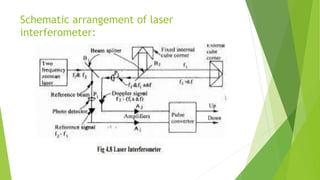
Laser interferometry utilizes an AC laser for precise distance measurements through the interference of beams of slightly different frequencies. The system includes components like beam splitters, cube corner reflectors, and photo detectors to achieve high accuracy, with measurement errors as small as 0.1μm over 100m. Advantages include high repeatability, ease of installation, and the ability to measure various parameters such as straightness and flatness.