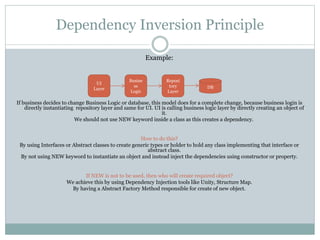
The document outlines the S.O.L.I.D principles in C#, which include the Single Responsibility Principle, Open Closed Principle, Liskov's Substitution Principle, Interface Segregation Principle, and Dependency Inversion Principle. Each principle is defined with guidelines on how to implement it, emphasizing the importance of class design, abstraction, and reducing dependencies to enhance code modularity and maintainability. Key recommendations involve avoiding over-engineering and assessing the appropriate application of S.O.L.I.D principles in relation to project size.