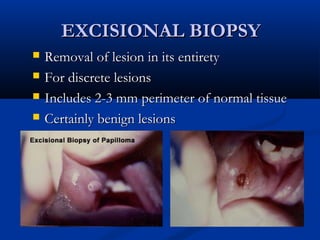
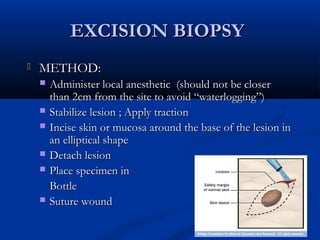
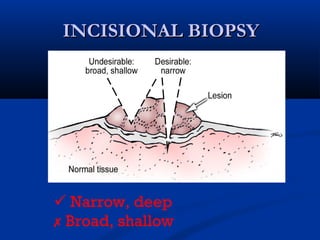
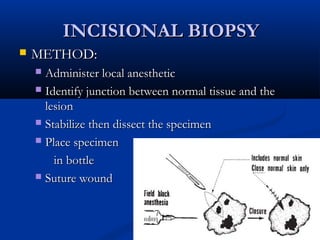
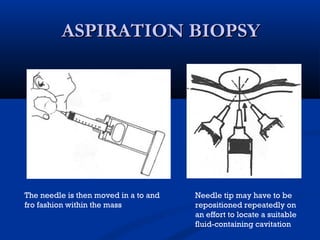
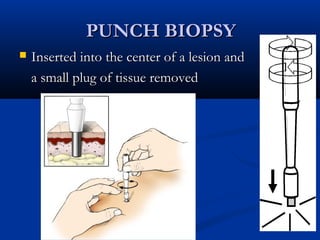
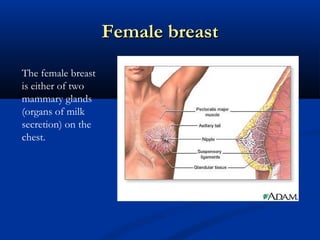
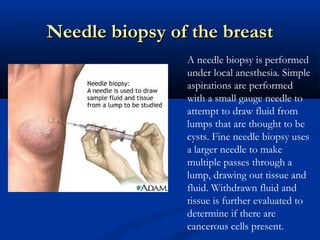
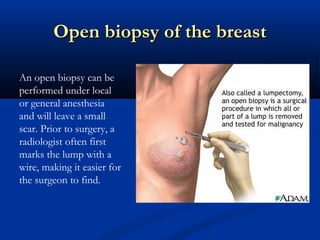
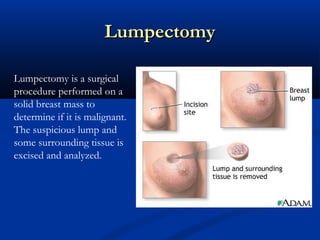
The document discusses different types of breast biopsies. It describes needle biopsies, which use thin or larger needles to remove tissue samples and include fine needle and core needle biopsies. Open biopsies involve surgically opening the breast and removing tissue and include incisional and excisional biopsies. Advanced techniques like ABBI and Mammotone/MIBB biopsies precisely locate lesions and remove larger contiguous tissue samples through a single needle insertion. The document provides details on performing and interpreting different biopsy procedures to diagnose breast abnormalities.