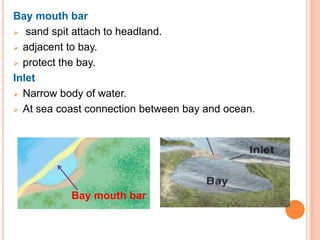
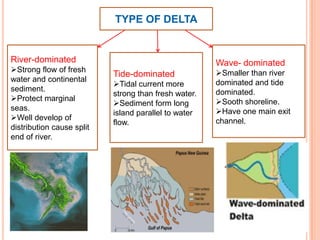
The document describes several large-scale coastal landforms that form through depositional processes, including sand spits, bay mouth bars, barriers islands, lagoons, sea islands, deltas, and drumlins/moraines. Sand spits form where longshore currents slow and curl offshore, depositing sand and gravel. Bay mouth bars are sand spits that are attached to headlands and protect adjacent bays. Barrier islands form from sediment accumulating on submerged rises and migrate inland as sea levels rise. Lagoons are bodies of water separated from the ocean by barrier islands or reefs. Deltas form at river mouths where sediment is deposited, taking different shapes based on river flow, tides, or wave dominance