This lecture discusses XML (eXtensible Markup Language) and its applications. Some key points:
- XML allows users to define their own tags for marking up documents with meta-information. This enables structured storage and interchange of data.
- XML uses elements defined by tags, attributes, and nesting. Documents can be validated against a DTD (Document Type Definition).
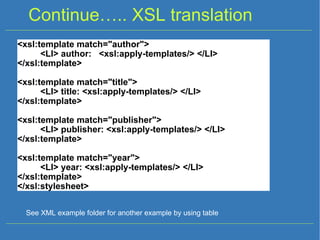
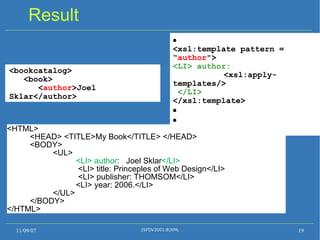
- XSL (eXtensible Stylesheet Language) allows XML documents to be transformed and presented in different formats (HTML, etc).
- XML enables storage, interchange, presentation of data between different applications and systems. It has many uses including web feeds (RSS), vector graphics (SVG), and more.

![Markup Marking information more than the text that you see General concept is meta-information Plays – Mark what the actors do 11/09/07 (SFDV2001:8)XML HORATIO. Peace! Who comes here? [Enter young Osric, a courtier.] OSRIC. Your lordship is right welcome back to Denmark. HAMLET. I humbly thank you, sir. [Aside to Horatio] Dost know this waterfly?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5xml-091030014208-phpapp01/85/Lecture-5-XML-2-320.jpg)






![DTD Example 11/09/07 (SFDV2001:8)XML <?xml version="1.0"?> <?xml-stylesheet href=“list.xsl" type="text/xsl"?> <!DOCTYPE bookcatalog [ <!ELEMENT book (author , title, publisher, year)> <!ELEMENT author (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT title (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT publisher (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT year (#PCDATA)> ]> <bookcatalog> <book> <author>Joel Sklar</author> <title>Princeples of Web Design</title> <publisher>THOMSOM</publisher> <year>2006</year> </book> </bookcatalog>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5xml-091030014208-phpapp01/85/Lecture-5-XML-11-320.jpg)