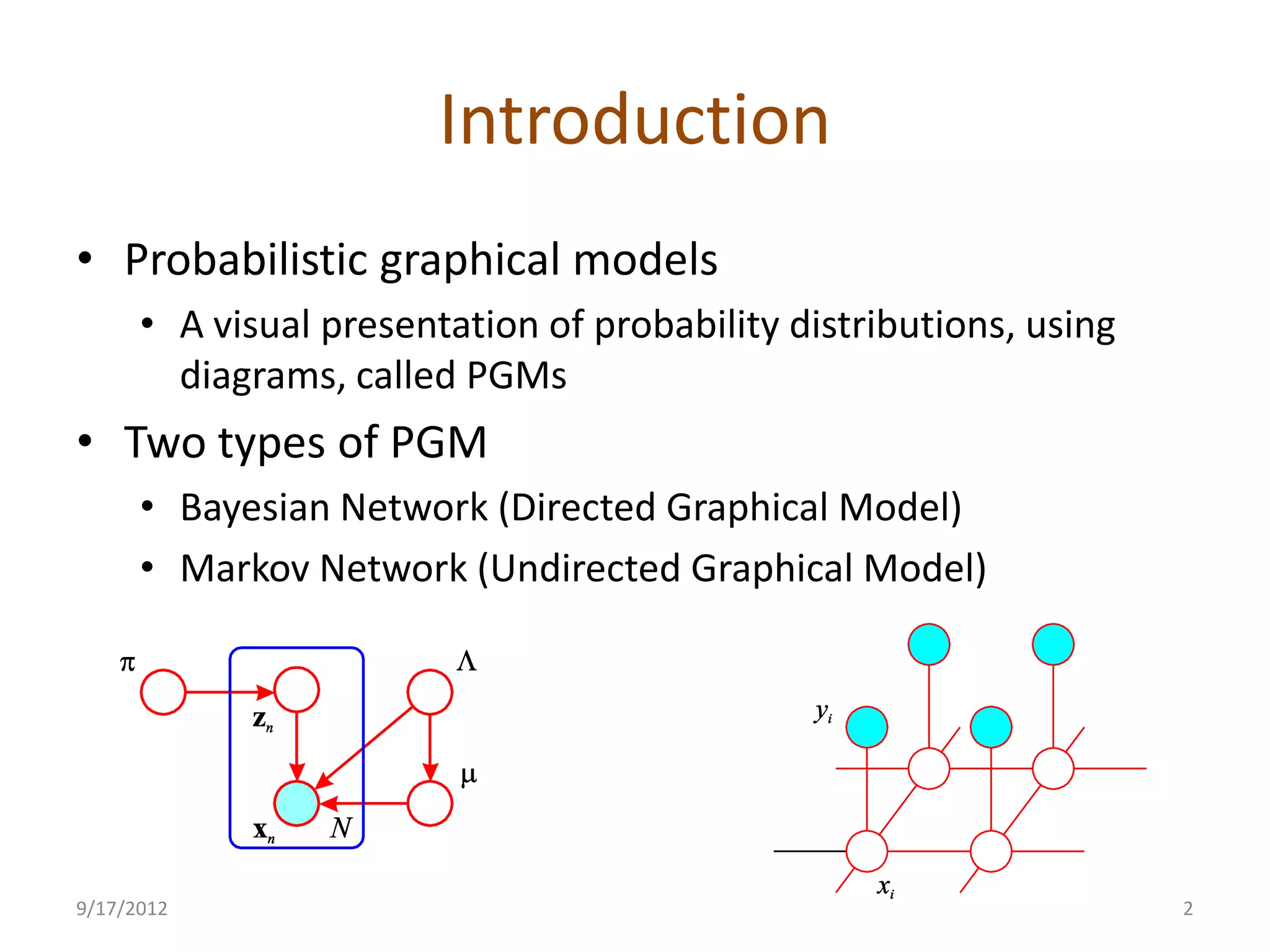
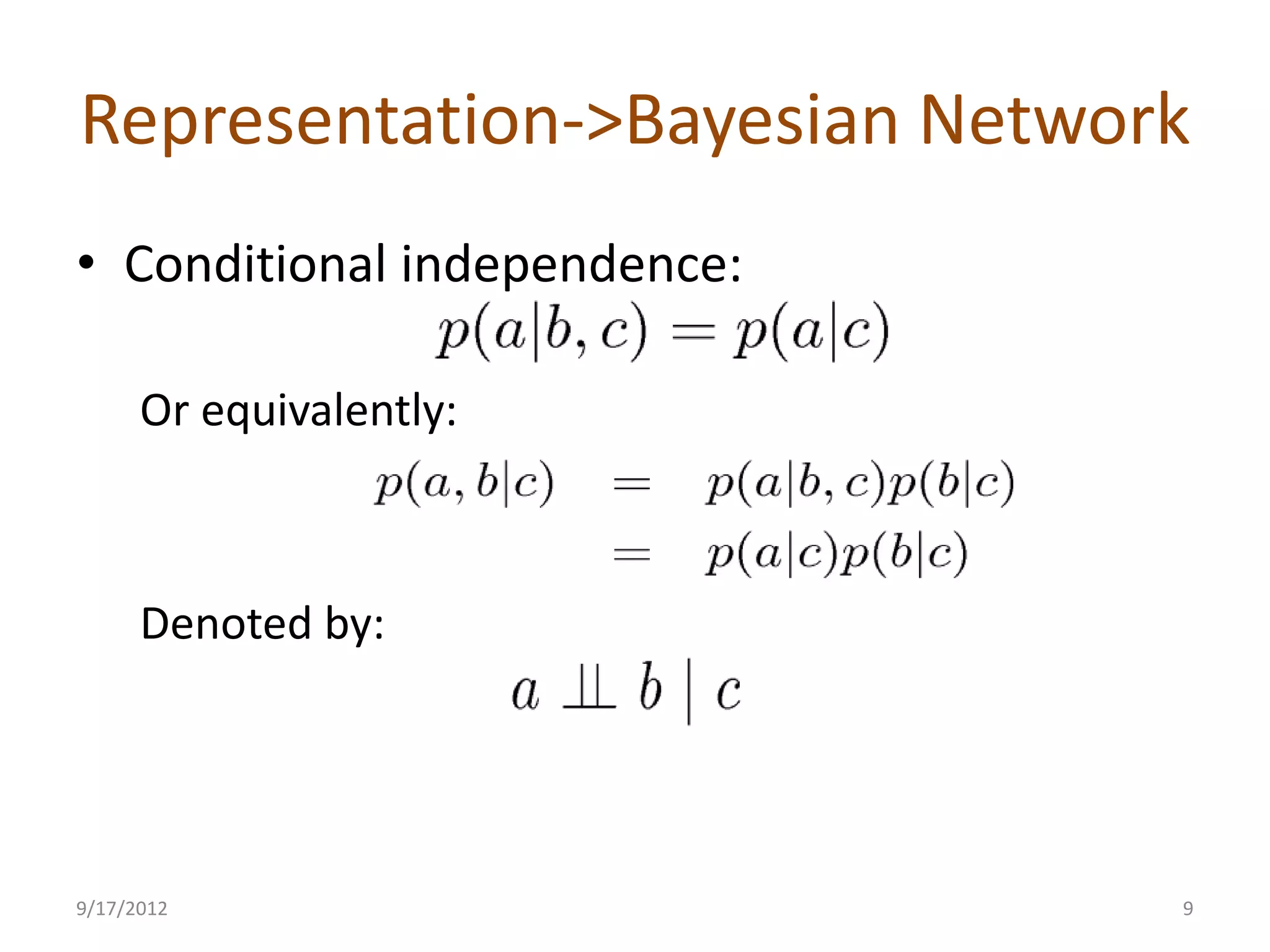
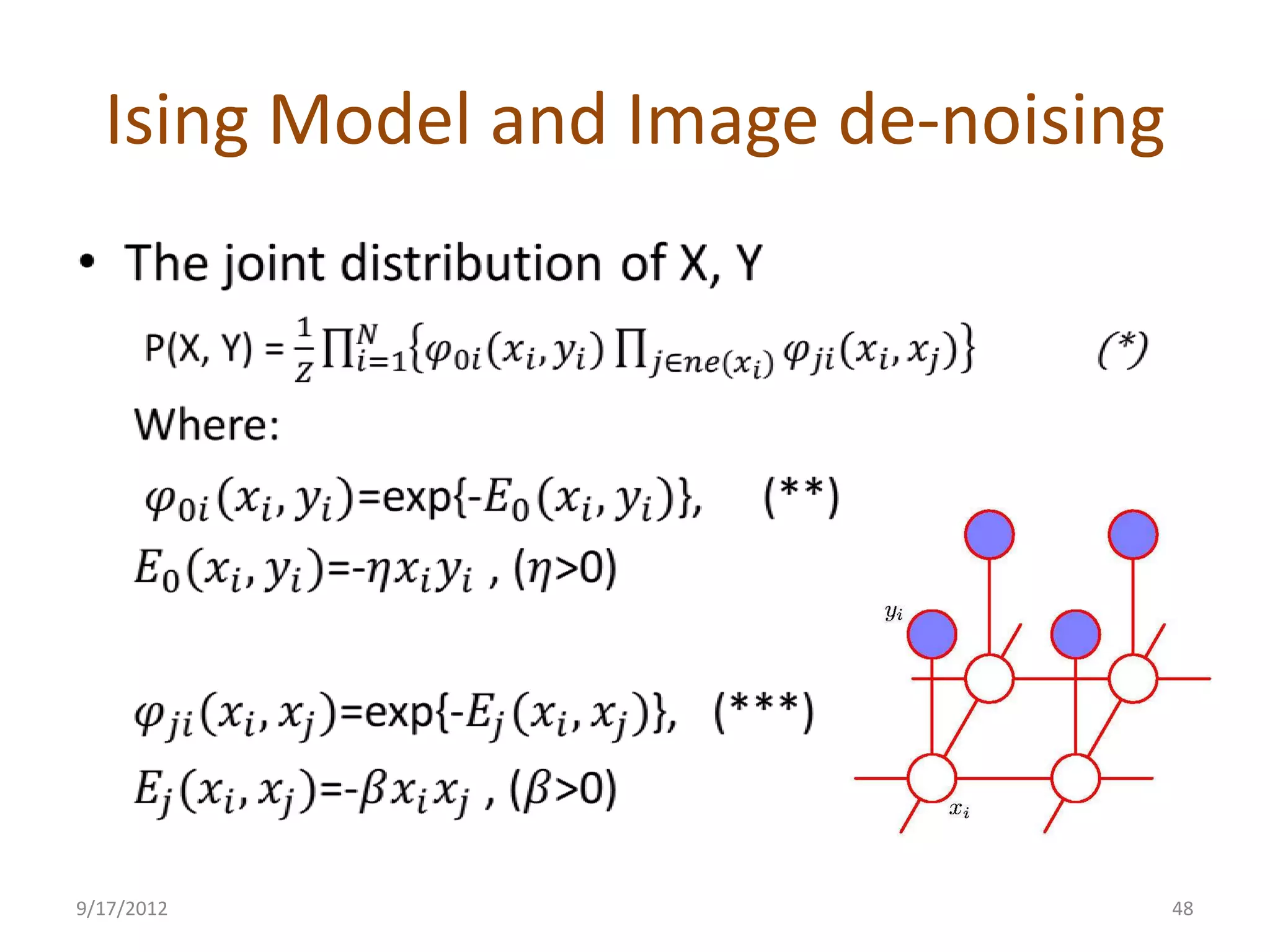
This document provides an overview of probabilistic graphical models. It discusses two types of probabilistic graphical models - Bayesian networks and Markov networks. Bayesian networks use directed graphs to represent conditional independence relationships between random variables. Markov networks use undirected graphs for the same purpose. The document outlines topics like representation, examples including naive Bayes classifiers and the Ising model, and inference and learning algorithms for probabilistic graphical models.