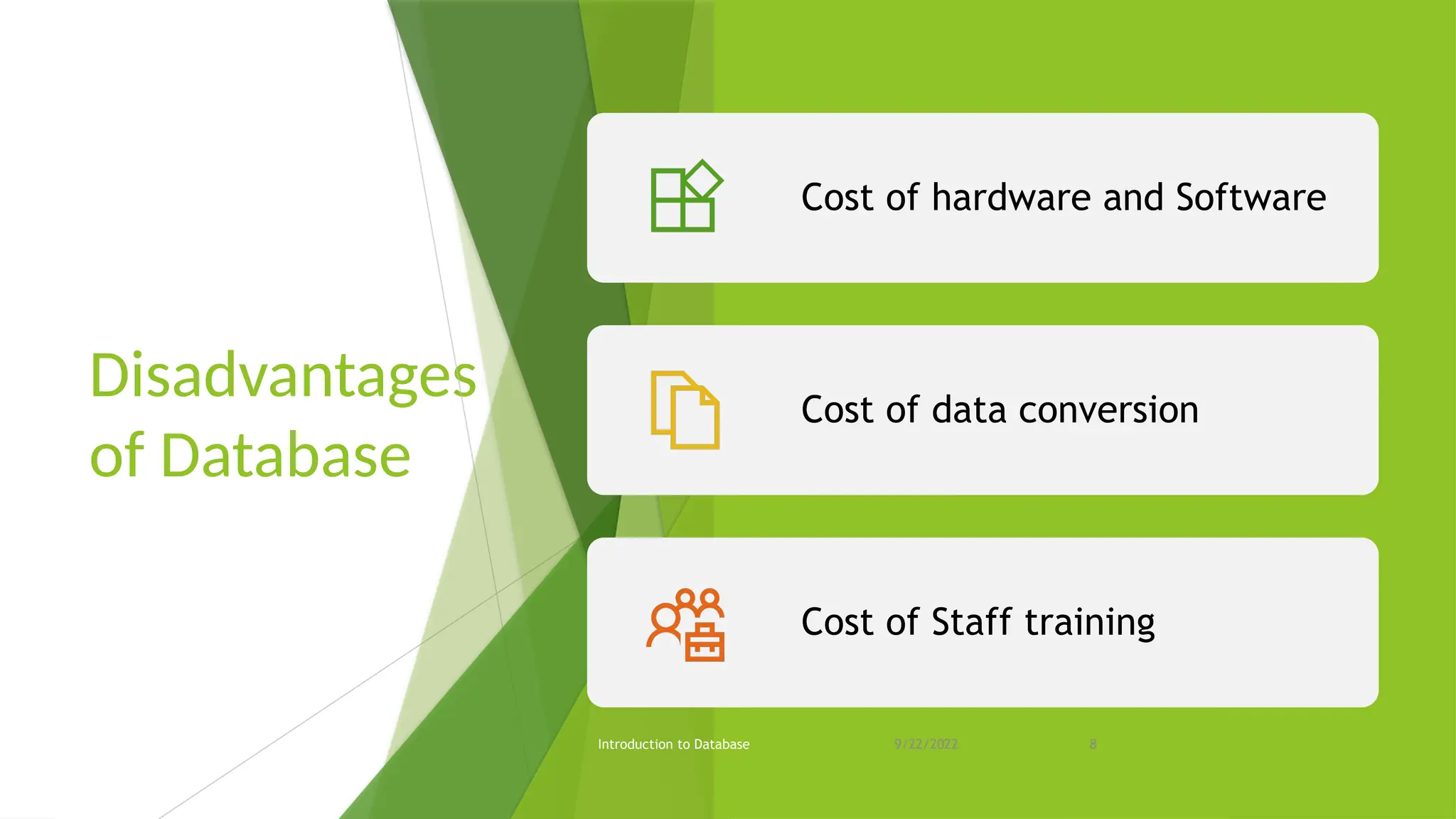
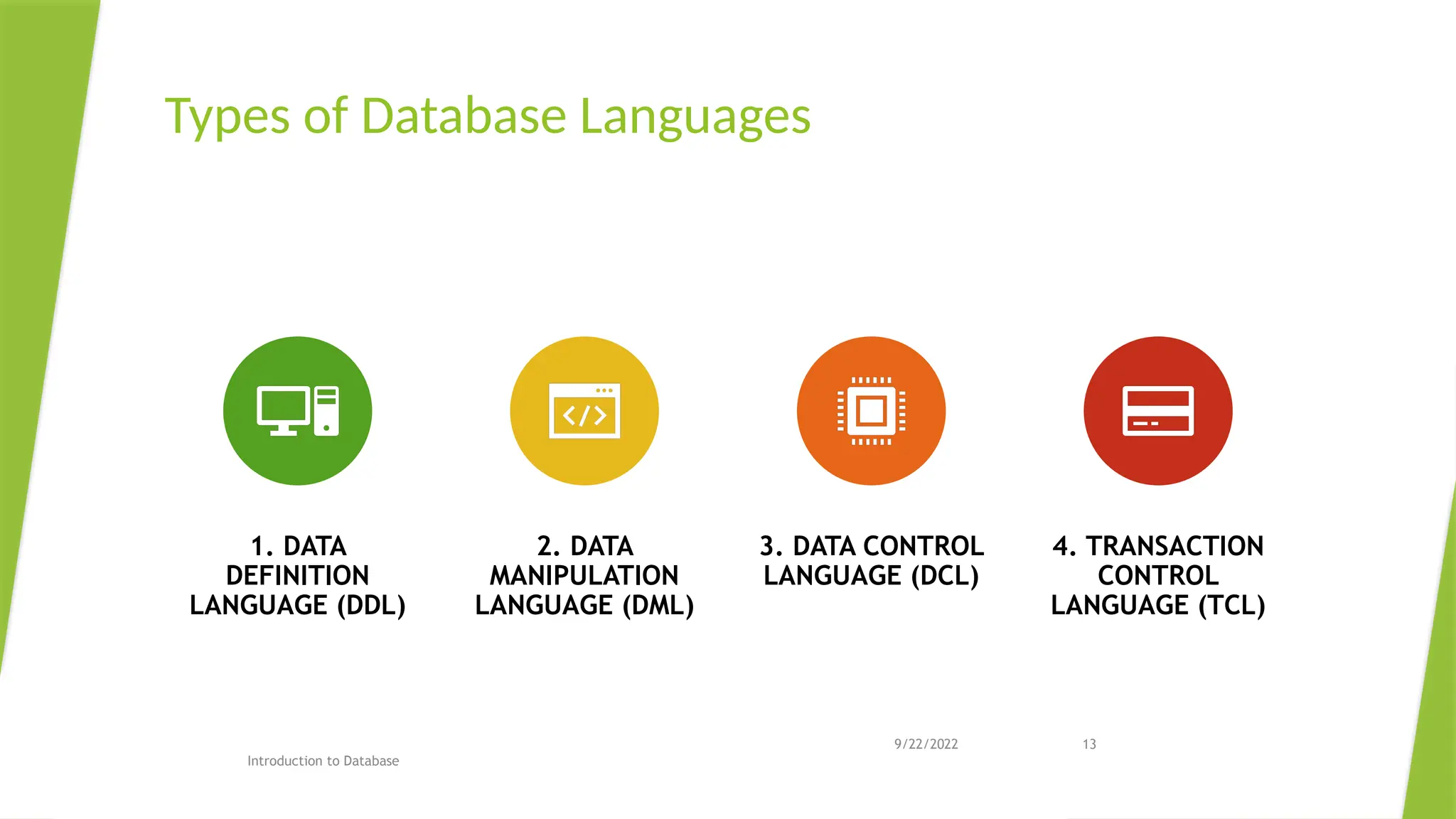
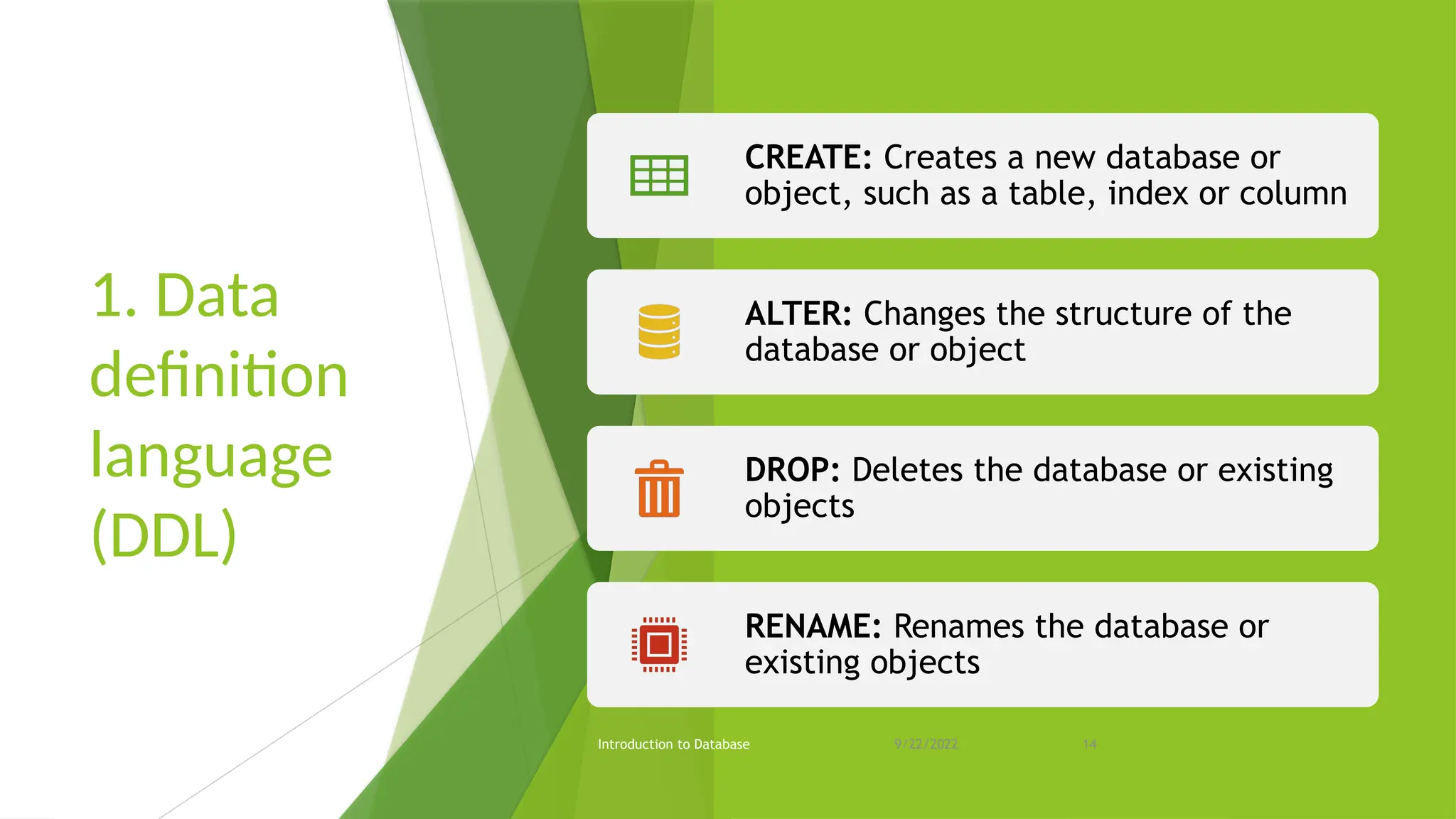
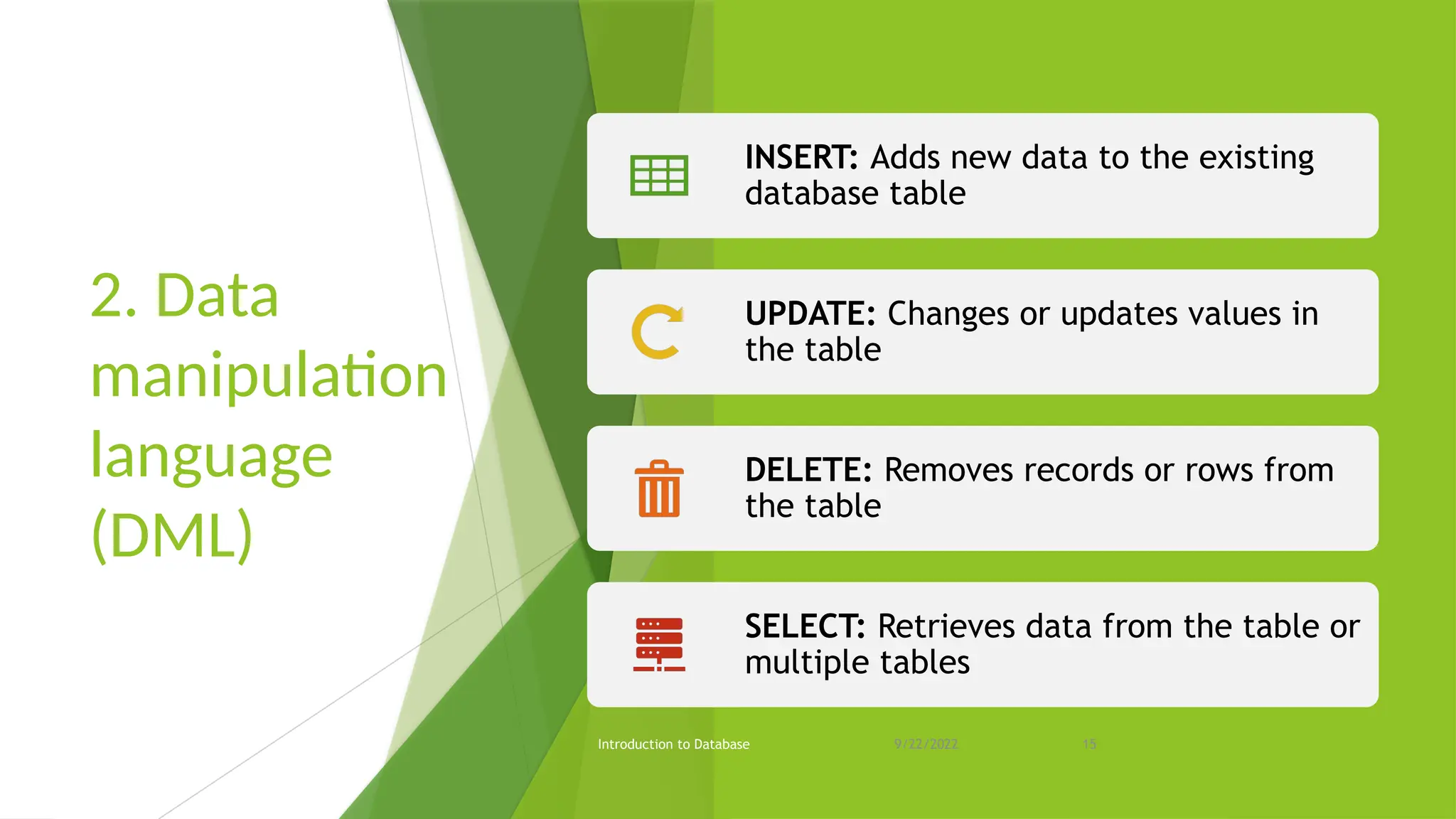
The document provides an overview of databases, including their purpose, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as types of keys and database languages. It explains that databases serve as repositories for data that can be retrieved and modified to support organizational functions. Additionally, it discusses the role of database management systems in ensuring data integrity, consistency, and durability.