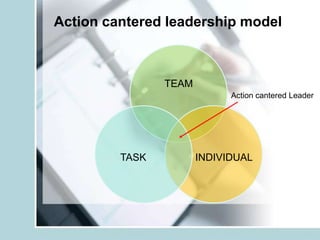
The document discusses various leadership theories and concepts including:
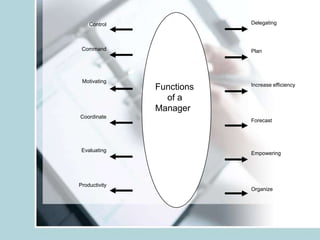
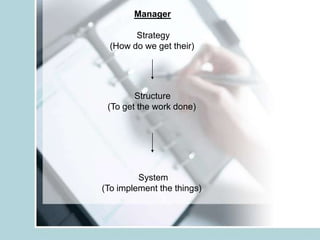
1. It defines management as forecasting, planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating and controlling while leadership is the ability to drive people willingly through different times.
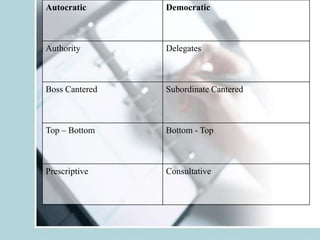
2. It discusses different leadership theories such as trait theory, functional theory, behavioral theory, situational theory and transformational theory.
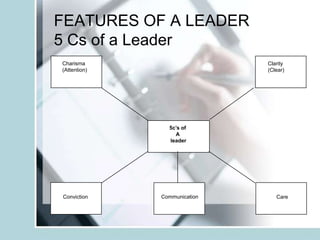
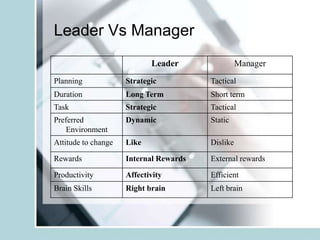
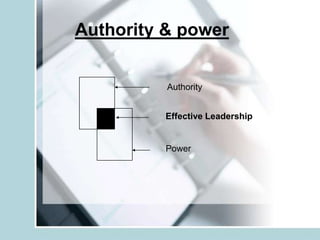
3. It also compares the differences between a leader and manager and outlines characteristics of an effective leader including vision, effective communication, shared vision, and conviction.