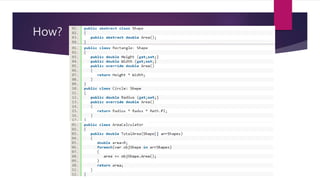
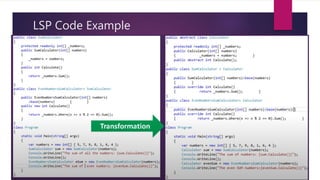
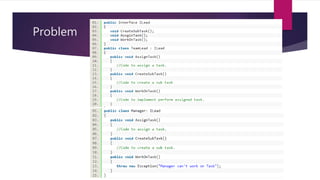
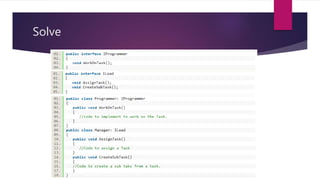
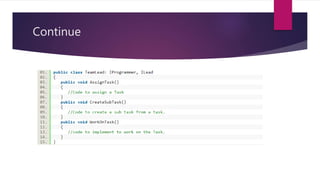
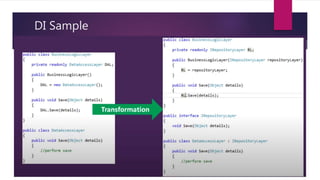
The document discusses the SOLID principles of object-oriented design, which are a set of five design principles intended to make software designs more understandable, flexible and maintainable. It defines each principle: single responsibility, open/closed, Liskov substitution, interface segregation, and dependency inversion. Following these principles helps produce code that is less complex, more readable, extensible, maintainable and reusable with looser coupling between modules and better testability compared to code not following these principles.