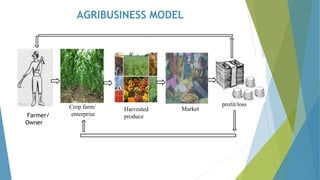
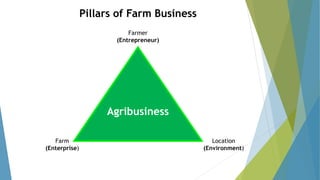
The document outlines the importance of treating farming as a business, emphasizing the need for farmers to adopt sound business principles and planning practices. It covers essential topics such as business definition, farm planning, record keeping, budgeting, and the entrepreneurial qualities necessary for success in agribusiness. The aim is to educate farmers on how to efficiently manage their operations to enhance productivity and profitability.