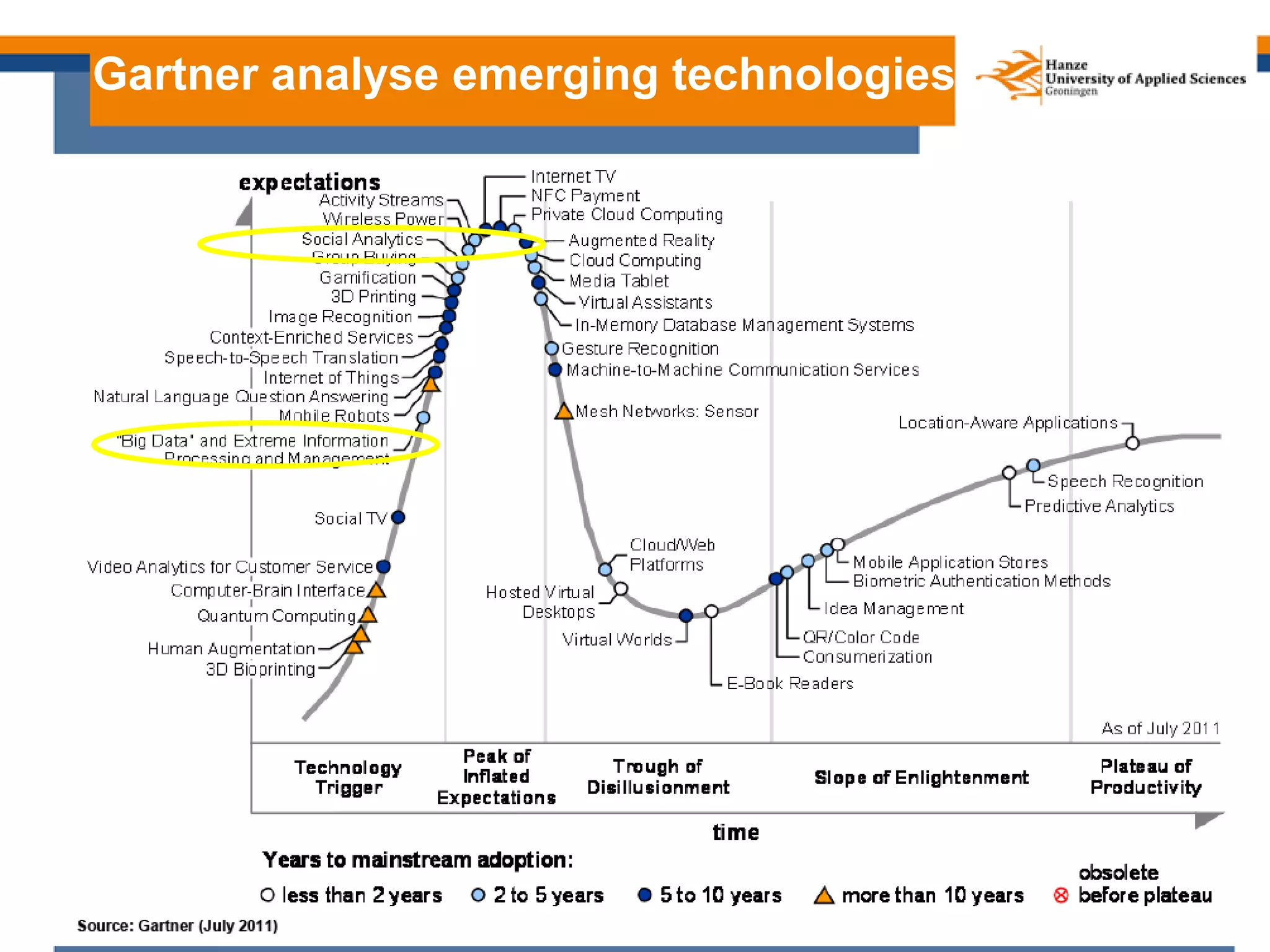
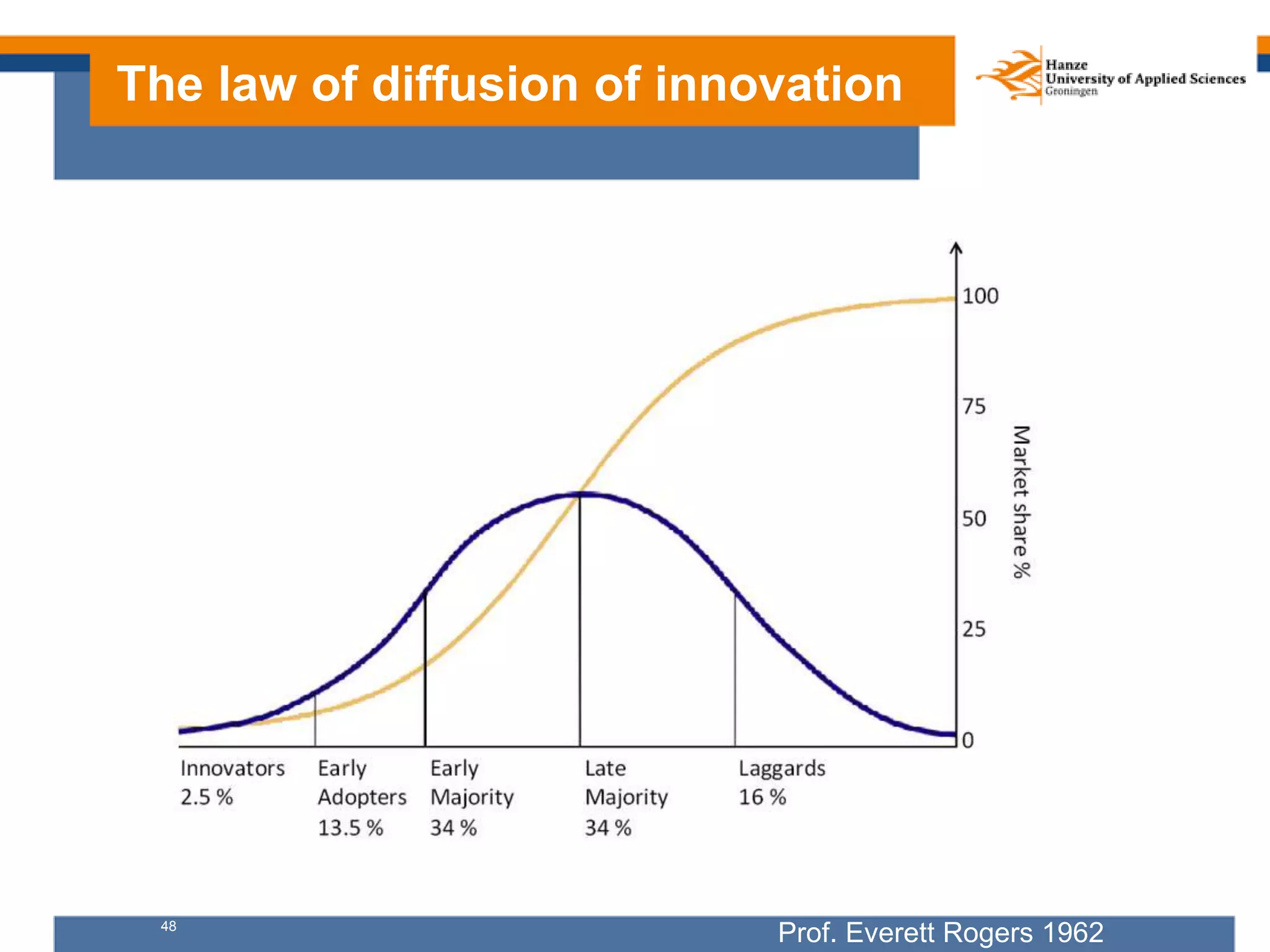
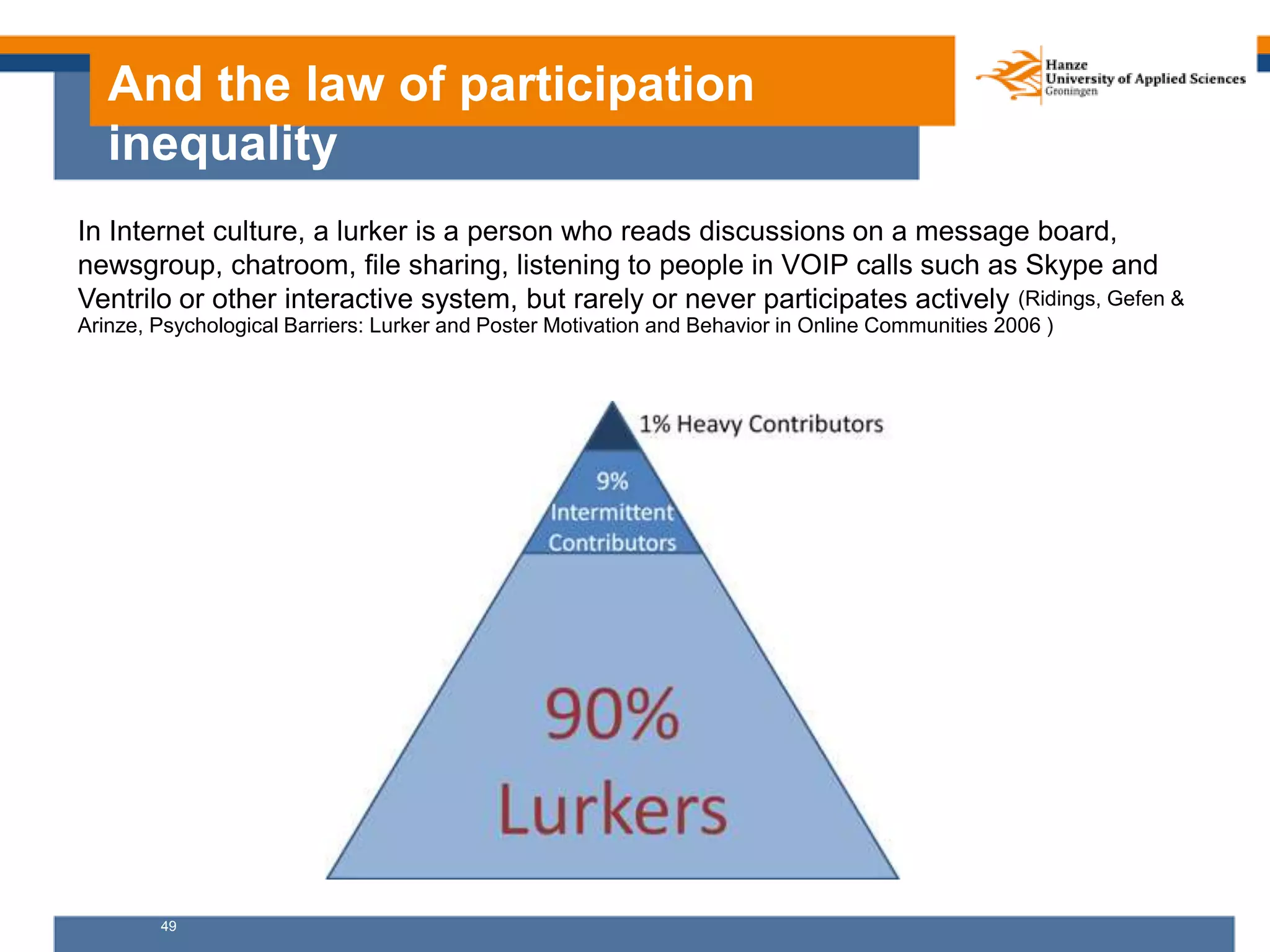
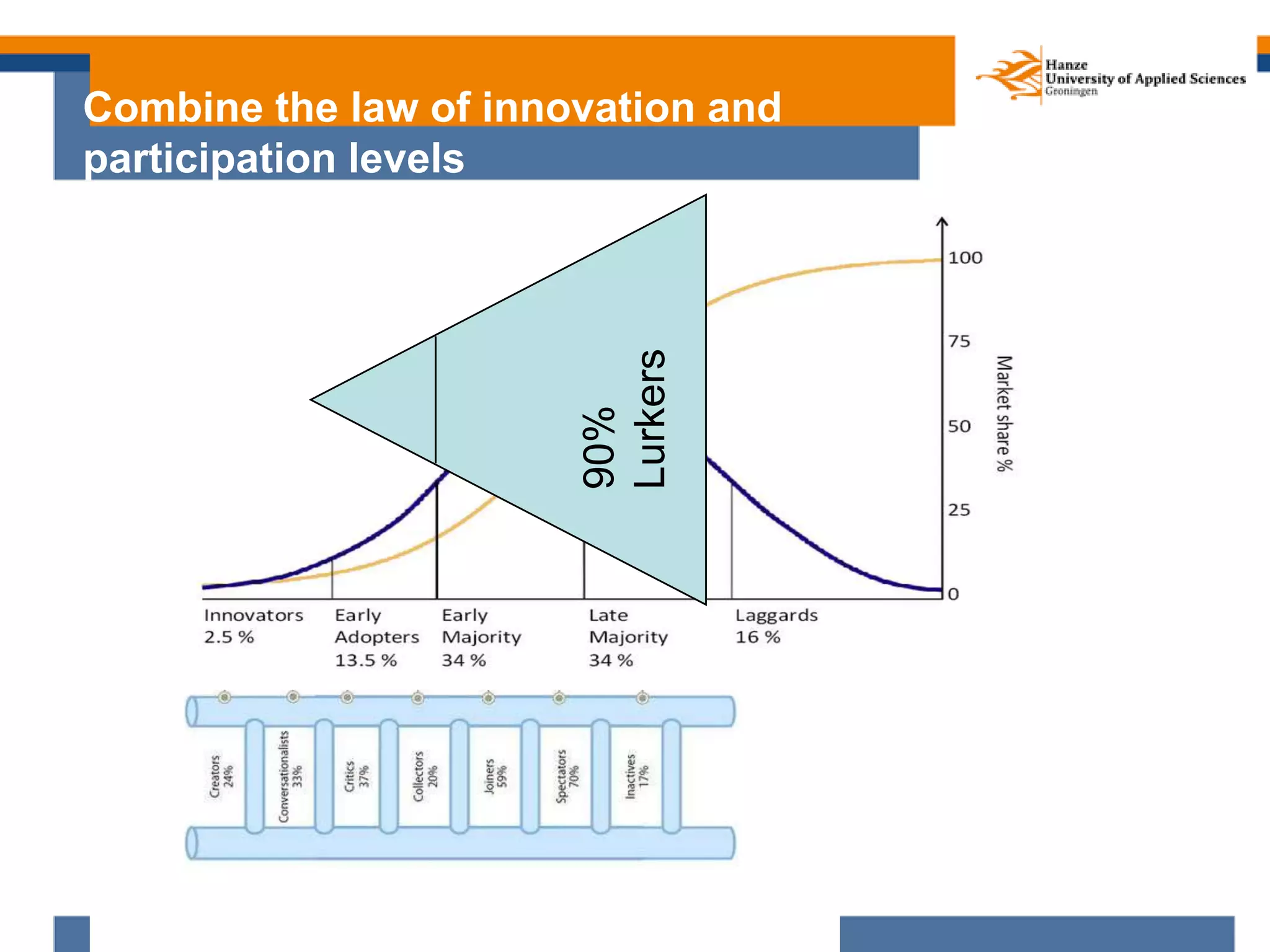
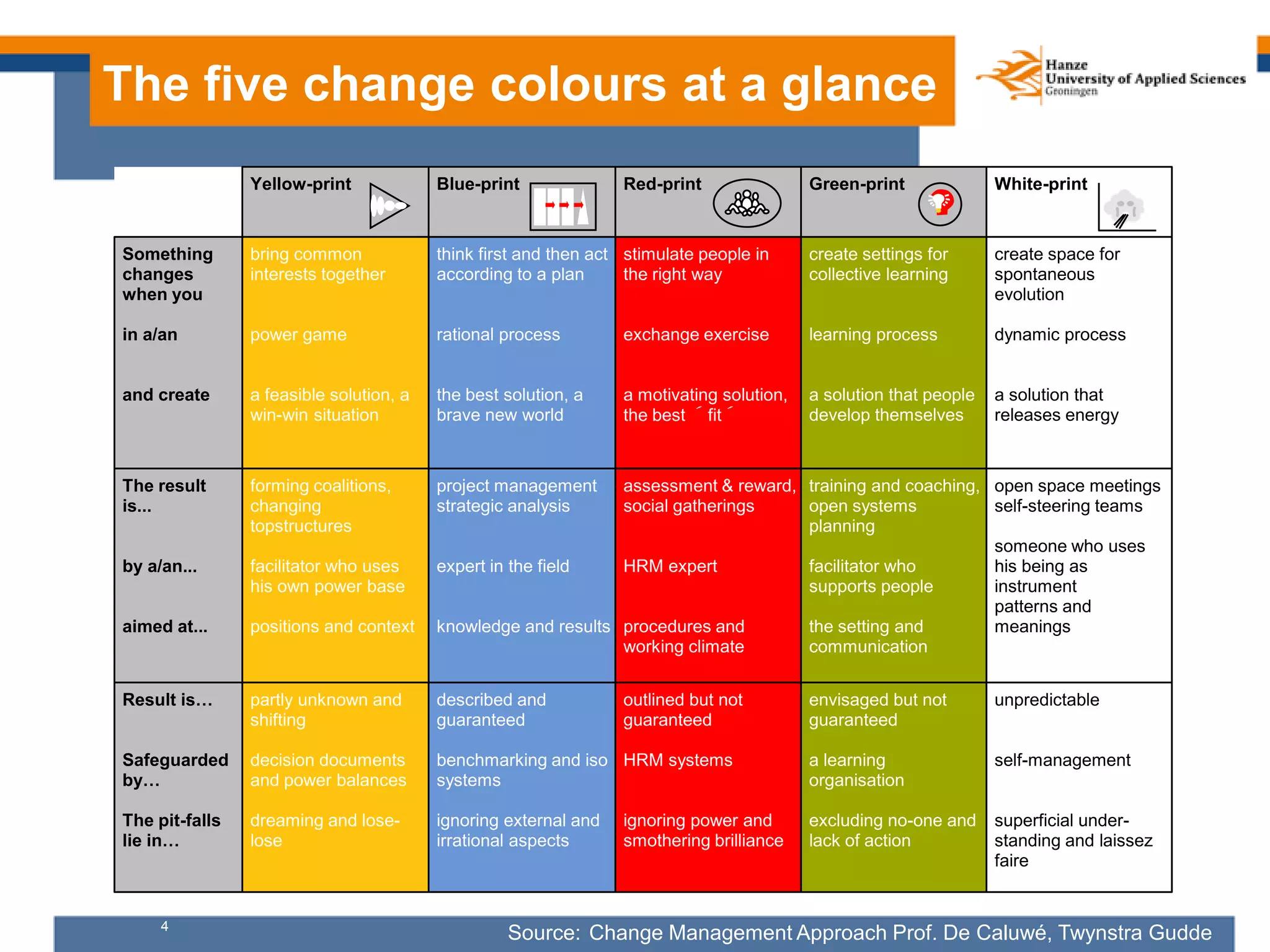
Here are my assessments of the objectives of the examples provided:
- Wikipedia is focused on energizing and embracing. It aims to connect enthusiastic contributors to share and improve information, integrating their ideas.
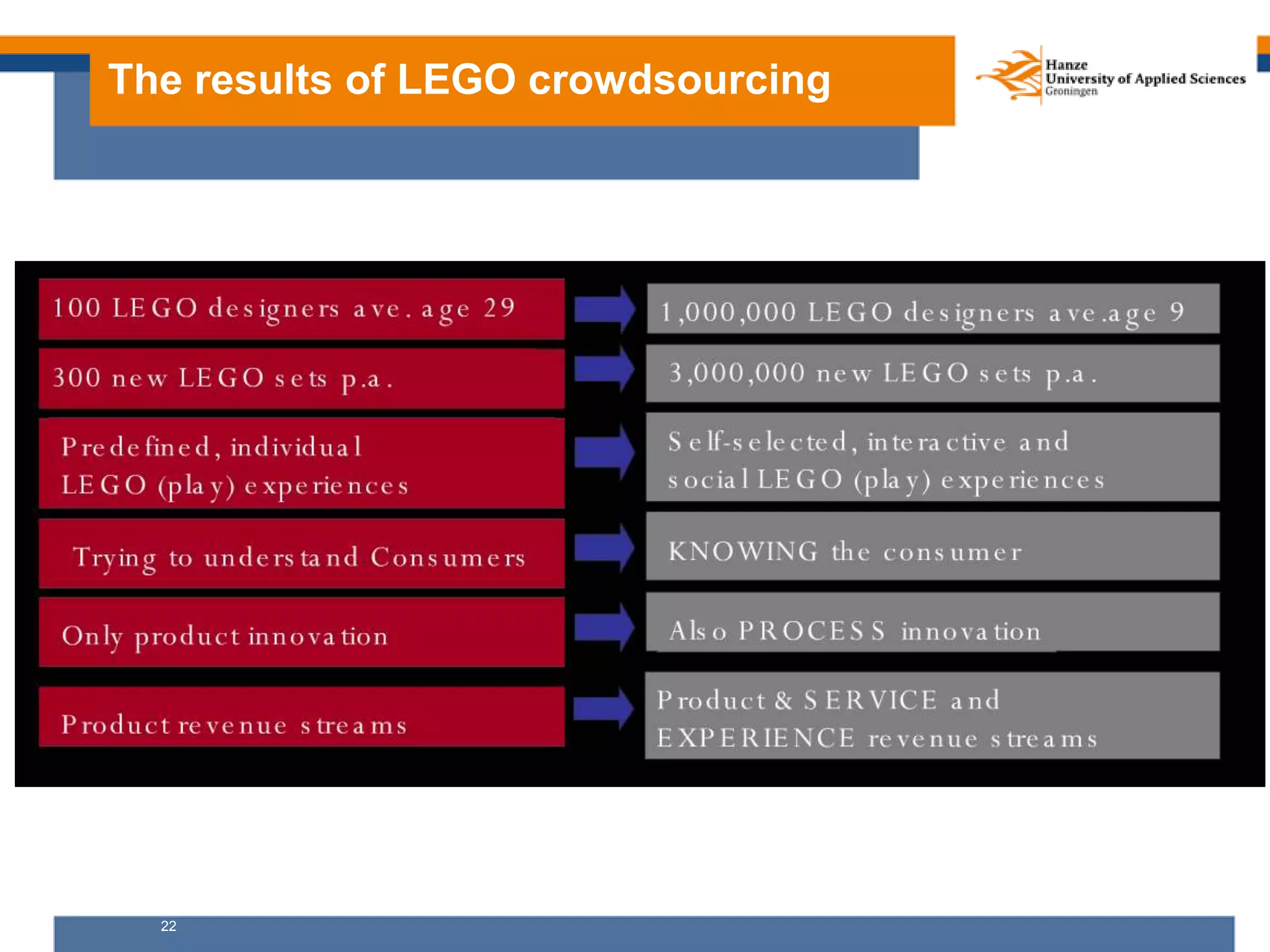
- Lego is focused on embracing. It aims to integrate the ideas of its community into improving its products.
- The fishermen community is focused on supporting. It aims to help fishermen help and support each other by sharing knowledge and data.
- Iens is focused on listening. It aims to listen to its community for research and better understanding of restaurant customers.
- The gardenbird counting is focused on energizing. It aims to connect enthusiastic amateur birdwatchers to supercharge data collection about bird movements.



![6
Open
Will
Open
Heart
Open
Mind
LISTENING 2:
from outside
disconfirming
[new] data
Downloading
habits of judgment
reconfirming old
opinions & judgments
Factual listening
noticing differences
LISTENING 3:
from within
seeing through
another person‘s eyes
emotional connection
Empathic listening
LISTENING 1:
from habits
LISTENING 4:
from Source
connecting to an
emerging future whole;
shift in identity and self
Generative listening
(from the future wanting to
emerge)
Theory U as ‘toolkit’ for leaders](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hgitsmlecture62011-2012crowdsourcingandsocialmedia-120111125751-phpapp01/75/Lecture-5-2011-2012-crowdsourcing-and-social-media-6-2048.jpg)