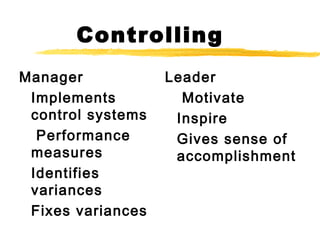
This document discusses leadership and the differences between managers and leaders. It provides 3 key points:
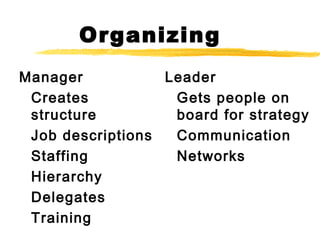
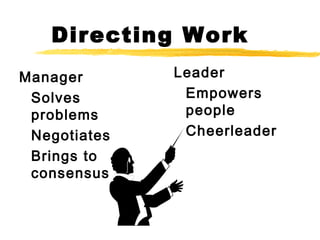
1) Leadership is about influencing and inspiring people, while management focuses more on planning, organizing, and controlling tasks. Leaders set a vision and strategy, while managers ensure goals and steps are being followed.
2) There are different types of leaders, defined by how they achieved their position, personality traits, moral example, or power and ability. Effective leadership also requires traits like intelligence, personality, and adaptability.
3) For new leaders, it is important to quickly learn about their organization, secure some early wins, and build credibility and momentum through an accessible leadership style. They must also avoid common traps like isolation