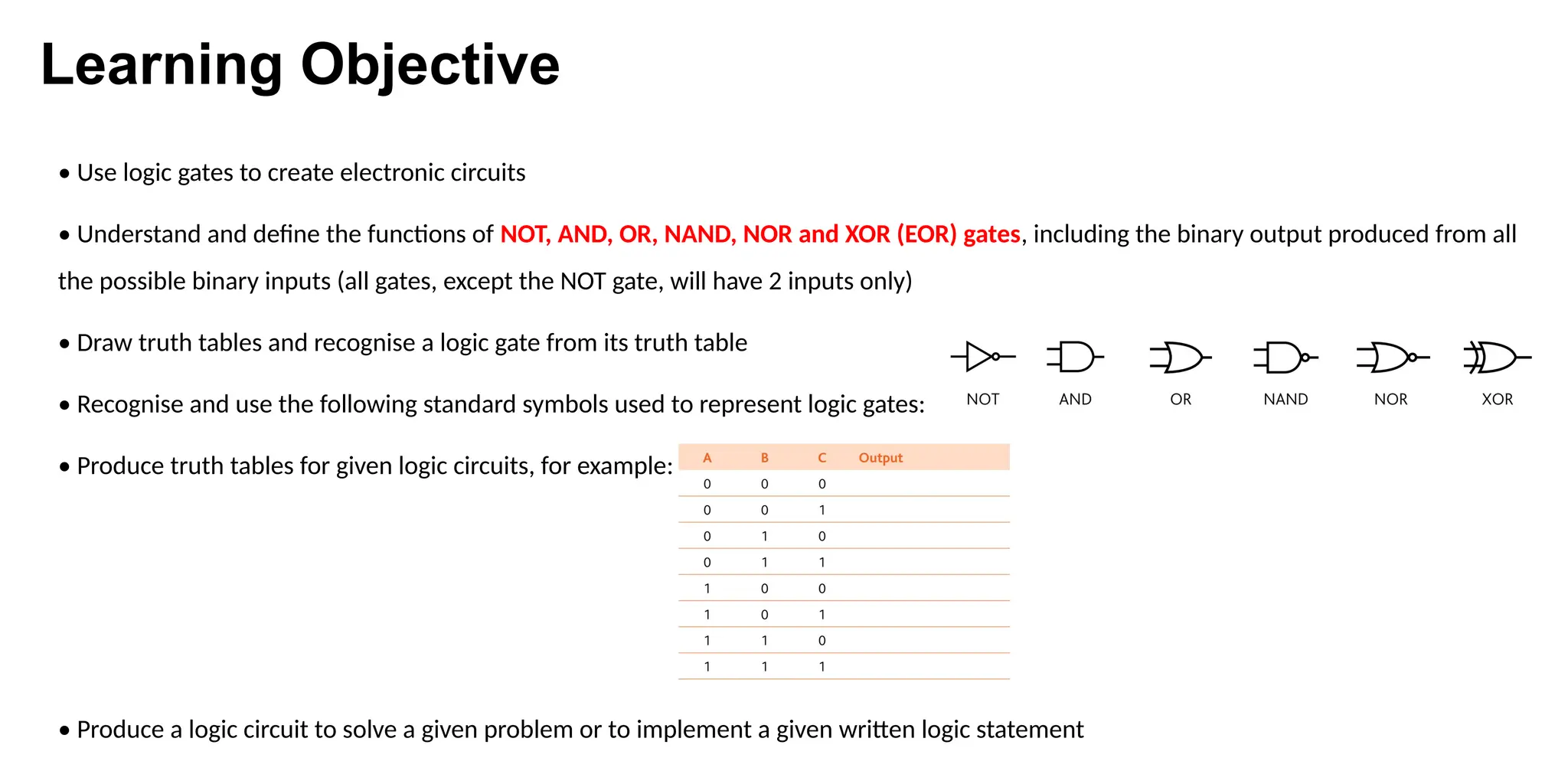
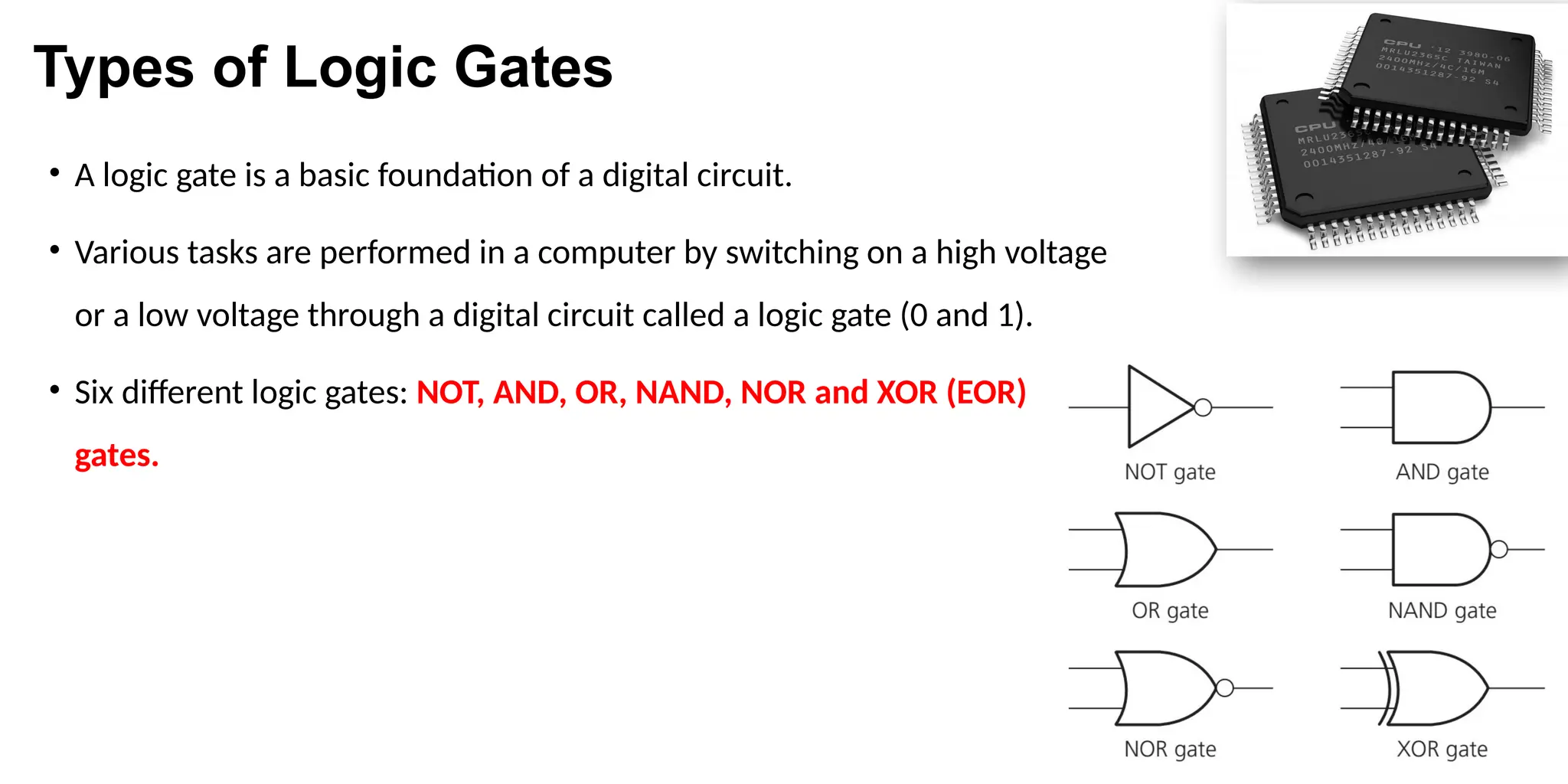
The document covers the use of logic gates in electronic circuits, focusing on the functions of six types: NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, and XOR gates, including their binary outputs and truth tables. It provides examples of creating circuit diagrams from logic statements and constructing truth tables for specific logic circuits. Additionally, it describes applications in safety systems for wind turbines and alarms based on various input conditions.