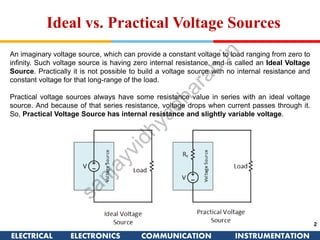
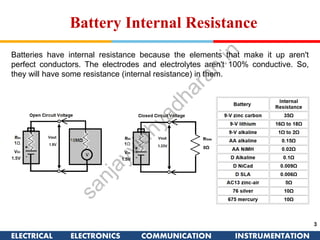
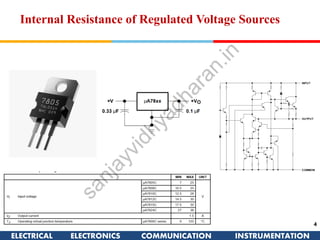
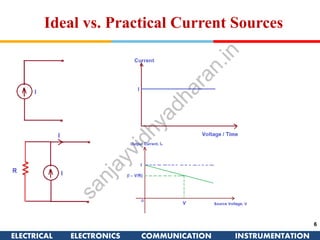
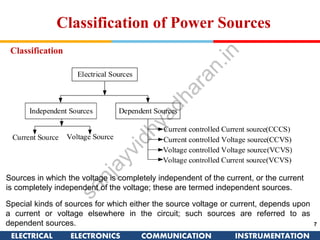
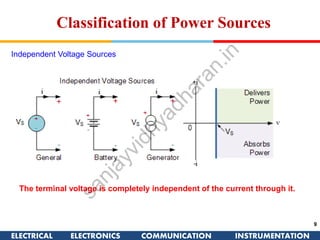
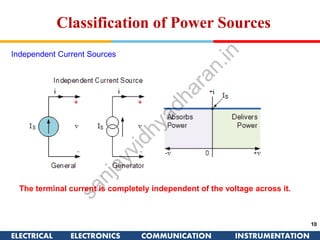
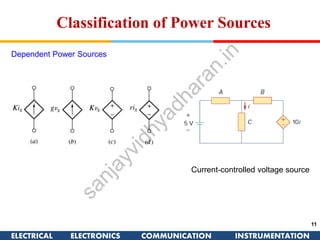
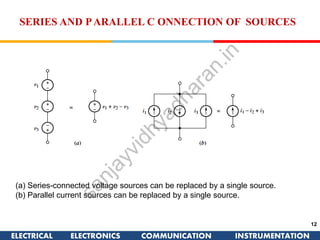
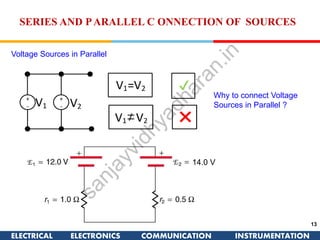
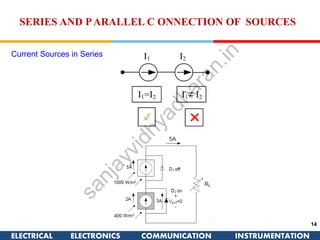
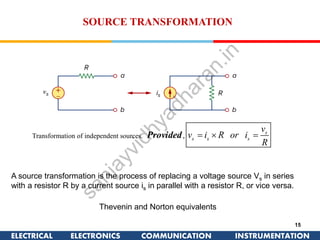
The document discusses ideal and practical voltage sources. An ideal voltage source has zero internal resistance and provides a constant voltage regardless of load. Practical voltage sources always have some internal resistance, so their voltage drops when current passes through. Batteries and regulated voltage sources like the DC205 also have internal resistance due to non-perfect conductivity of their components. The document also classifies power sources as independent sources where voltage or current does not depend on load, and dependent sources where voltage or current is controlled by another in the circuit.