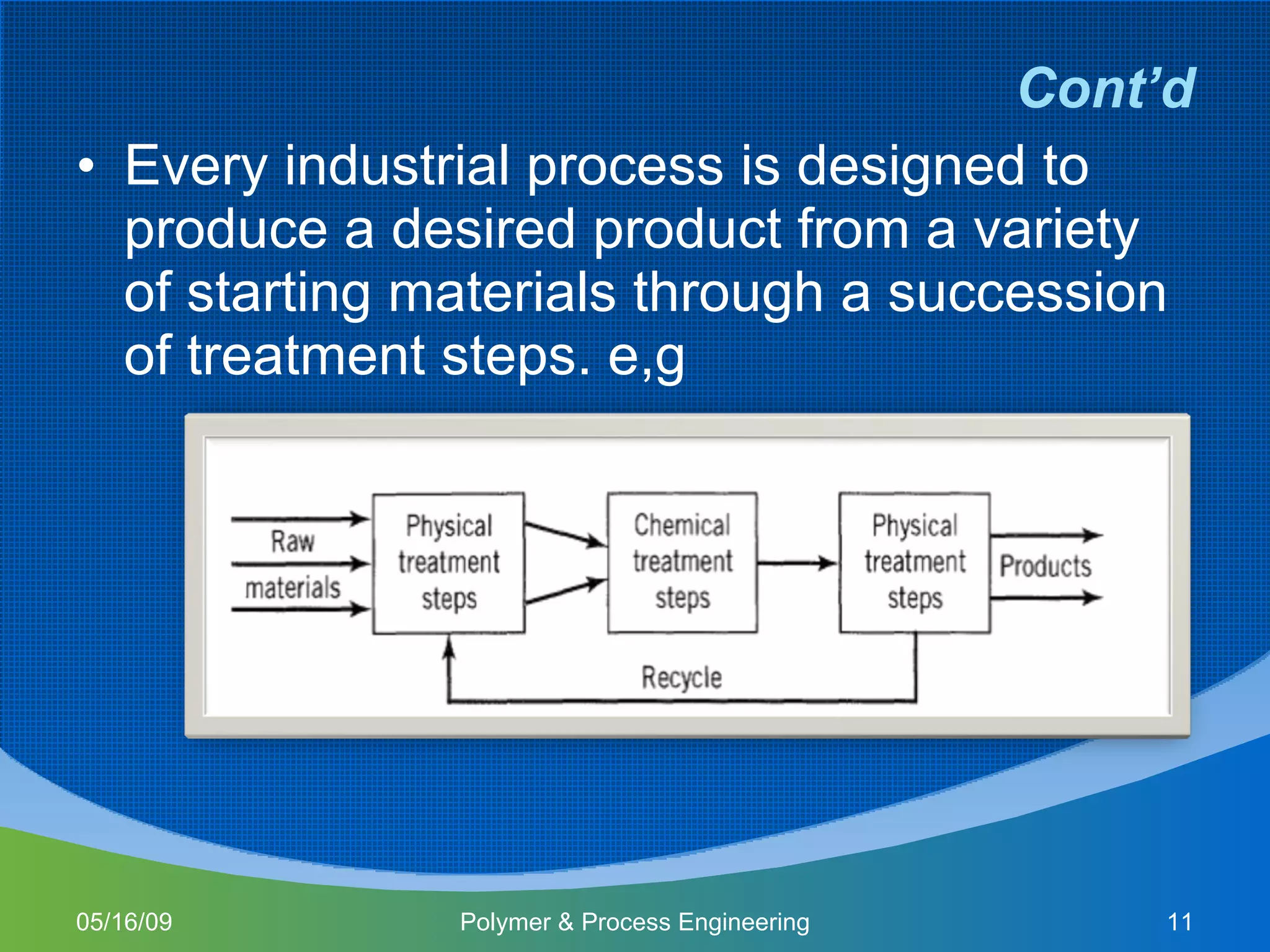
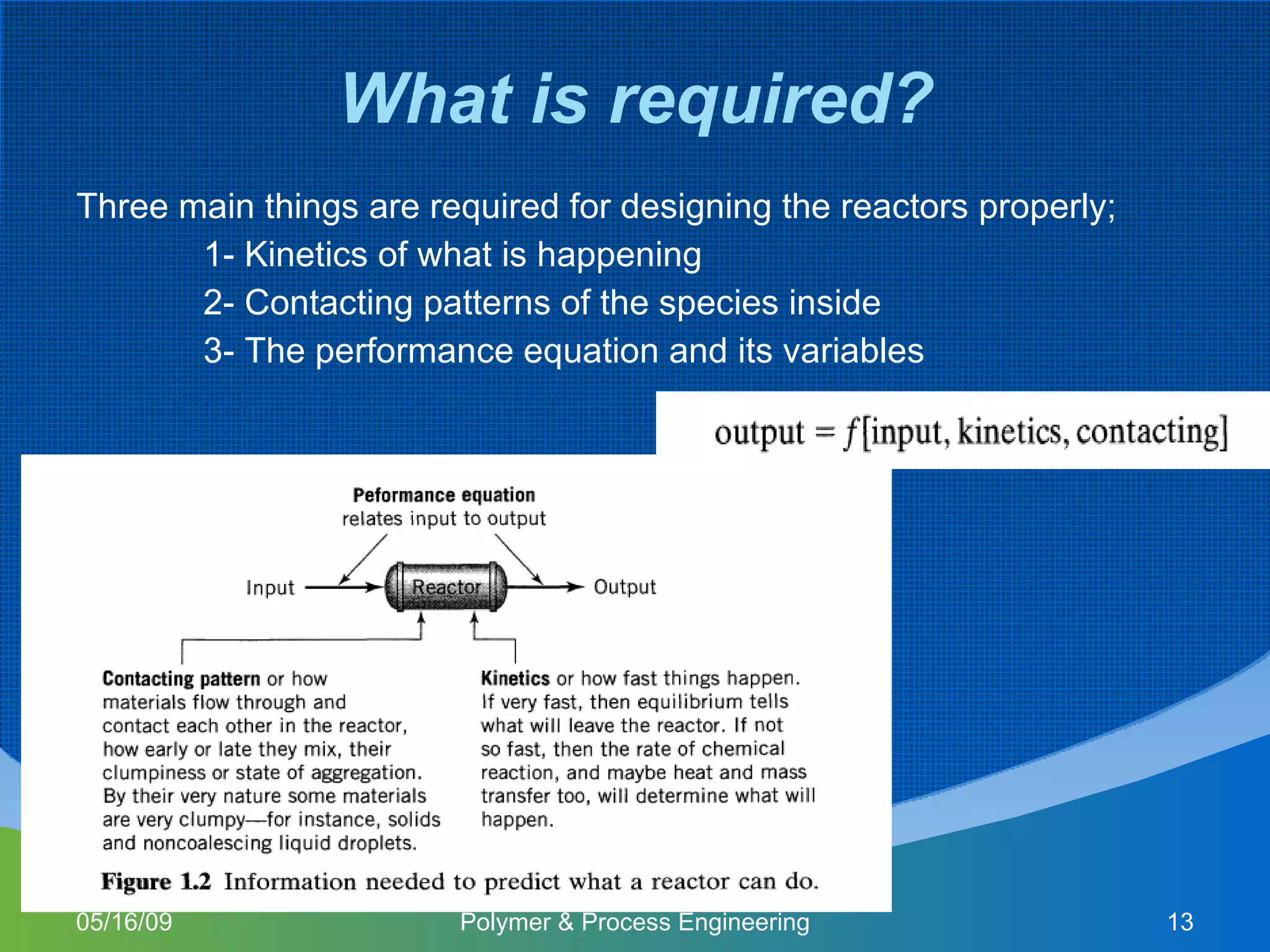
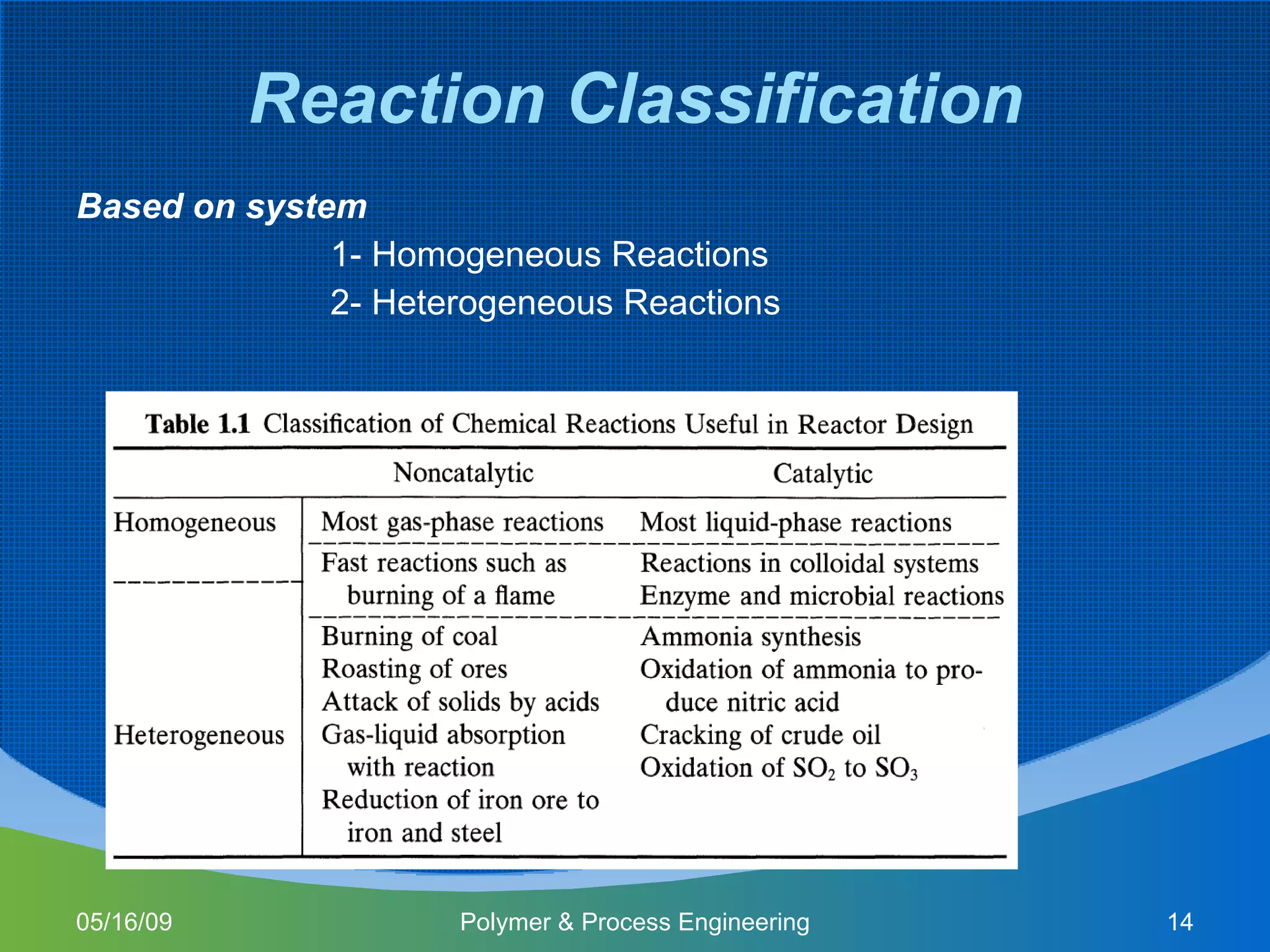
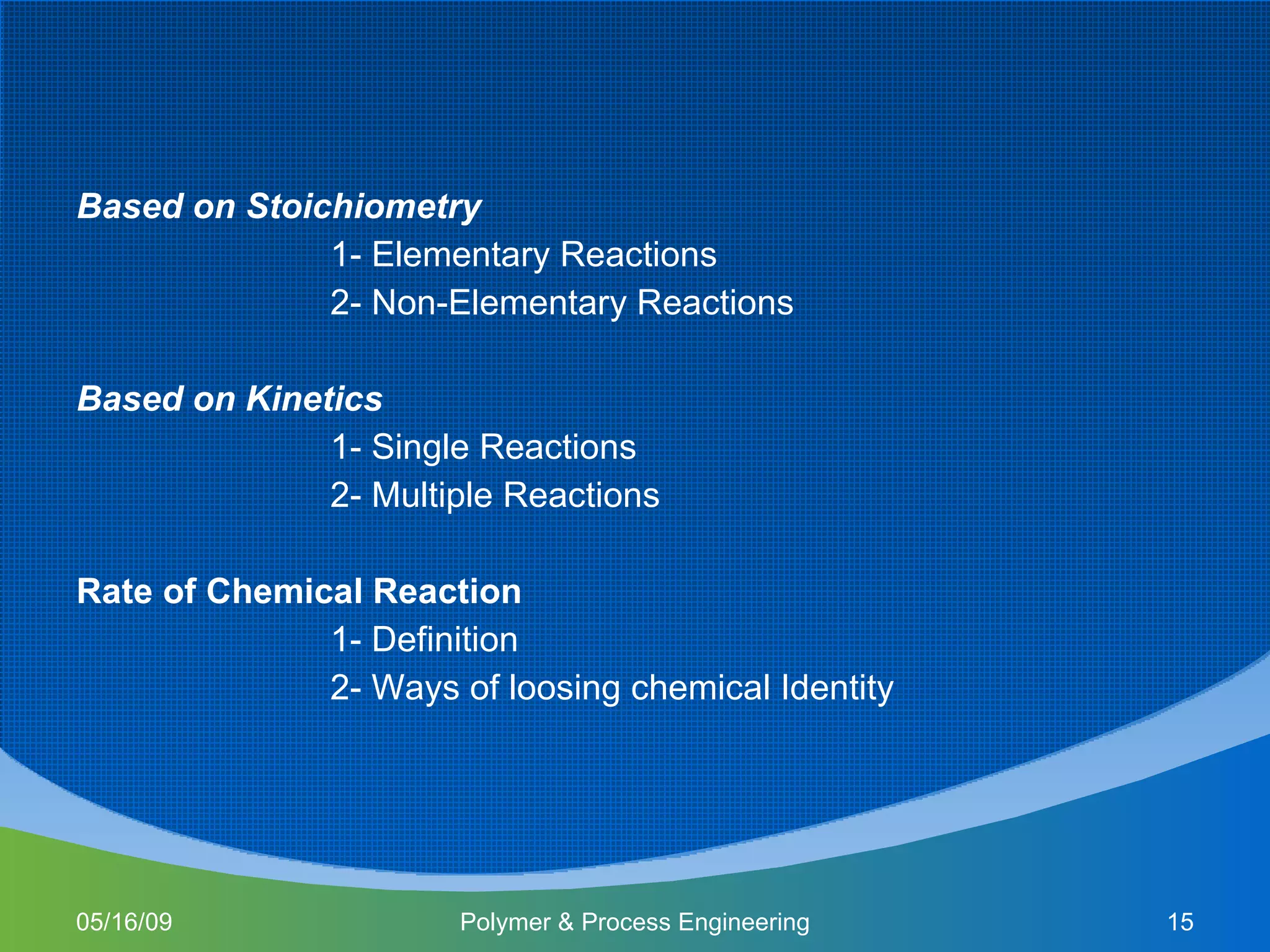
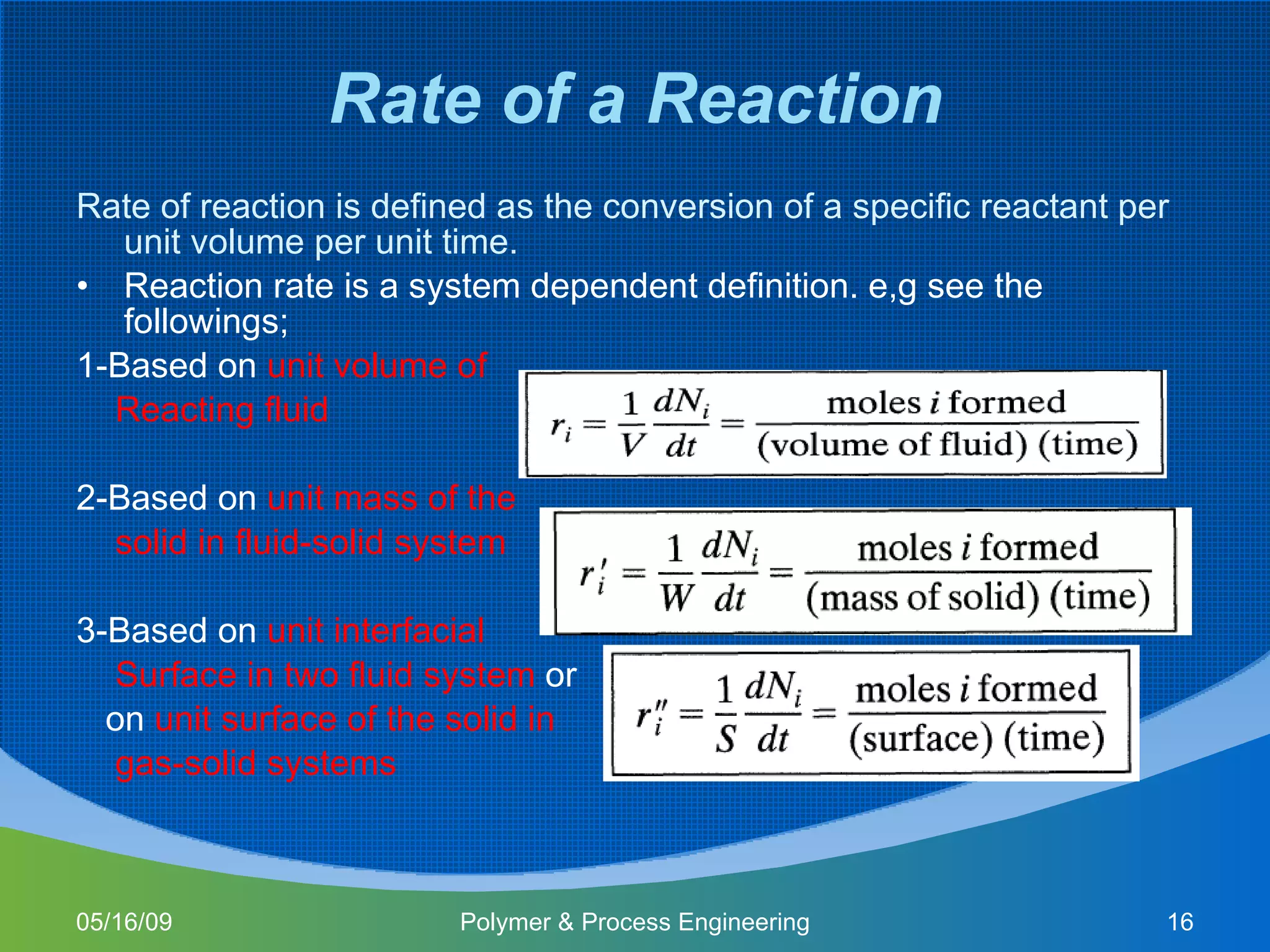
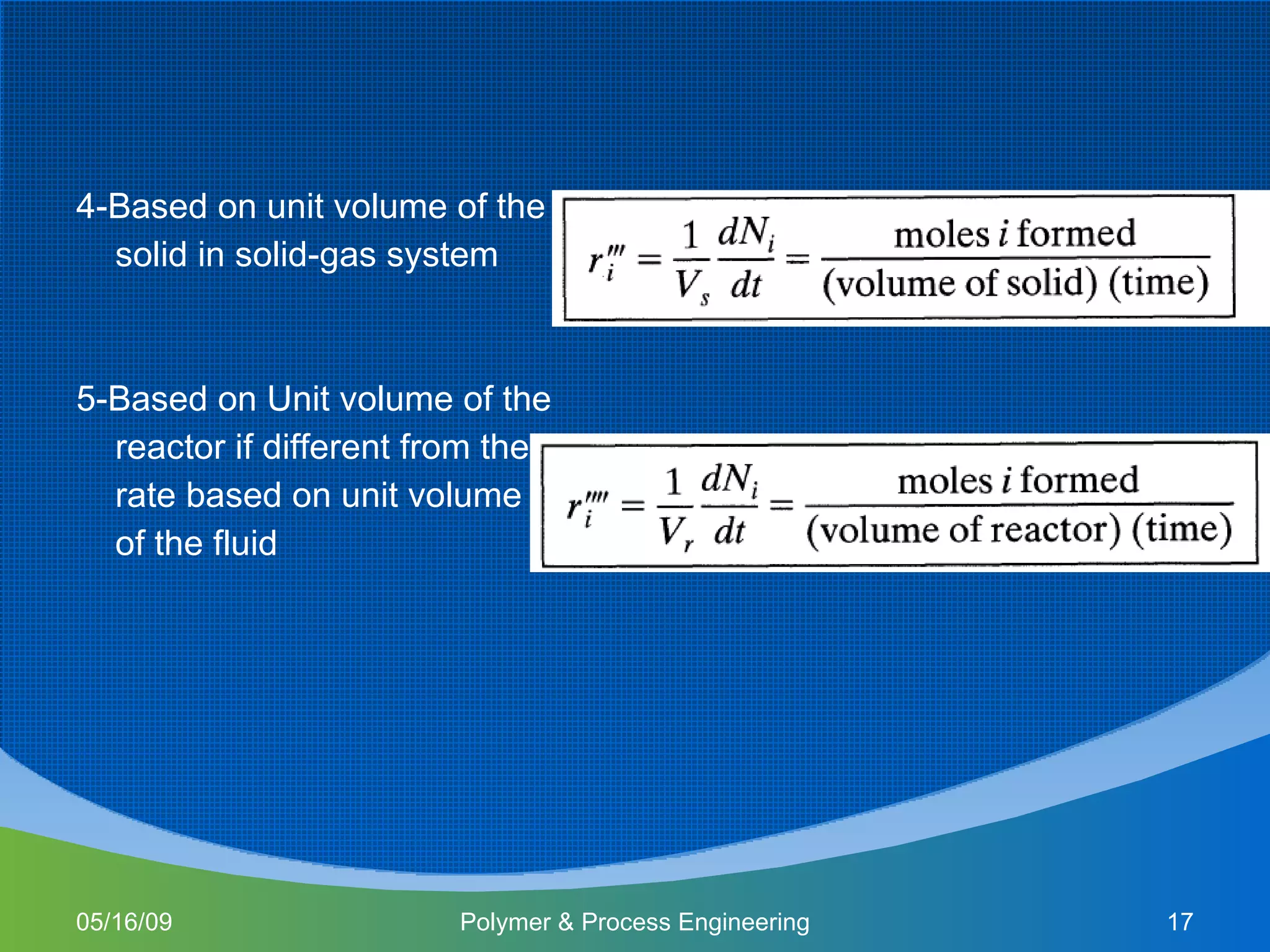
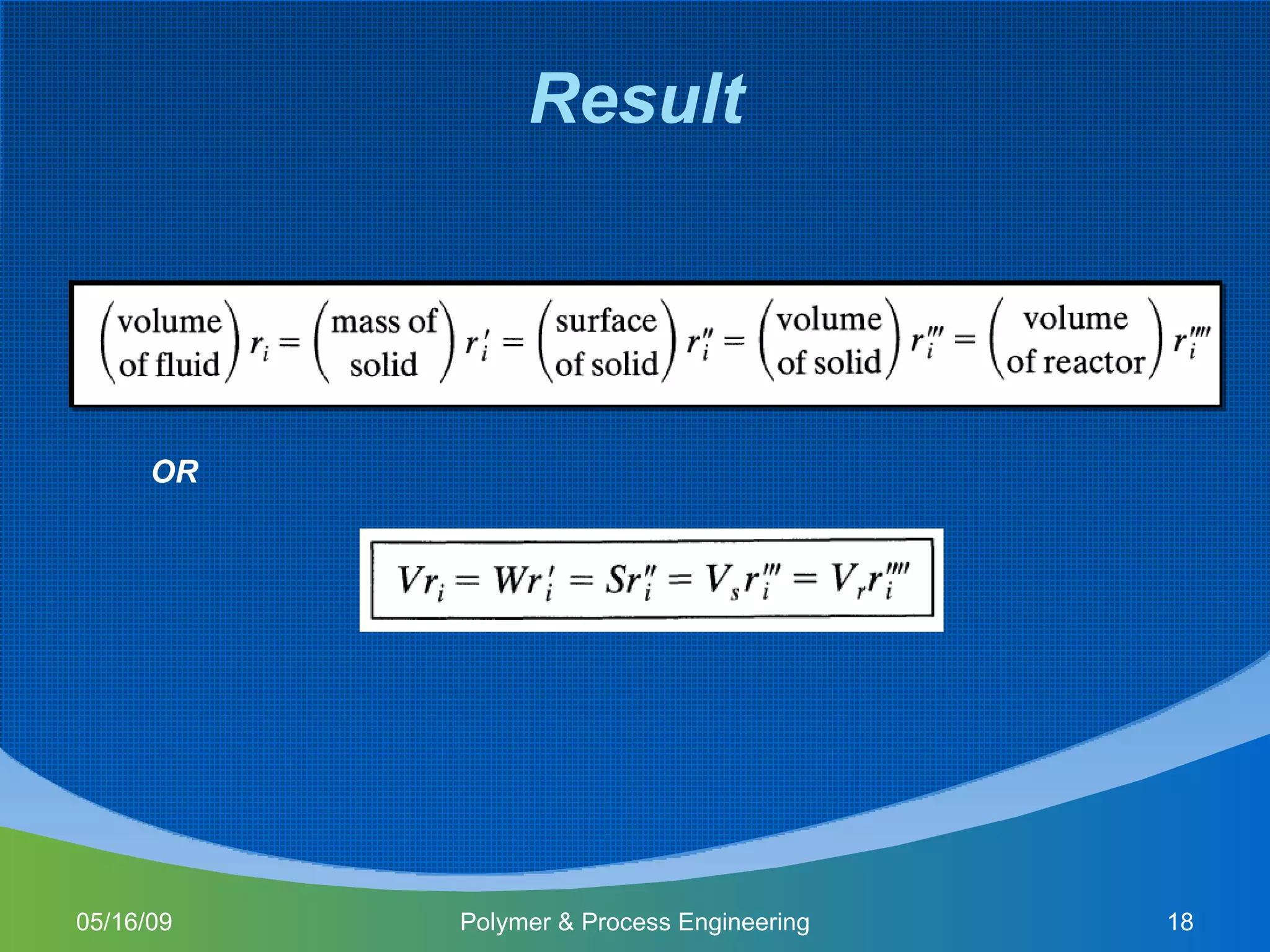
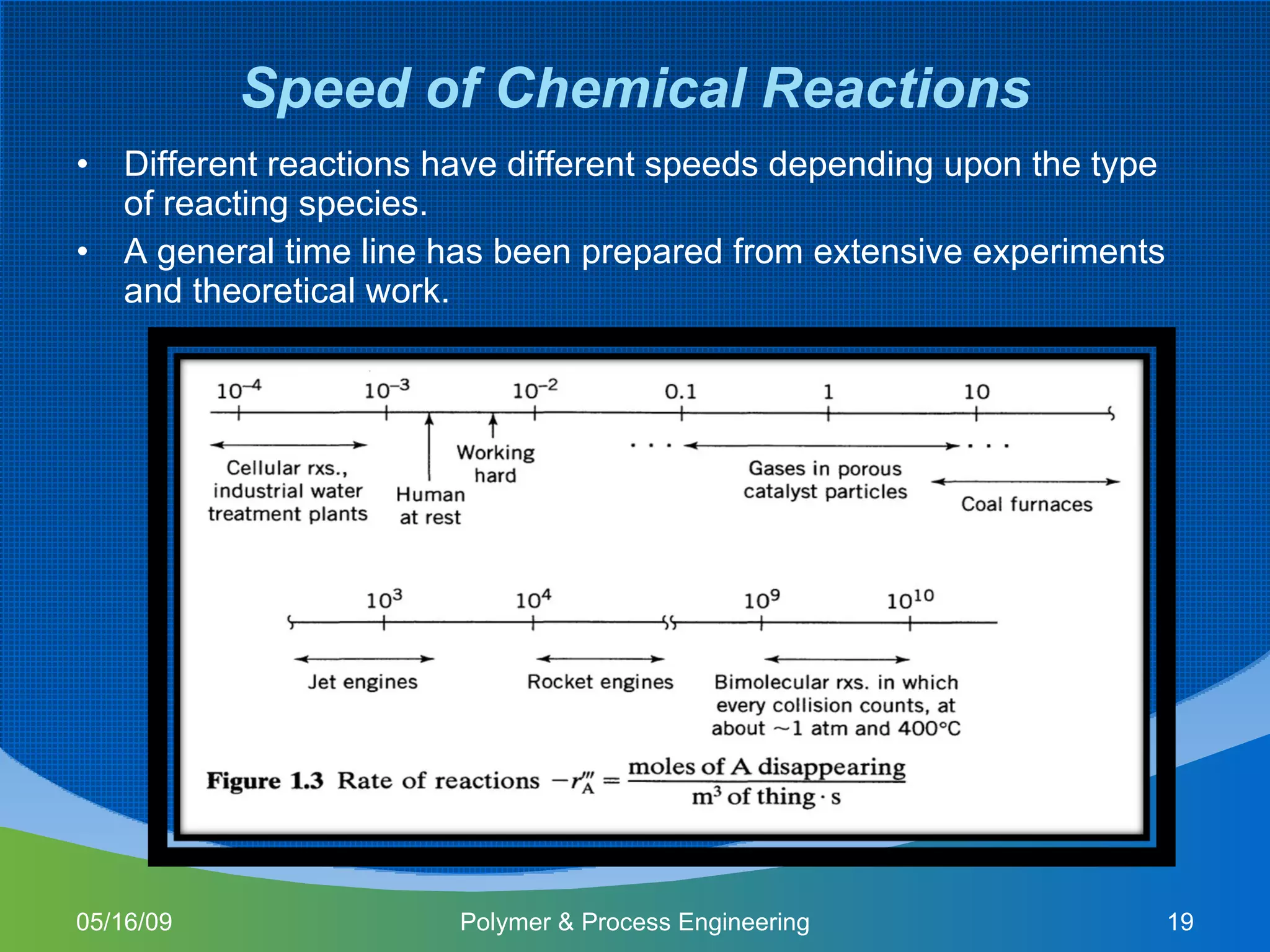
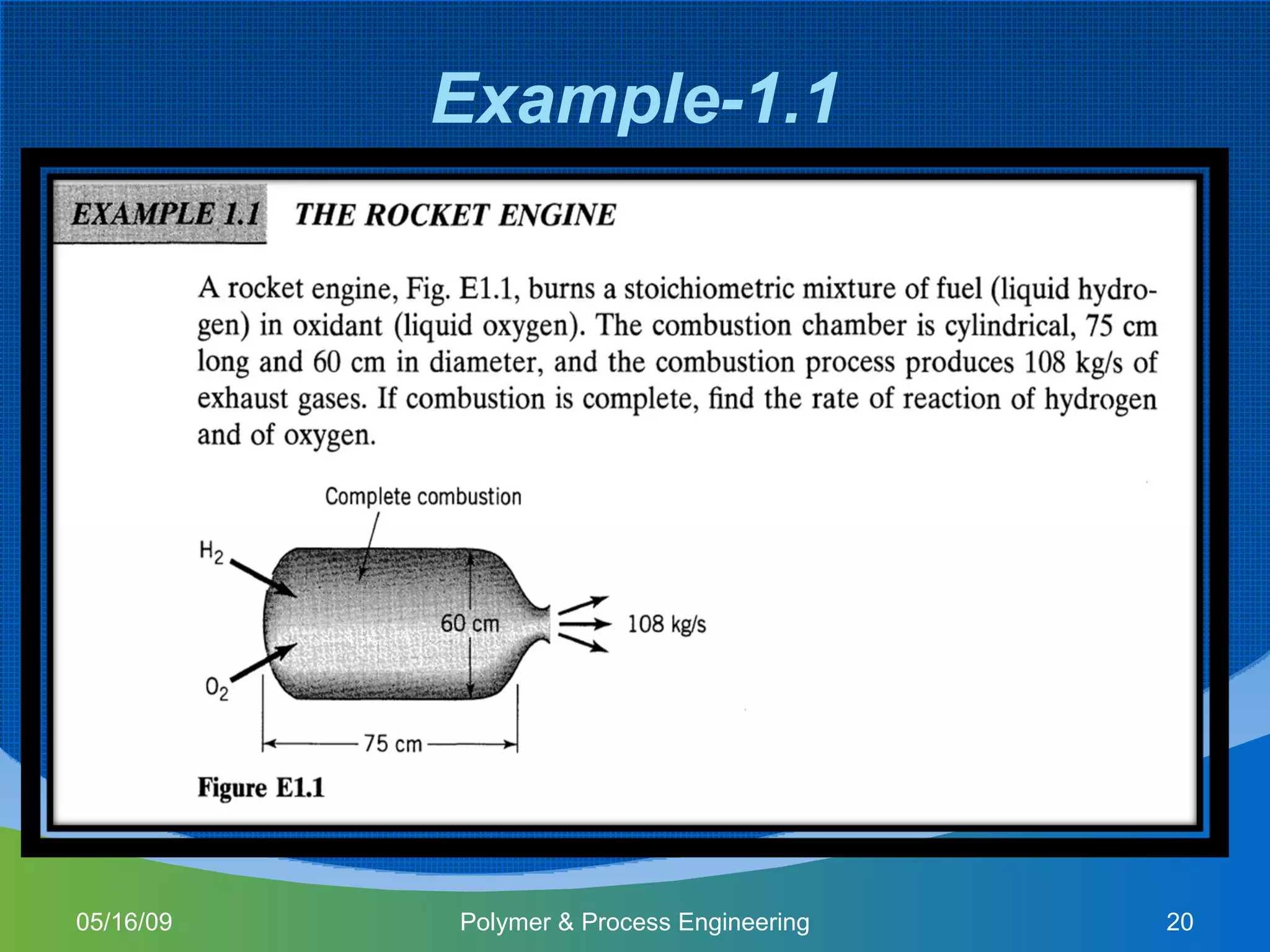
This document provides an overview of a Polymer Reaction Engineering course. The course goals are to introduce students to reaction engineering, polymerization reactions, kinetics, and reactor design. The course objectives are for students to understand reaction kinetics and apply this to the conceptual design of reactors. The schedule outlines 16 weeks of topics like batch and continuous reactor design, polymerization reactions, and a final design project.