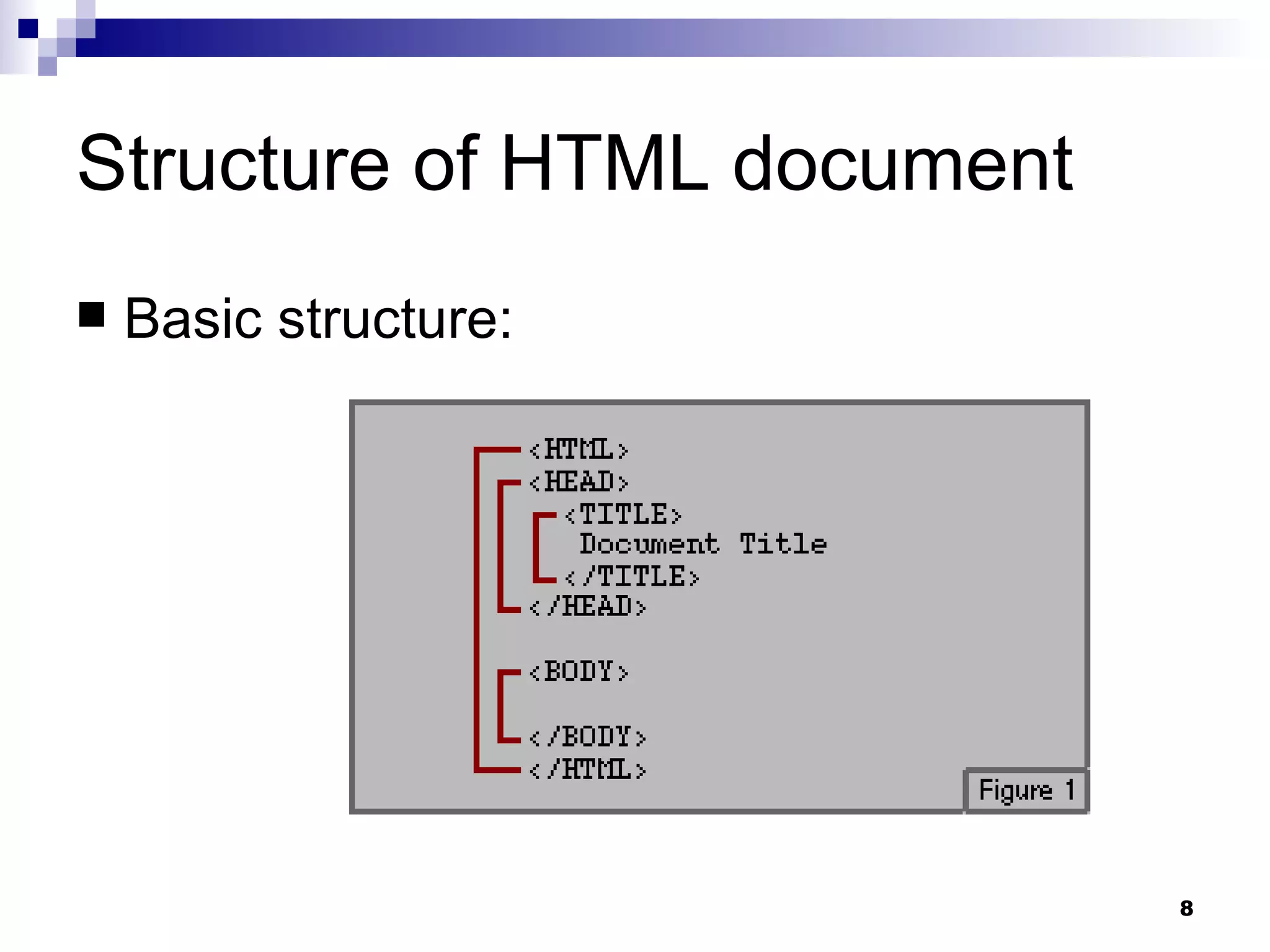
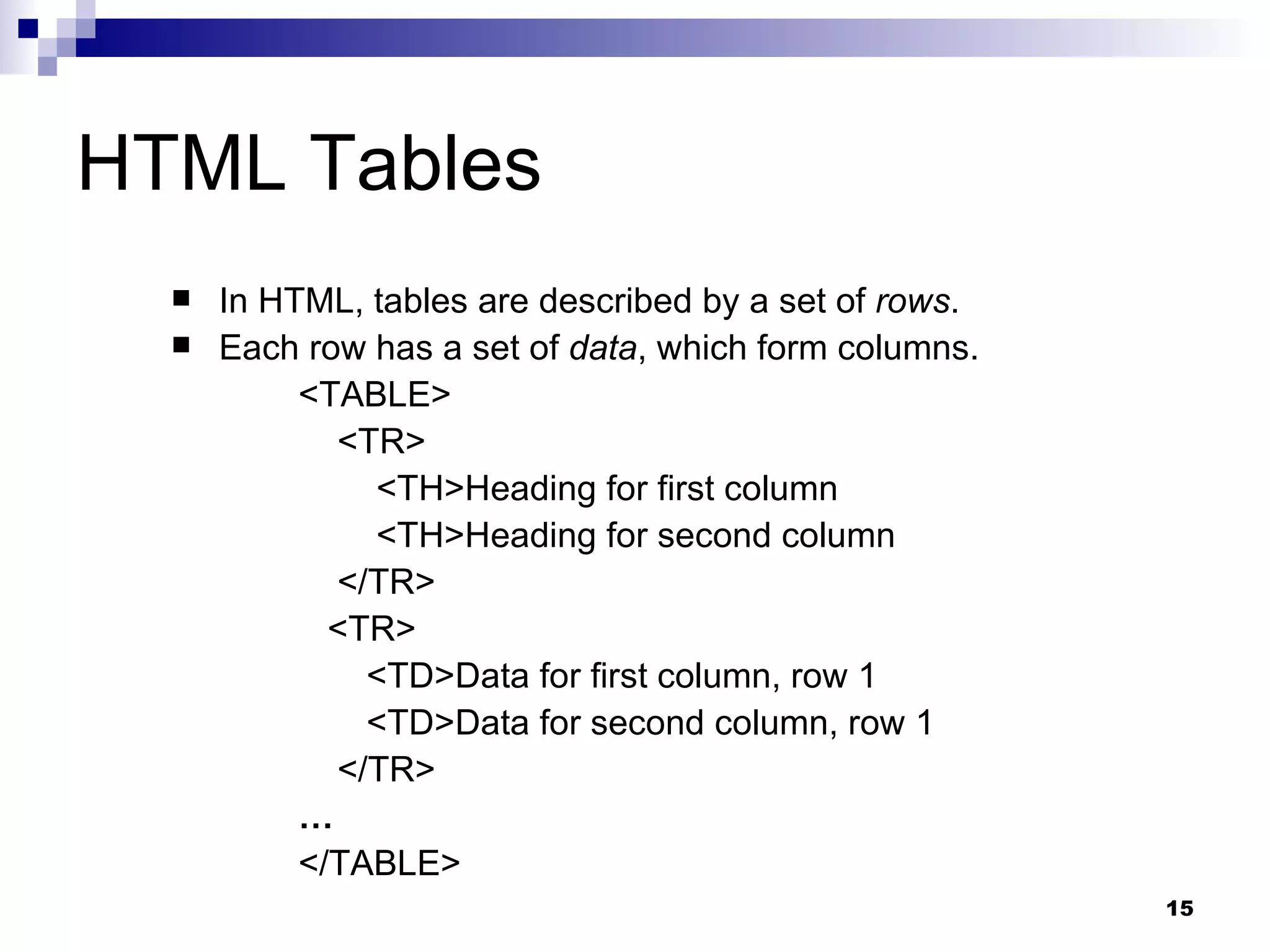
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is the code that defines the structure and layout of web pages. HTML uses tags to mark elements like headings, paragraphs, lists, and more. A web page is created by writing HTML code which is then displayed in web browsers. Common tags include headings, paragraphs, lists, links, images, and tables.