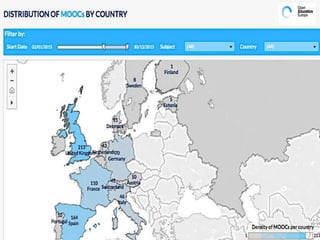
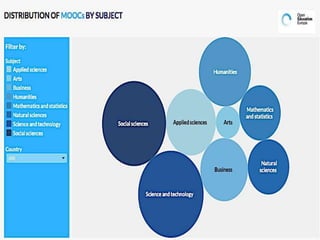
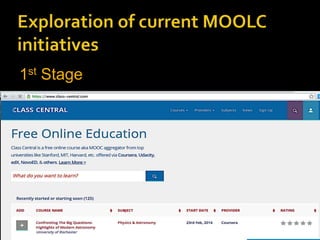
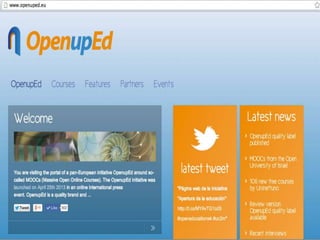
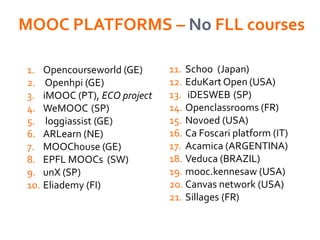
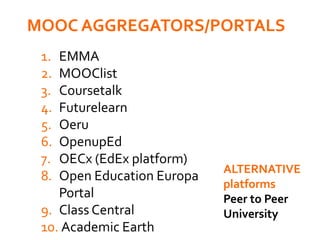
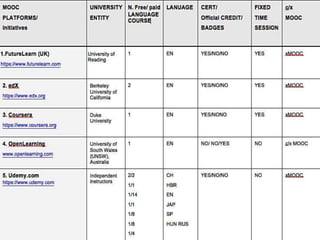
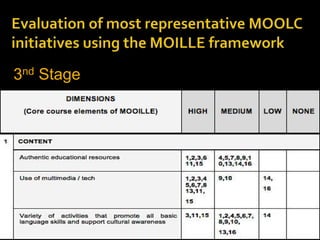
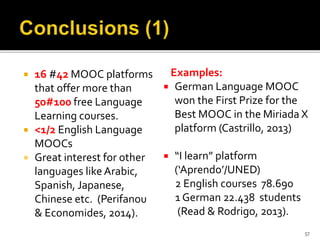
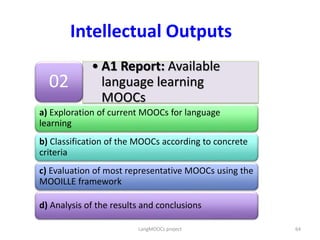
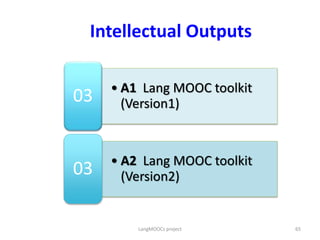
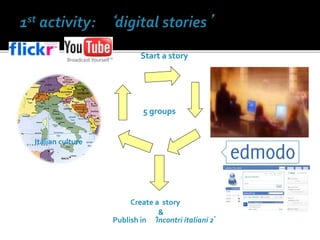
The document discusses the role of MOOCs in language learning and the importance of multilingualism and multi-literacies in the 21st century. It outlines the LANGMOOC project, which aims to improve language education through interactive online platforms and emphasizes the need for effective language learning environments. The document also explores various MOOC platforms and initiatives available for language courses, highlighting the challenges and opportunities in the current educational landscape.







![What is learning?
‘Learning is an active process
of constructing rather than
acquiring knowledge and
instruction is a process of
supporting that construction
rather than communicating
knowledge ’ [Duffy, T. M. &
Cunningham, D. J , 1996].
Successful learning involves a
mixture of work and fun](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maltapresentationm-151204122748-lva1-app6891/85/Language-Literacy-MOOCs-9-320.jpg)