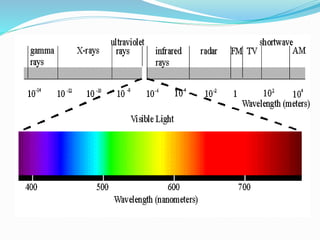
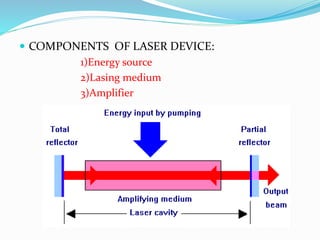
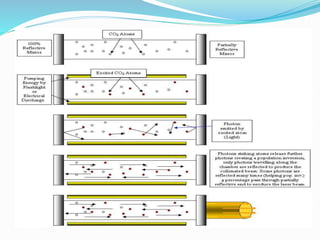
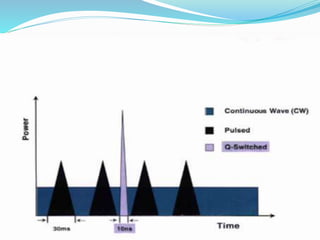
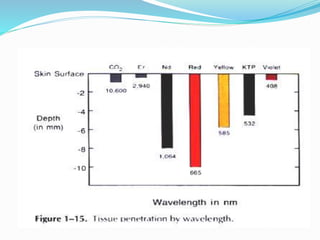
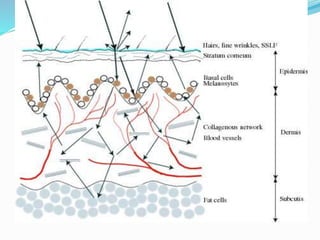
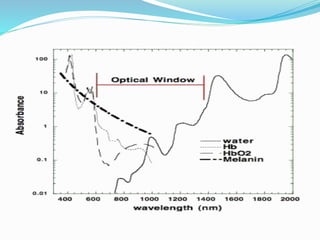
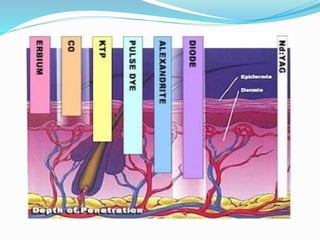
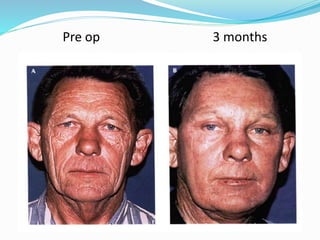
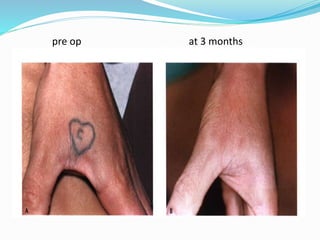
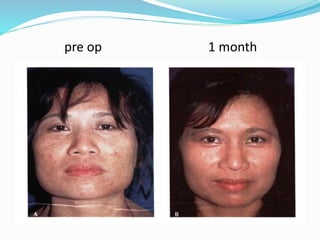
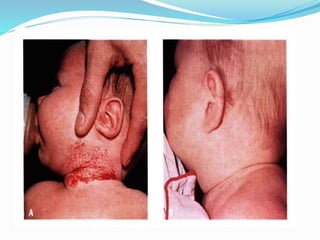
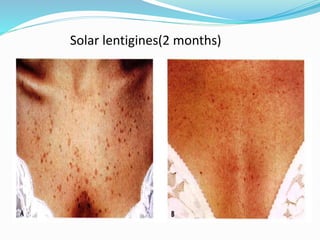
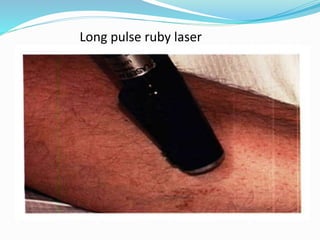
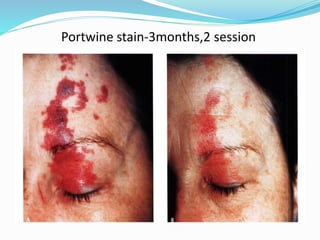
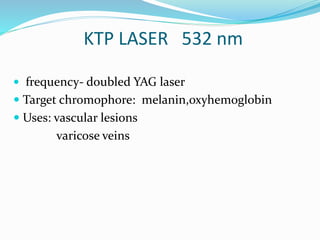
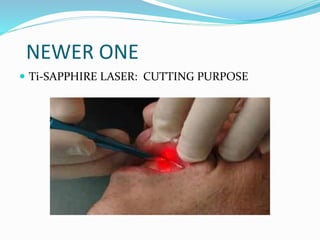
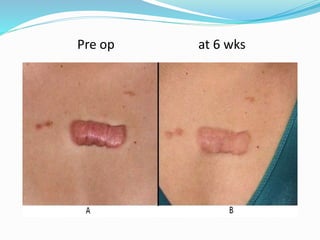
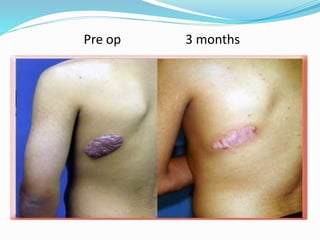
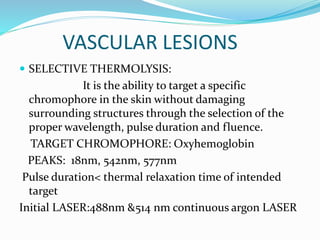
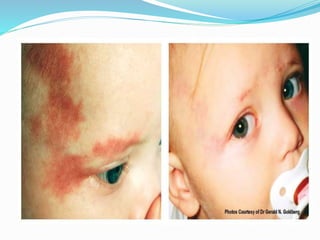
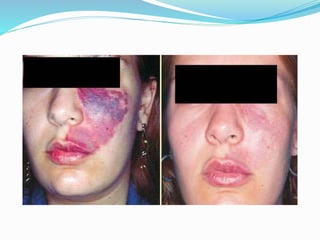
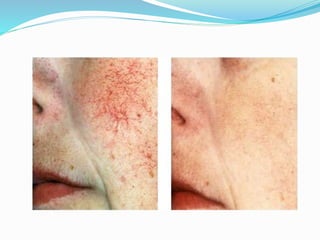
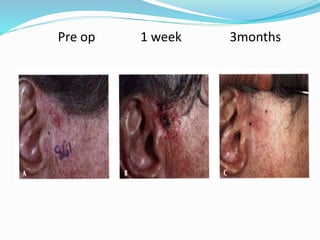
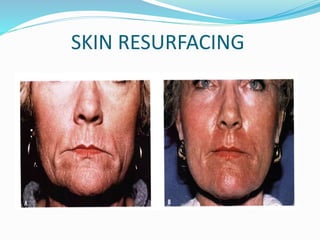
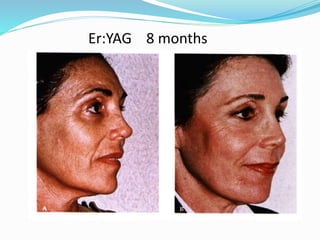
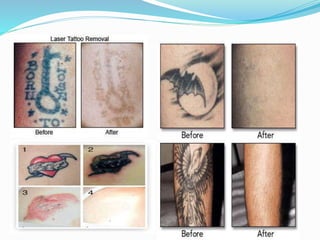
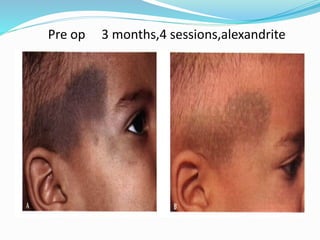
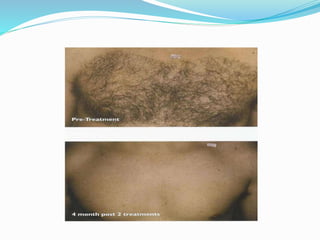
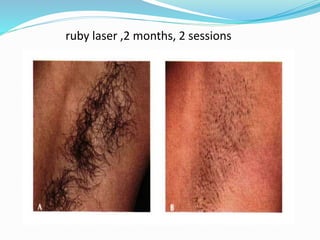
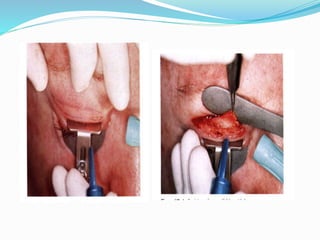
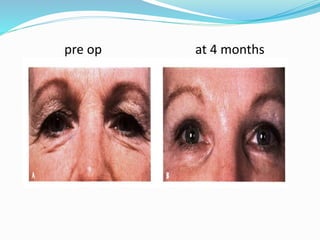
This document provides an overview of laser dermatology and summarizes the history and components of lasers. It describes different types of lasers (solid, liquid, gas) and their applications in dermatology such as treating vascular lesions, pigmented lesions, tattoos, skin resurfacing, and hair removal. Safety considerations and post-laser outcomes are also discussed.