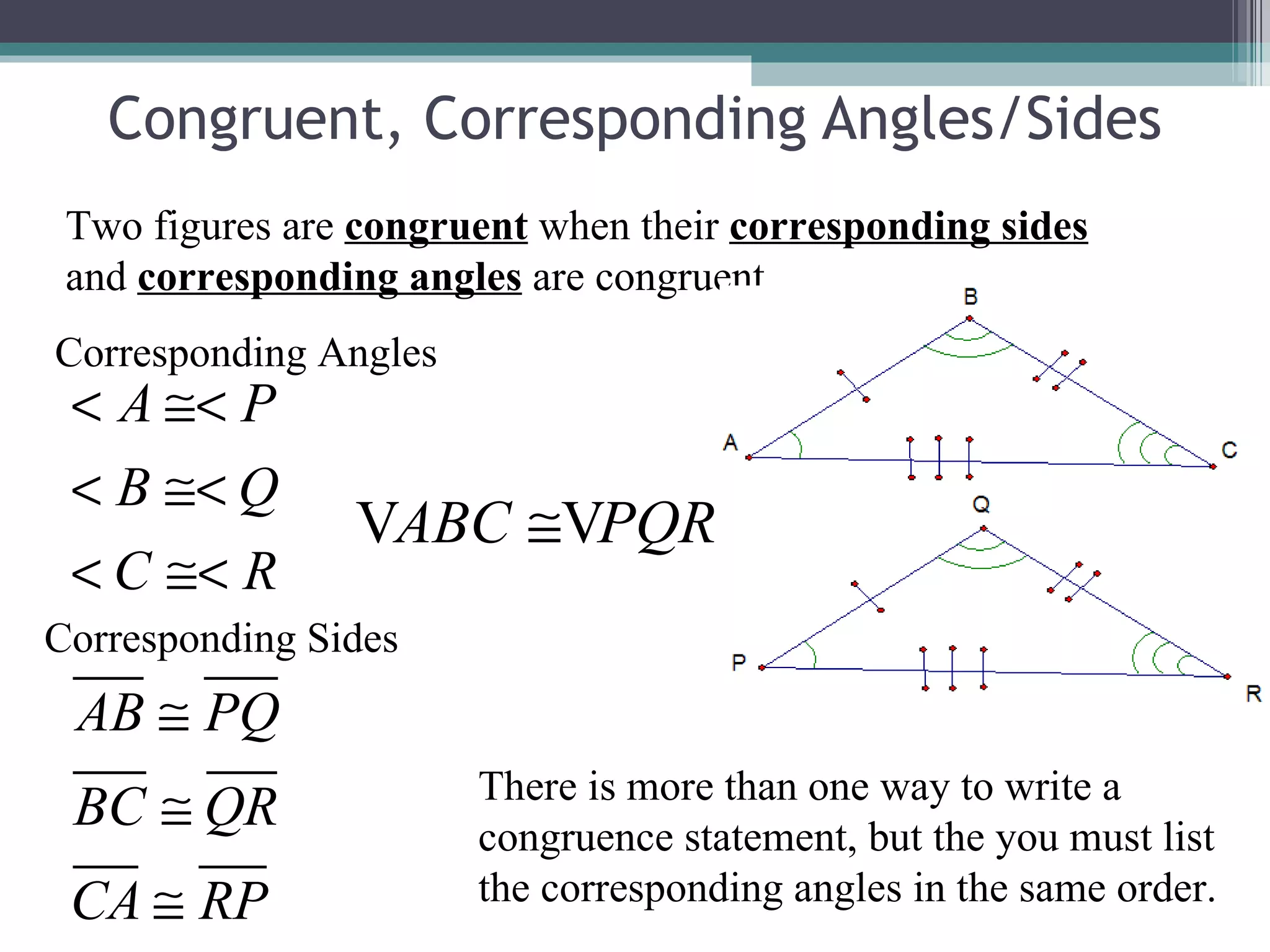
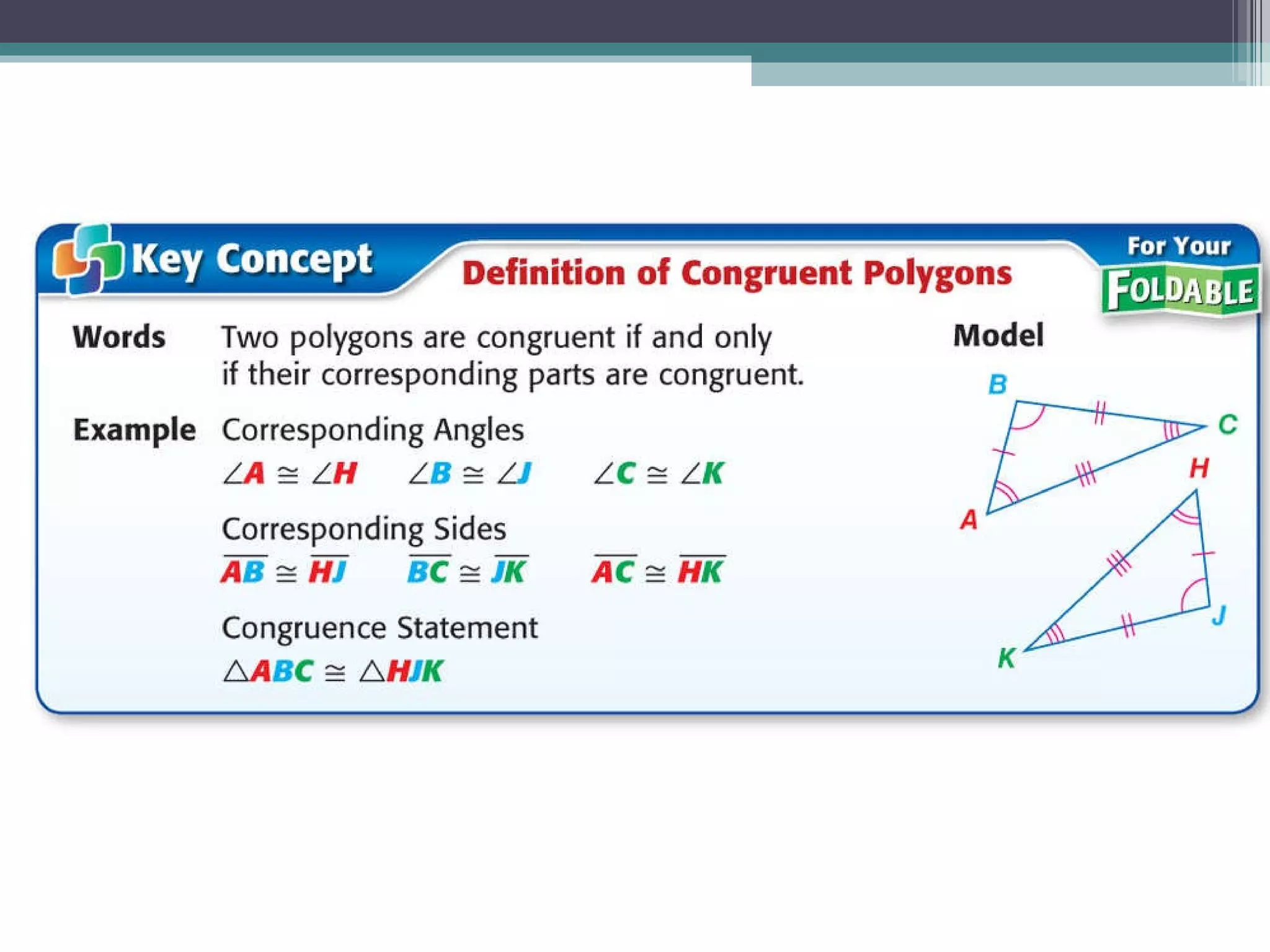
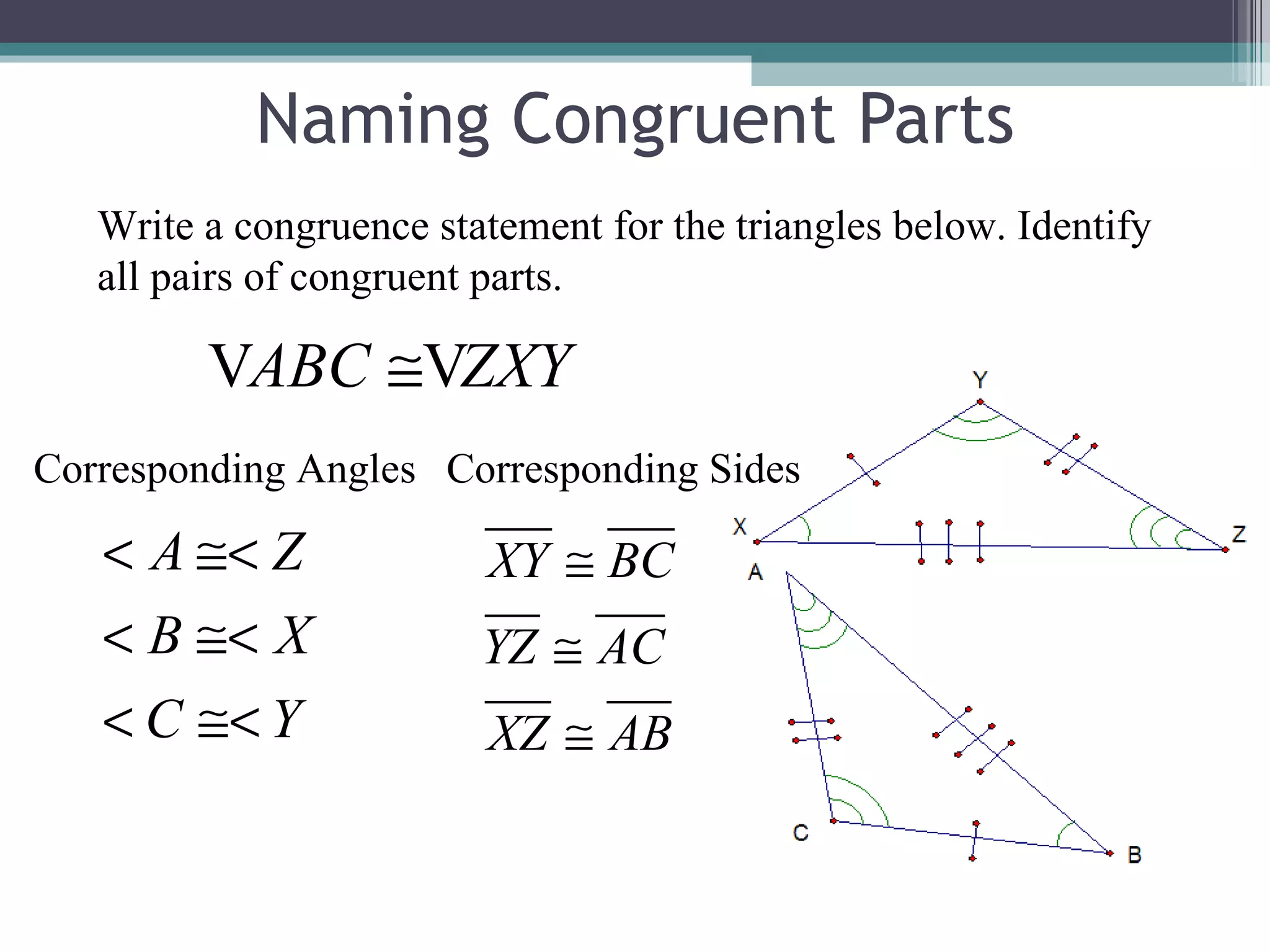
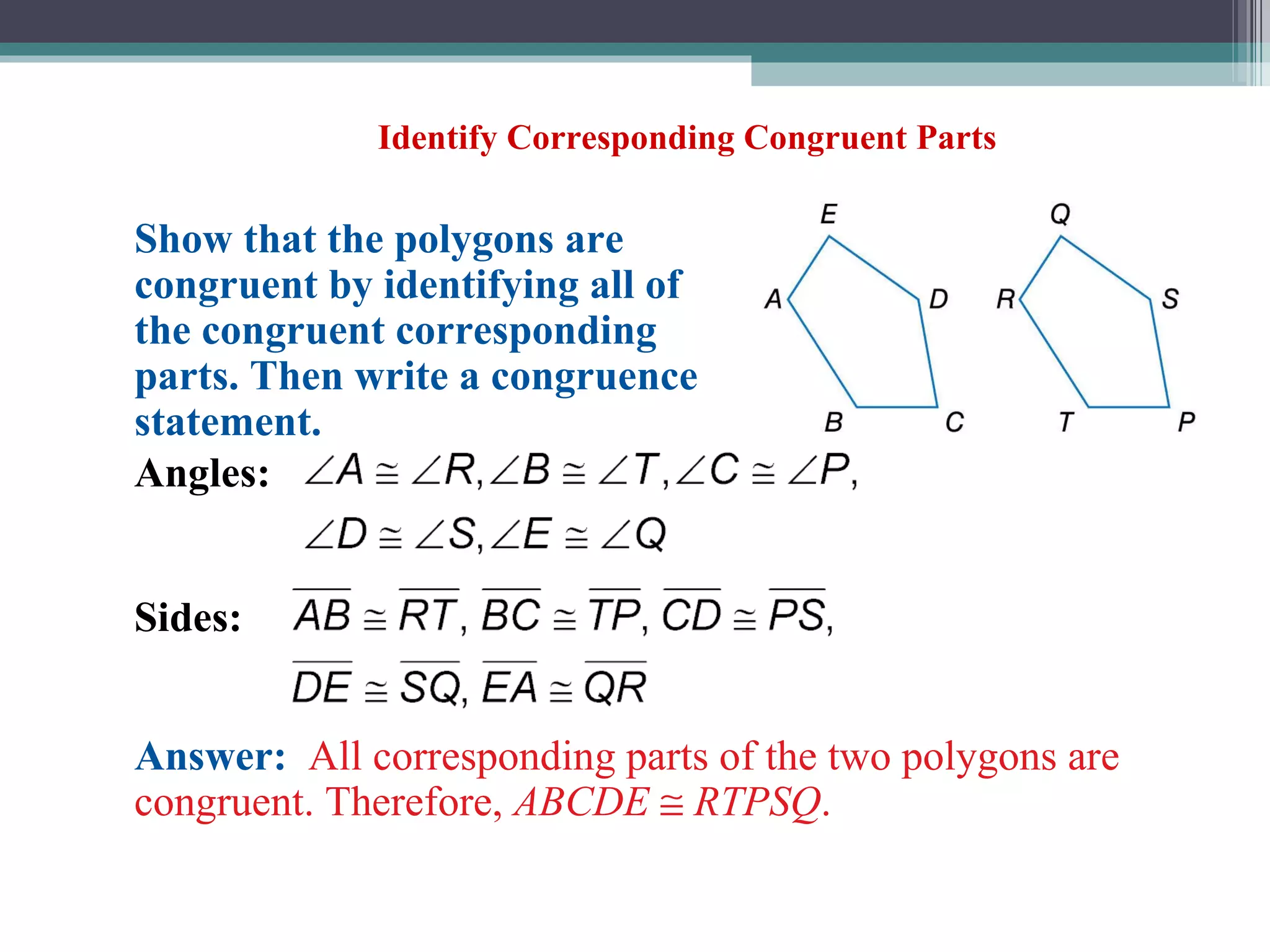
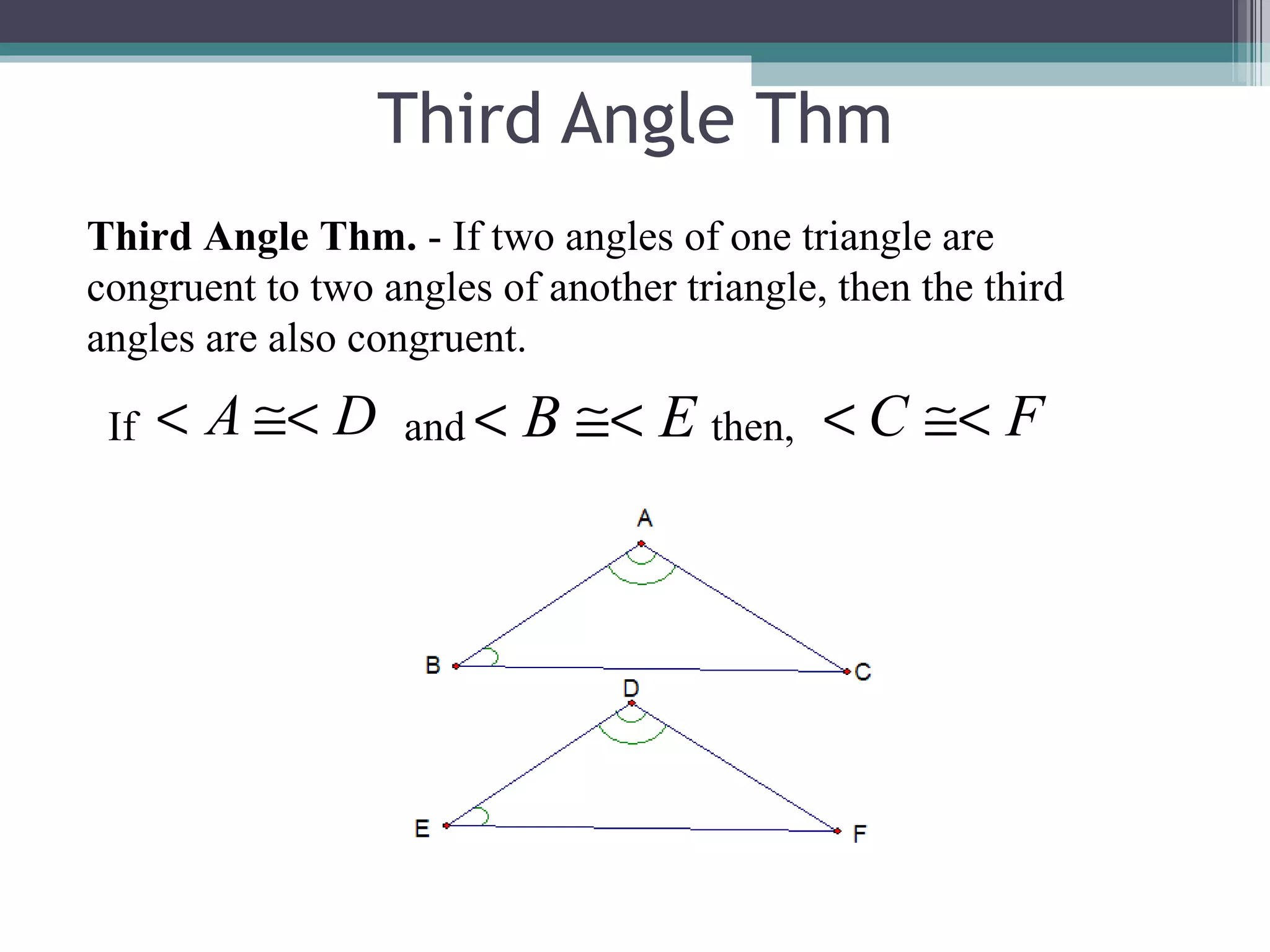
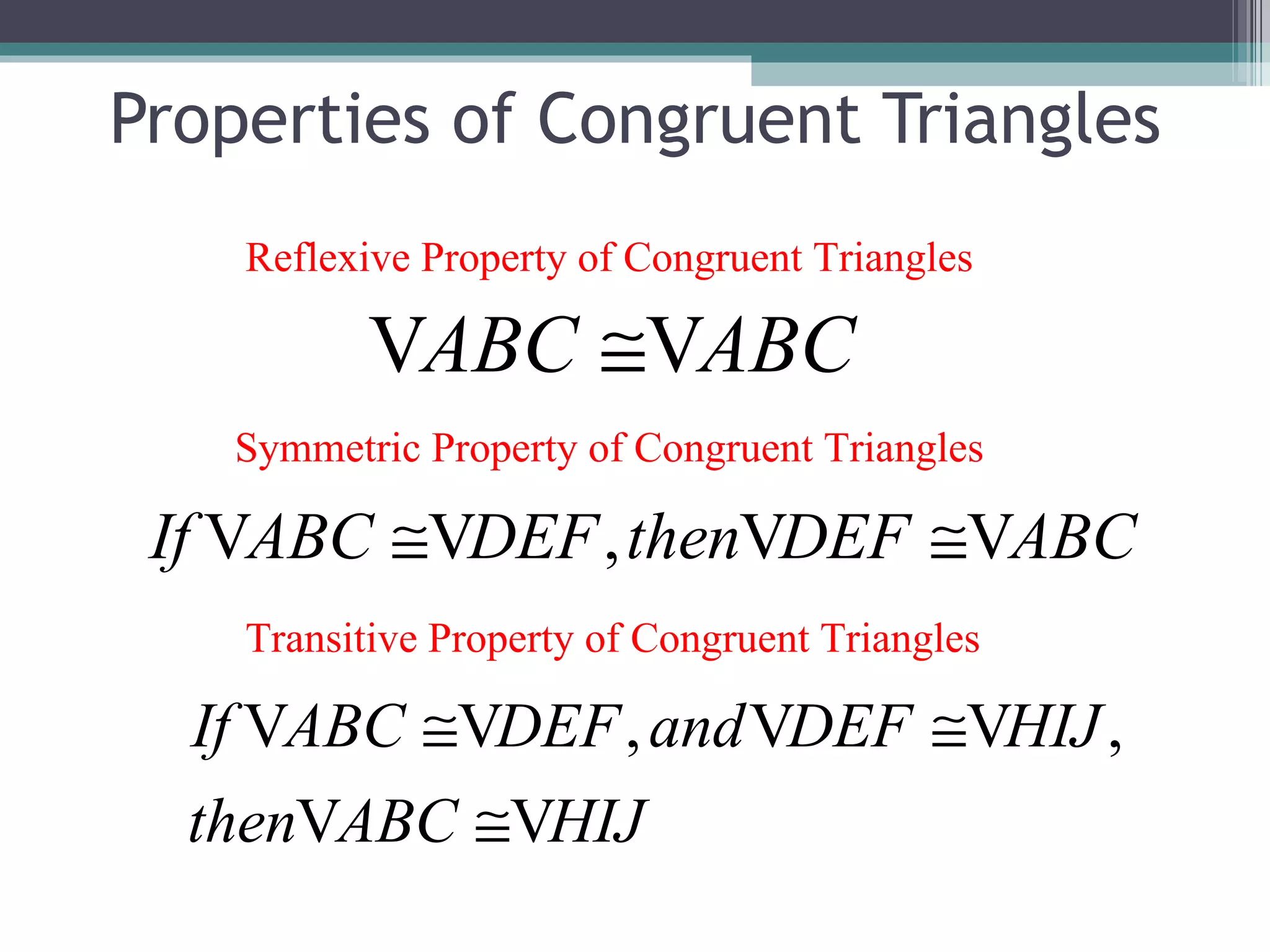
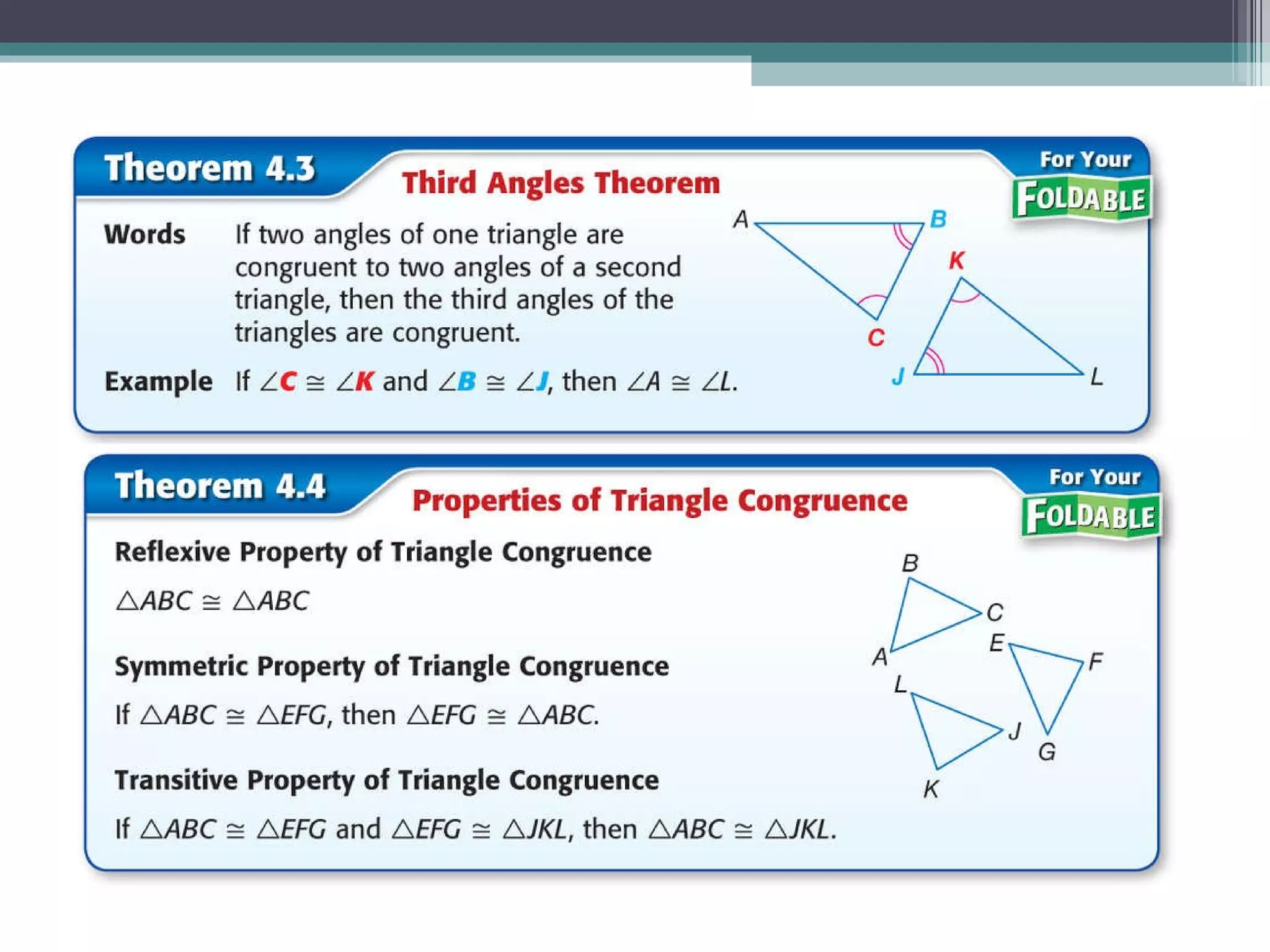
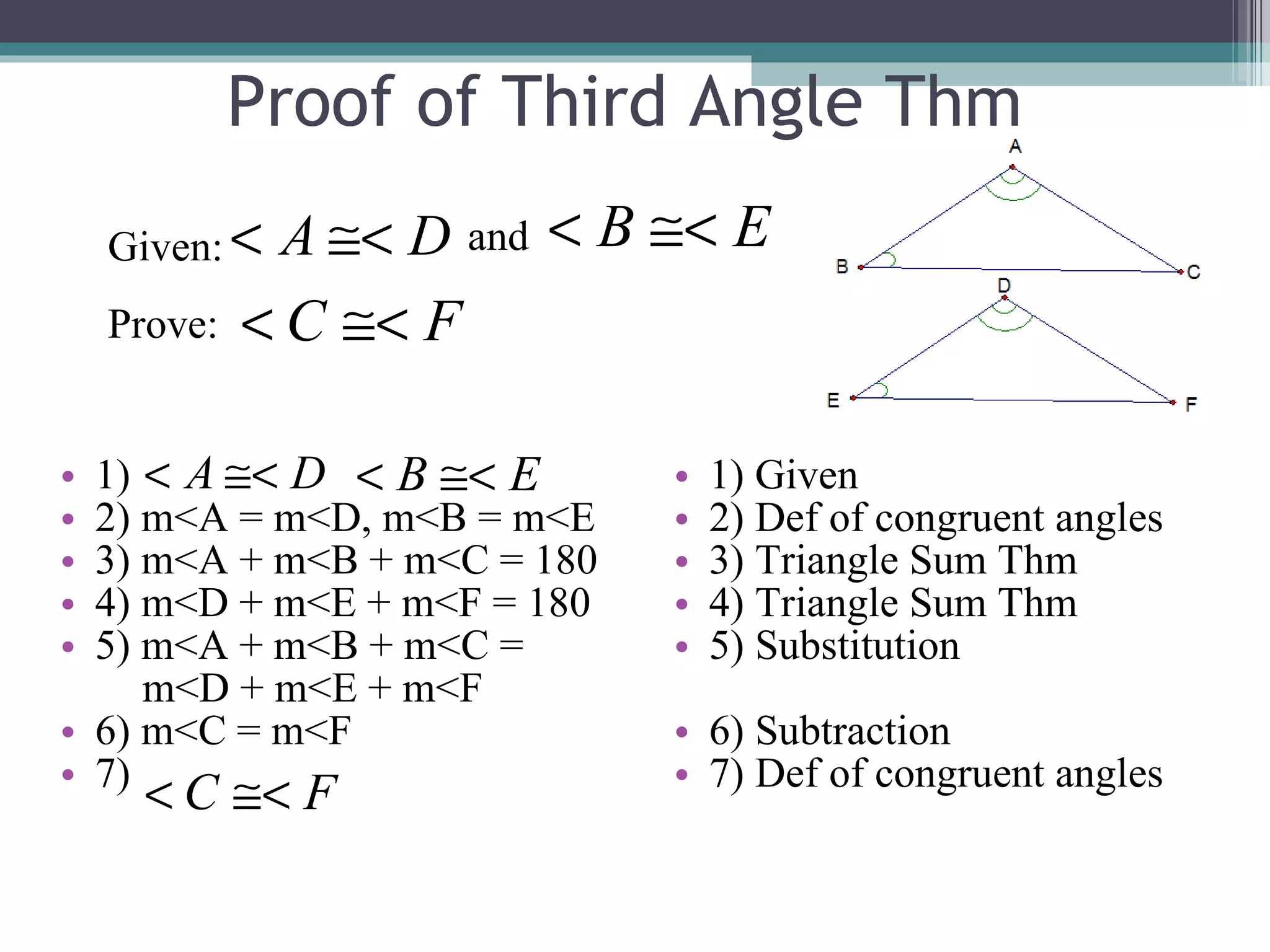
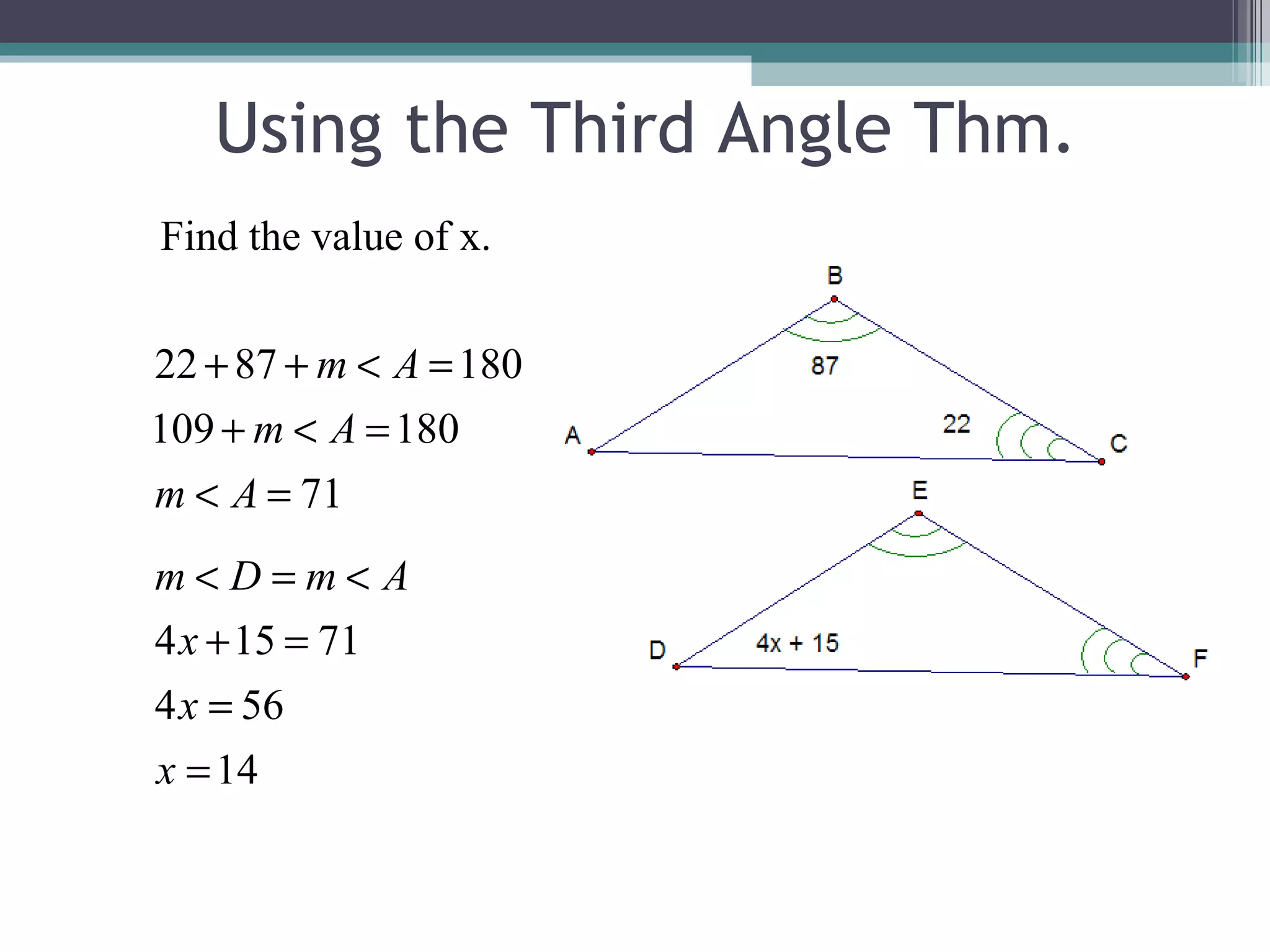
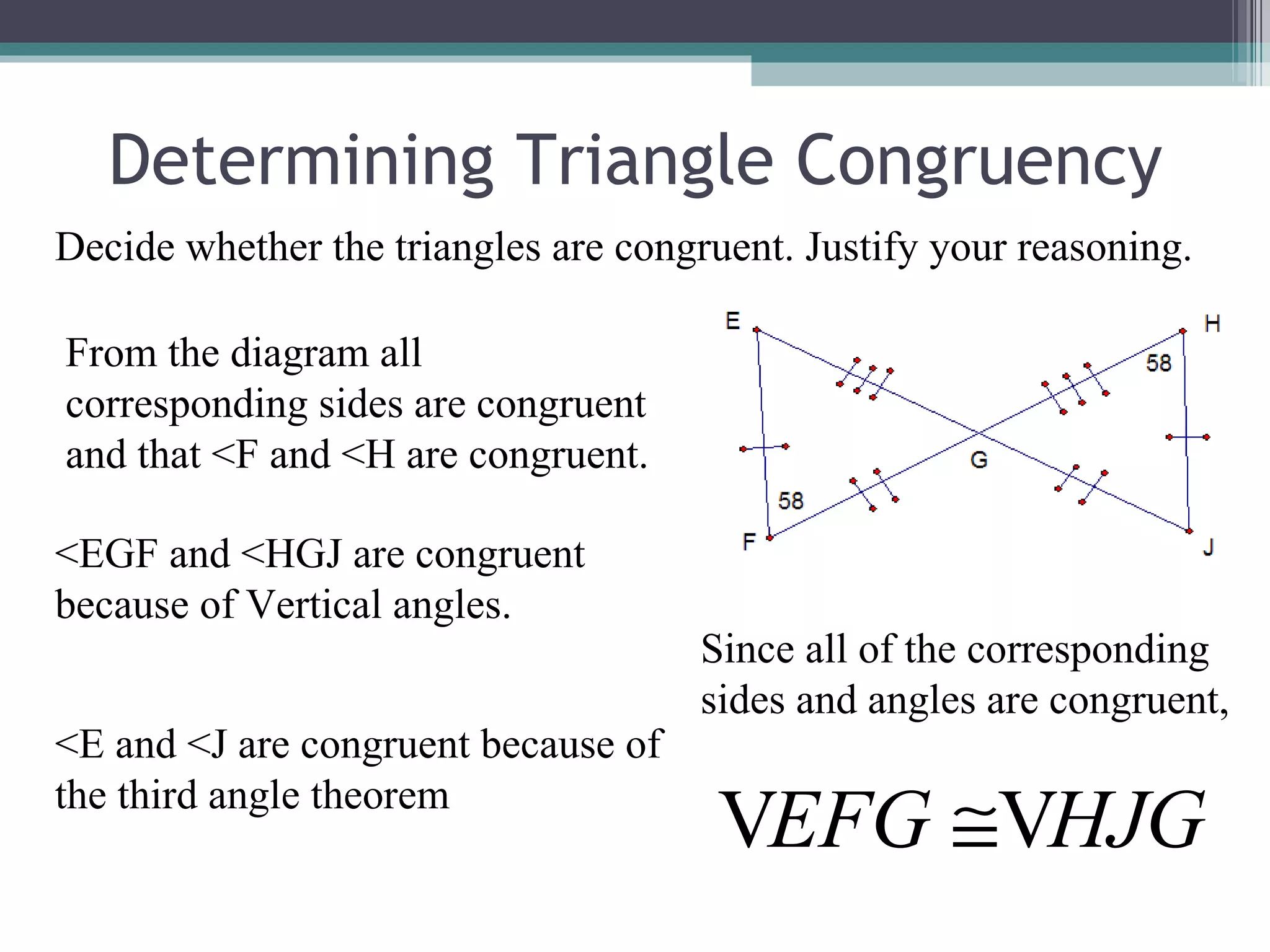
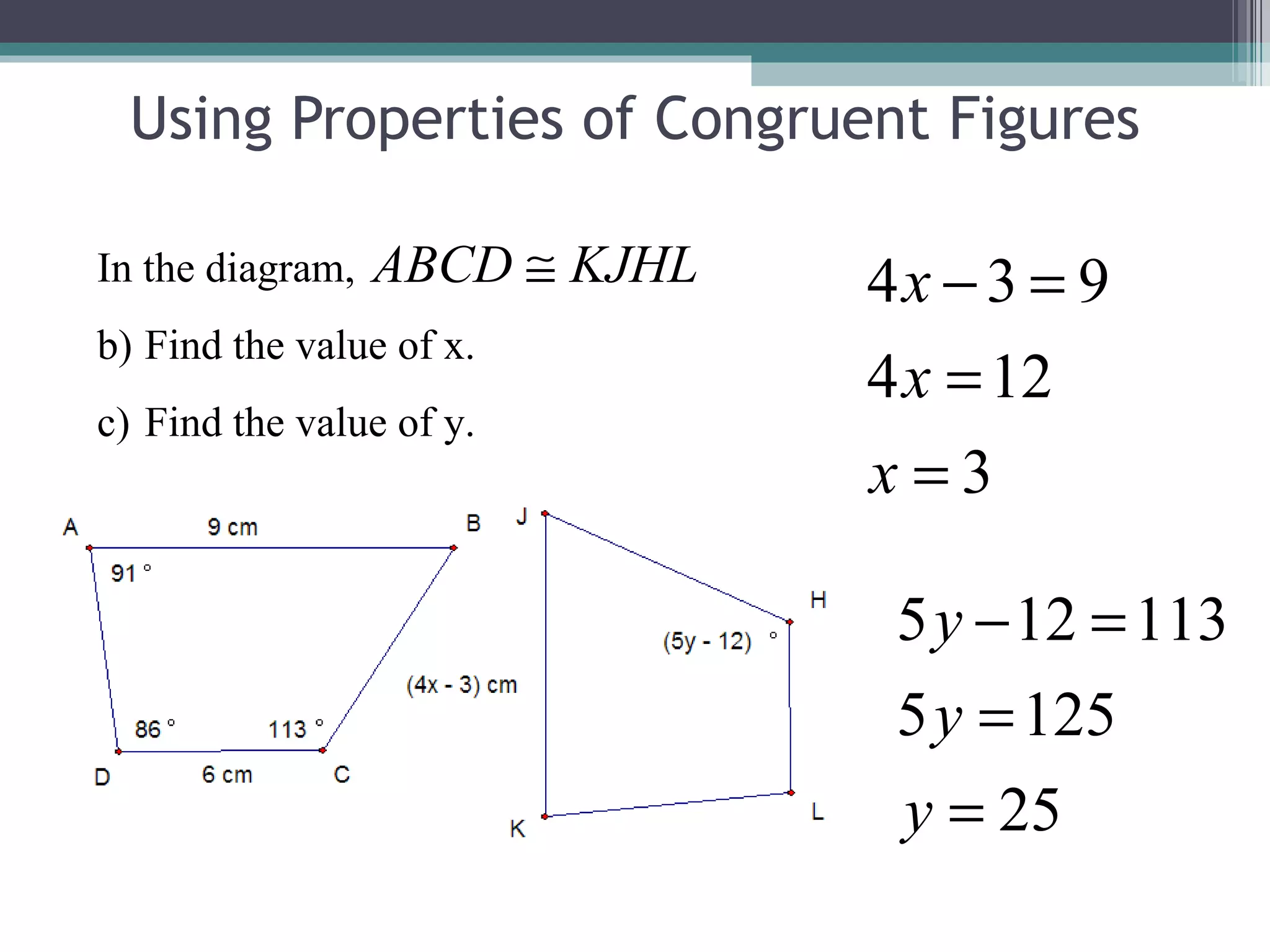
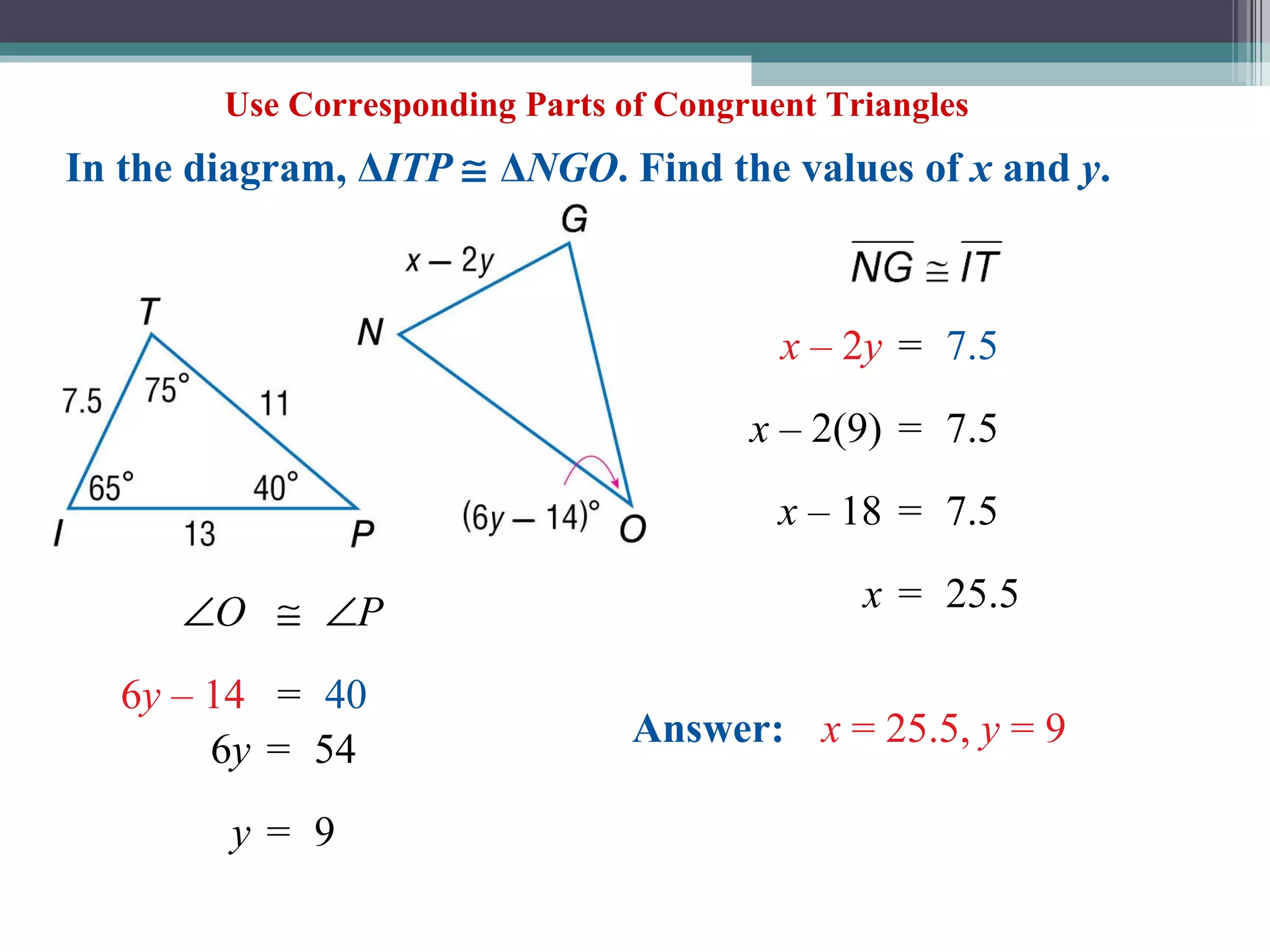
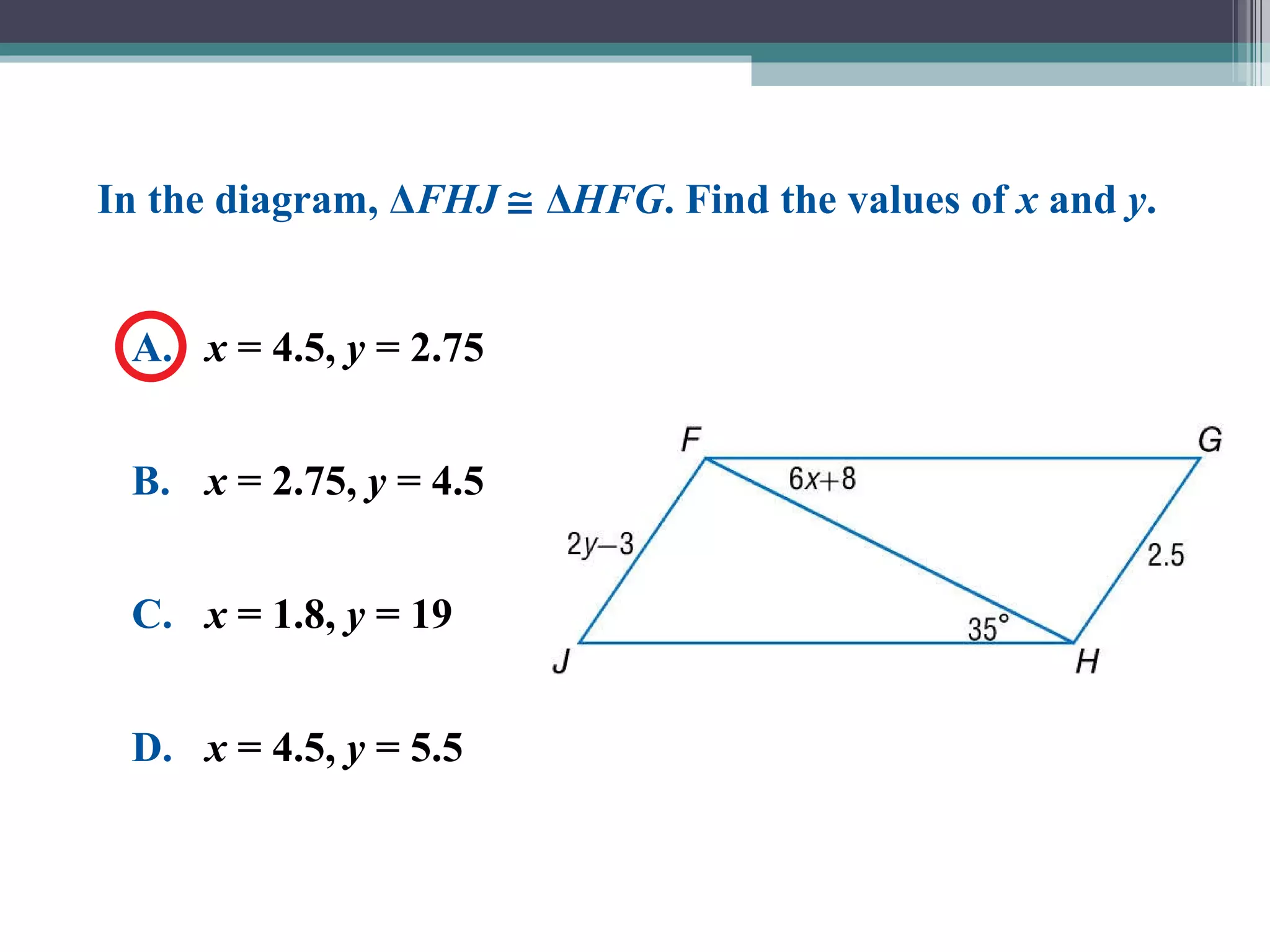
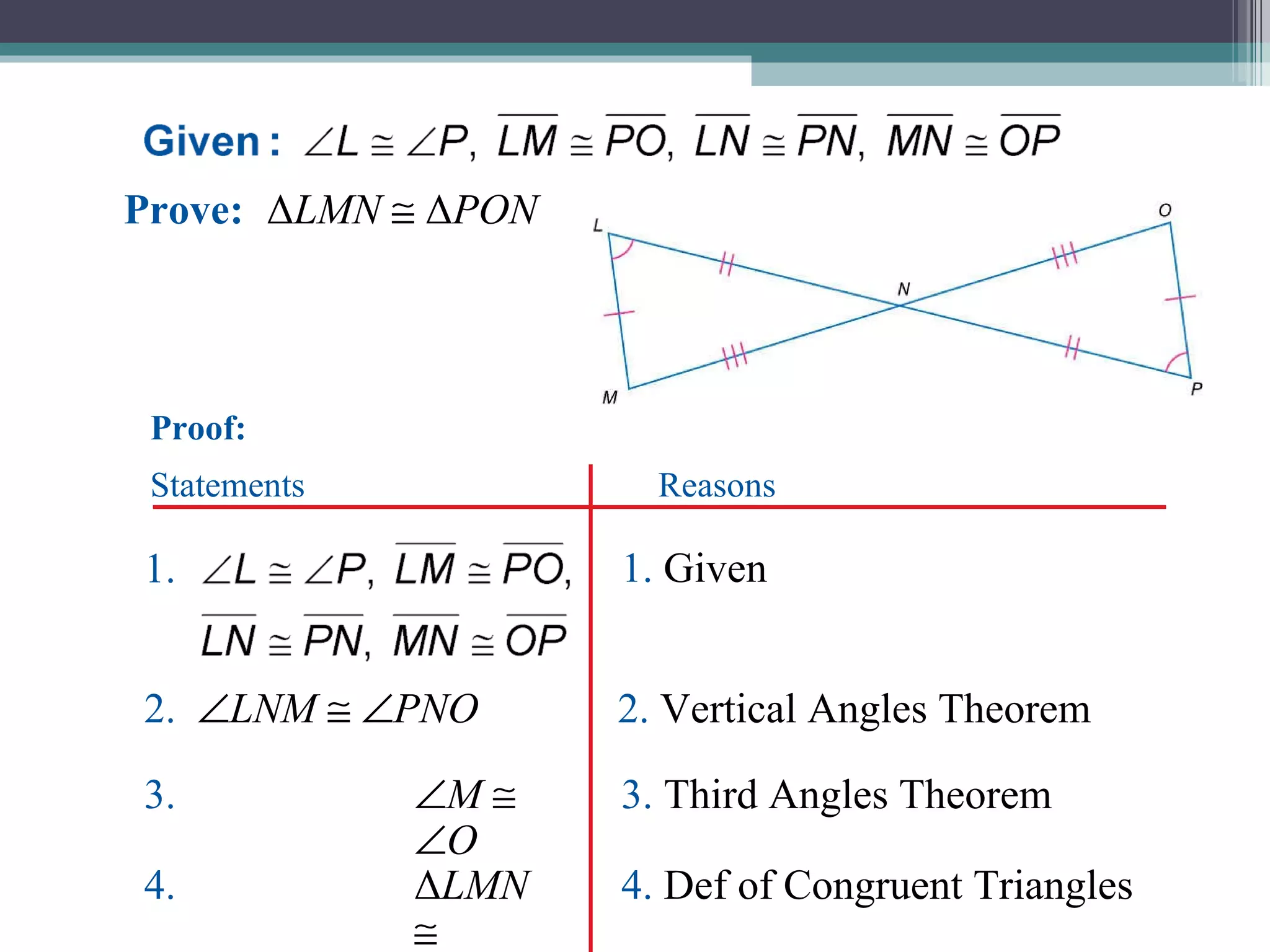
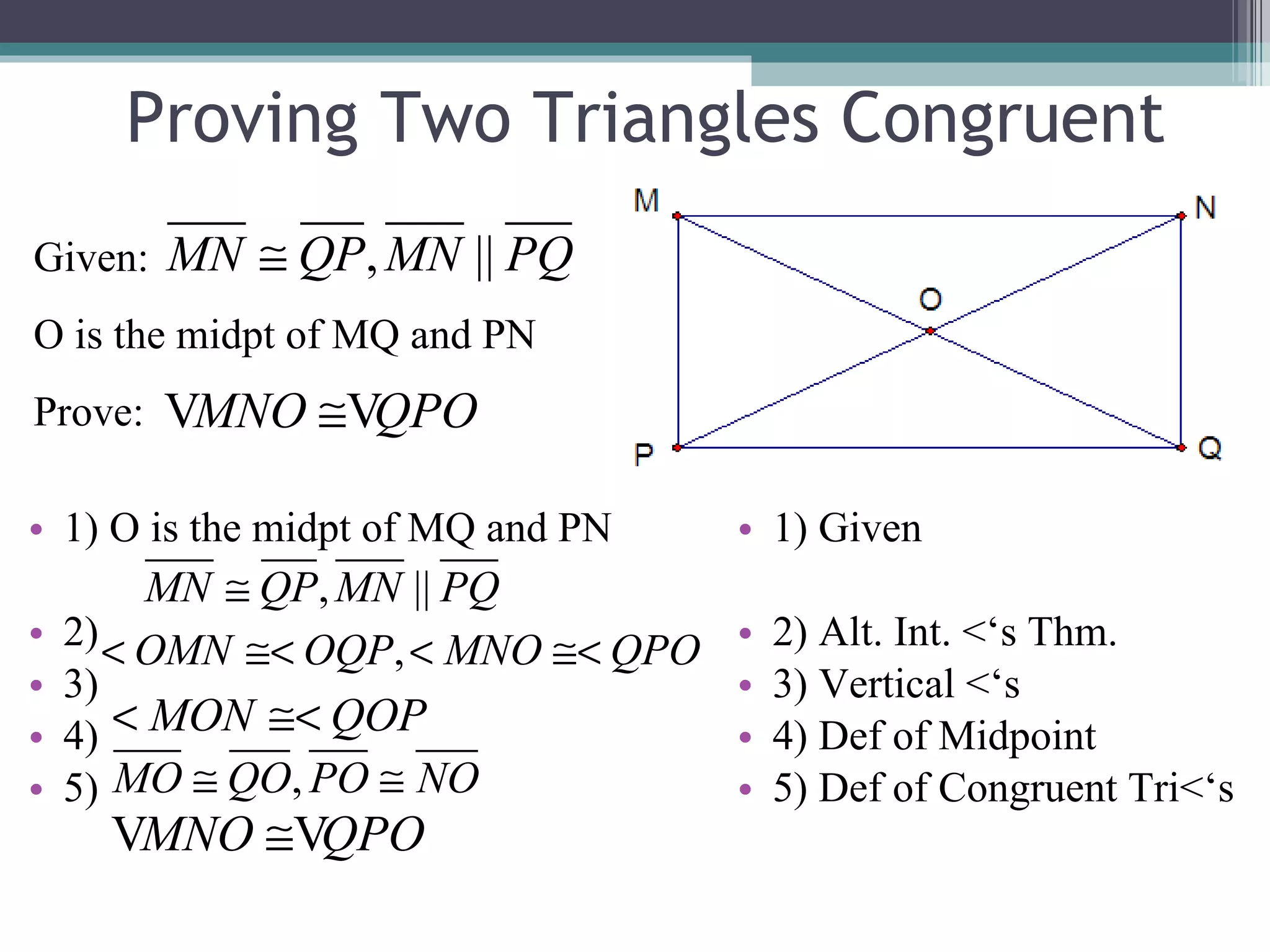
The document discusses congruent triangles and their properties. It defines congruent figures as those with corresponding sides and angles that are congruent. It presents several ways to prove triangles are congruent, including using corresponding parts, vertical angles, the third angle theorem, and properties of congruent figures like the transitive property. It provides examples of writing congruence statements and determining if triangles are congruent based on given information.