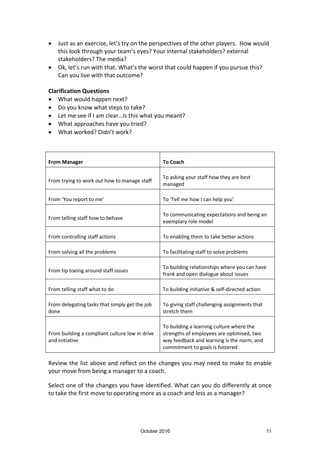
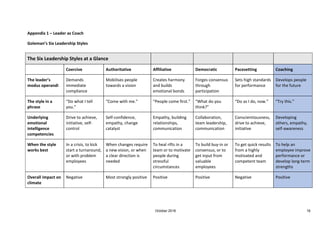
This document discusses coaching and its benefits for organizations, leaders, and team members. It defines coaching as a process that helps people maximize their own performance by discovering solutions themselves, rather than being taught. Coaching focuses on the future and eliciting ideas from the person being coached. The benefits include developing leadership capability, empowering employees, boosting performance, and increasing engagement, discretionary effort, and retention. Effective coaching skills allow leaders to enhance capacity, delegate more confidently, and achieve goals through empowered employees.