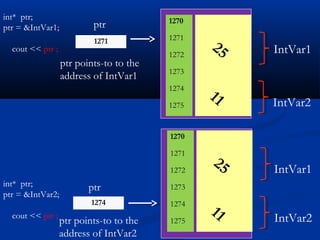
Pointers are used to access array elements, pass arguments to functions by reference, pass arrays and strings to functions, obtain memory from the system, and create data structures like linked lists. Memory addresses refer to the locations where variables are stored. A pointer variable stores the address of another variable. The indirection operator (*) is used to dereference a pointer and access the value of the variable it points to. A void pointer can point to data of any type.