The document discusses pointers in C++, including how to access addresses and contents using pointers, how to access array elements using indexes and pointers, and how pointers can be used to pass arguments to functions by reference or by pointer. It also provides examples of pointer usage and briefly describes bubble sort as a sorting algorithm.



![Array Accessing Using Index
int main()
{
int intarray[5] = { 31, 54, 77, 52, 93 };
for(int j=0; j<5; j++)
cout << intarray[j] << endl;
getch();
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-38-39-pointers-130222002656-phpapp02/85/Lec-38-39-pointers-4-320.jpg)
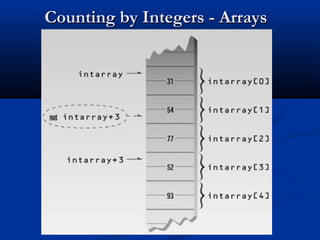
![Array Accessing Using Pointers
int main()
{
int intarray[5] = { 31, 54, 77, 52, 93 };
for(int j=0; j<5; j++)
cout << *( intarray + j ) << endl;
getch();
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-38-39-pointers-130222002656-phpapp02/85/Lec-38-39-pointers-5-320.jpg)



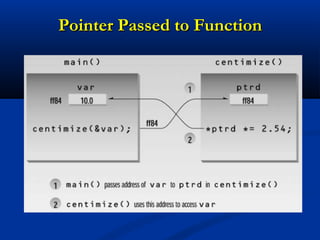
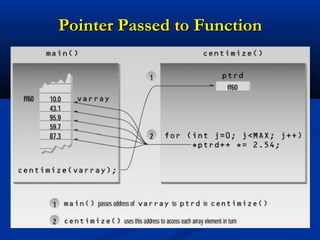
![Passing Arrays to Function
const int MAX = 5;
void centimize(double*);
int main()
{ double varray[MAX] = { 10.0, 43.1, 95.9, 59.7, 87.3 };
centimize(varray);
for(int j=0; j<MAX; j++)
cout << varray[j] << endl;
getch(); return 0; }
void centimize(double* ptrd)
{ for(int j=0; j<MAX; j++)
*ptrd++ = *ptrd * 2.54; } //*ptrd++ = *(ptrd++)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-38-39-pointers-130222002656-phpapp02/85/Lec-38-39-pointers-11-320.jpg)