latent heat of fusion and vaporization for igcse physics
•Download as PPT, PDF•
0 likes•37 views
Heat is the transfer of energy between objects due to temperature differences, while temperature measures the average kinetic energy of particles. The document discusses key concepts related to heat and temperature including different temperature scales, thermal energy, heat transfer processes, and phase changes. It provides examples to illustrate differences between temperature and thermal energy, and explains concepts like specific heat capacity and the laws of thermodynamics.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to latent heat of fusion and vaporization for igcse physics
Similar to latent heat of fusion and vaporization for igcse physics (20)
Sci 10 Lesson 2 April 14 - Temperature, Thermal Energy and Heat

Sci 10 Lesson 2 April 14 - Temperature, Thermal Energy and Heat
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...

Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...
GEOLOGICAL FIELD REPORT On Kaptai Rangamati Road-Cut Section.pdf

GEOLOGICAL FIELD REPORT On Kaptai Rangamati Road-Cut Section.pdf
The importance of continents, oceans and plate tectonics for the evolution of...

The importance of continents, oceans and plate tectonics for the evolution of...
word2vec, node2vec, graph2vec, X2vec: Towards a Theory of Vector Embeddings o...

word2vec, node2vec, graph2vec, X2vec: Towards a Theory of Vector Embeddings o...
ESR_factors_affect-clinic significance-Pathysiology.pptx

ESR_factors_affect-clinic significance-Pathysiology.pptx
Cancer cell metabolism: special Reference to Lactate Pathway

Cancer cell metabolism: special Reference to Lactate Pathway
Mammalian Pineal Body Structure and Also Functions

Mammalian Pineal Body Structure and Also Functions
insect taxonomy importance systematics and classification

insect taxonomy importance systematics and classification
Comparative structure of adrenal gland in vertebrates

Comparative structure of adrenal gland in vertebrates
Earliest Galaxies in the JADES Origins Field: Luminosity Function and Cosmic ...

Earliest Galaxies in the JADES Origins Field: Luminosity Function and Cosmic ...
National Biodiversity protection initiatives and Convention on Biological Di...

National Biodiversity protection initiatives and Convention on Biological Di...
A Giant Impact Origin for the First Subduction on Earth

A Giant Impact Origin for the First Subduction on Earth
latent heat of fusion and vaporization for igcse physics
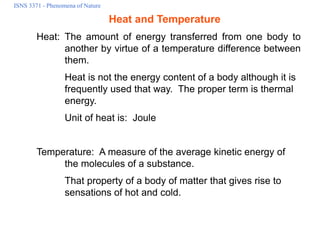
- 1. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature Heat and Temperature Heat: The amount of energy transferred from one body to another by virtue of a temperature difference between them. Heat is not the energy content of a body although it is frequently used that way. The proper term is thermal energy. Unit of heat is: Joule Temperature: A measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance. That property of a body of matter that gives rise to sensations of hot and cold.
- 2. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature Temperature and Thermal Energy Why does water burn your skin so much quicker than air? Why is falling into a 32º F lake more dangerous than standing outside naked on a 32º F? Temperature - measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance - particles in box on right have higher temperature - higher velocity = more KE = higher temperature Both boxes have same temperature - particles have same average velocity/KE - box on right has more thermal energy - energy contained in a substance - more particles
- 3. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. This diagram compares three common temperature scales. The Fahrenheit scale is used in the United States, but nearly all other countries use the Celsius scale. Scientists prefer the Kelvin scale because O K represents absolute zero, the coldest possible temperature.
- 4. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature TEMPERATURE SCALES WATER __________________________ ABSOLUTE ZERO FREEZING POINT BOILING POINT _________________________________________________ FAHRENHEIT -459° 32° 212° CELSIUS -273° 0° 100° KELVIN (ABSOLUTE) 0° 273° 373° CONVERSIONS: CELSIUS TO FAHRENHEIT F = 9/5C + 32 FAHRENHEIT TO CELSIUS C = 5/9 x (F - 32) CELSIUS TO KELVIN K = C + 273.
- 5. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature Thermal Energy Thermal Energy: Total of all energies, kinetic plus potential, internal to a substance. Quantity of Heat: Calorie or Joule 1 calorie = Amount of thermal energy required to change the temperature of 1 gram of water 1°C. 1 joule = 0.239 calories (1 Calorie = 4.187 joules) 1 kilocalorie = 1,000 calories (usually spelled with a capital C)
- 6. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature Specific Heat Capacity, c: Thermal inertia Specific Heat Capacity is the quantity of heat required to change the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1° C. If Q units of of thermal energy added to 1 gram a substance produce a temperature change of ∆T, Q = c x ∆T Specific heat , c, of a substance is the heat capacity per unit mass. For m grams of a substance, Q = cm ∆T Water has high specific heat capacity - used as a cooling fluid. Specific heat capacity of water is 1calorie per gram-deg. C.
- 7. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature Heat Transfer Processes Conduction – transfer of heat from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature by increased kinetic energy moving from molecule to molecule through collisions between molecules. Occurs in solids. Convection – transfer of heat from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature by the flow of higher energy molecules. Occurs in gases and liquids. Radiation – transfer of heat by emission and absorption of radiant energy (energy that can travel through space as electromagnetic radiation, like visible light).
- 8. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law: Whenever heat flows in or out of a system, the gain or lass of thermal energy equals the amount of heat transferred. Second Law: Heat never spontaneously flows from a cold substance to a hot substance. Third law: No system can reach absolute zero.
- 9. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature The state or phase of matter is determined by its temperature. Consider water: Below 32º F - ice - relatively low KE - each molecule tightly bound to it neighbors - solid At 32º F molecules have enough energy to break solid bonds of ice - remain together but move relatively freely - liquid At 212º F water boils and turns to gas - molecules break free of all bonds with neighbors - move independently of other molecules - gas
- 10. ISNS 3371 - Phenomena of Nature Phase/State Changes Melting - when a solid changes to a liquid Evaporation - when a liquid changes to a gas Sublimation - when a solid changes directly to a gas Condensation - when a gas changes to a liquid Freezing - when a liquid changes to a solid Energy is absorbed Energy is released Heat transfer always occurs whenever a substance changes phase