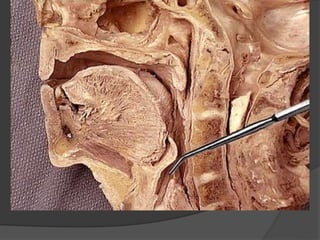
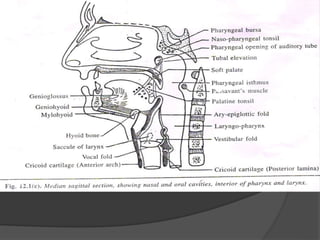
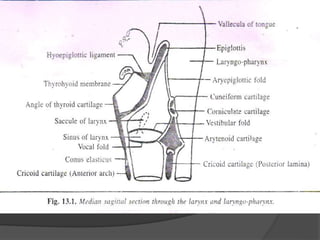
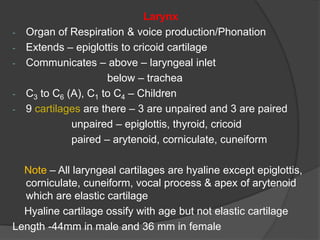
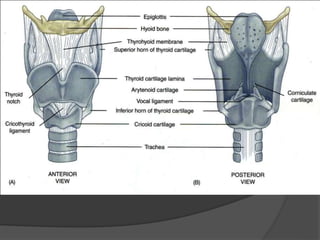
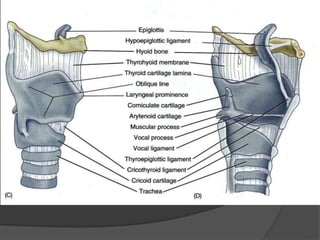
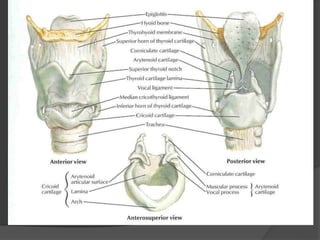
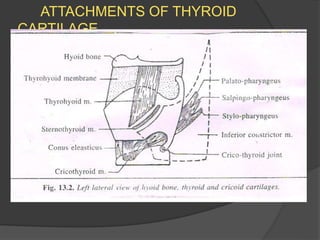
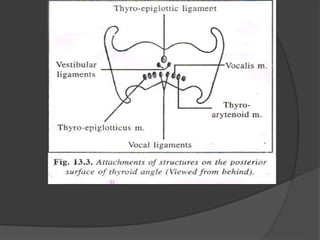
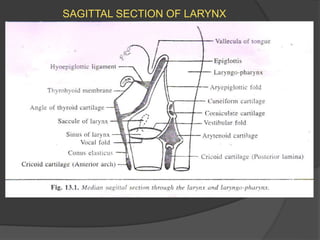
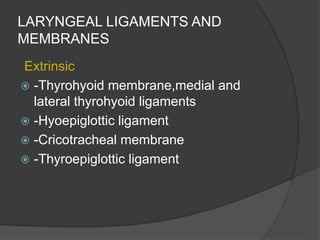
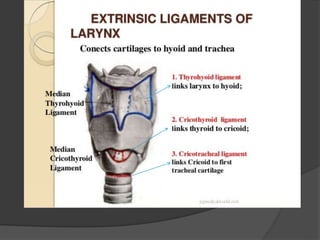
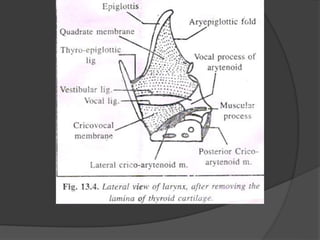
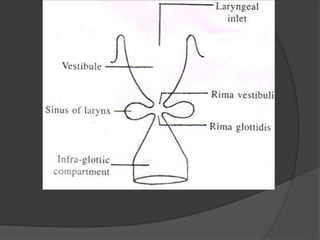
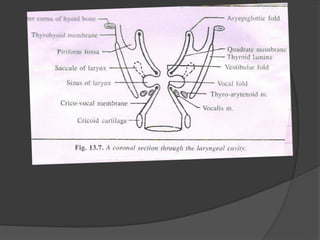
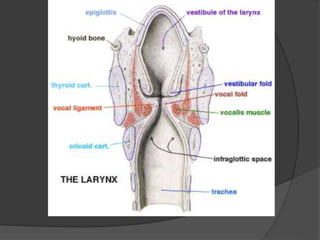
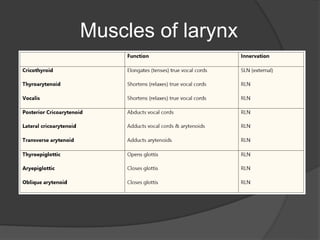
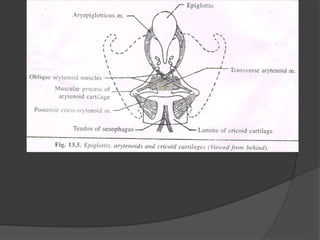
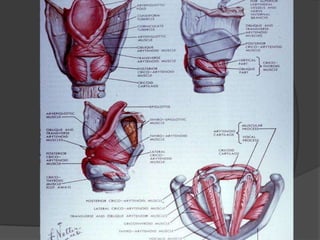
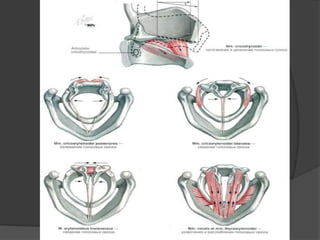
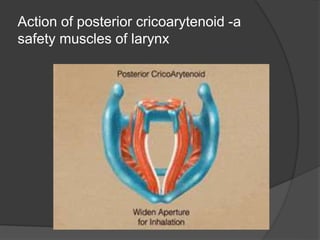
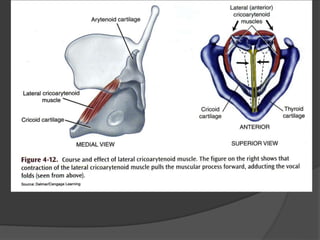
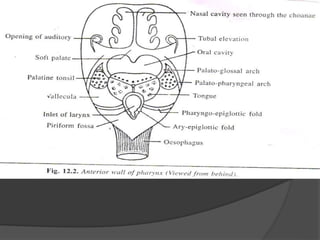
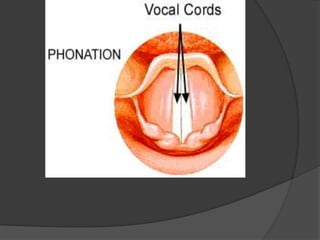
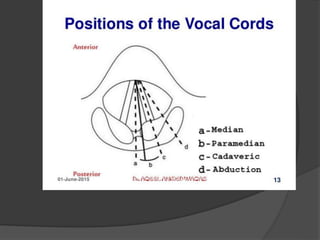
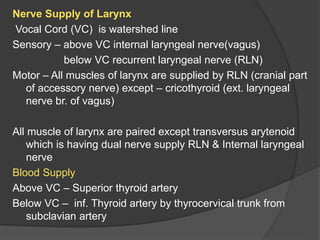
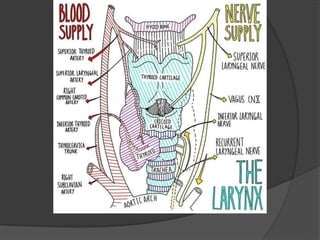
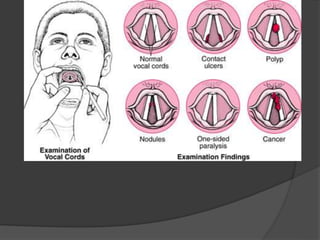
The document summarizes the anatomy of the larynx. It describes the cartilages that make up the larynx, including the epiglottis, thyroid, cricoid, and arytenoid cartilages. It discusses the ligaments, muscles, blood supply, nerve supply, and movements of the larynx. Key structures mentioned include the vocal folds, which divide the larynx into supraglottic and infraglottic regions. The recurrent laryngeal nerve is described as the main motor nerve to the laryngeal muscles, except for the cricothyroid muscle.