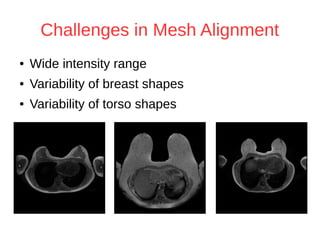
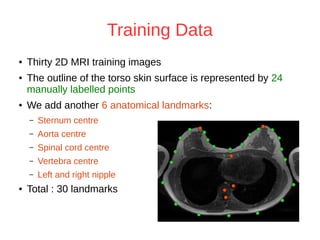
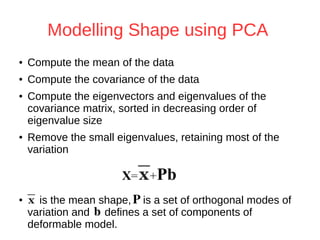
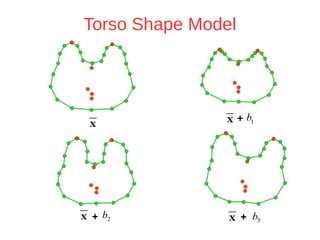
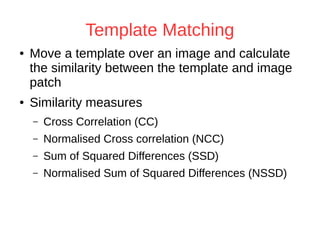
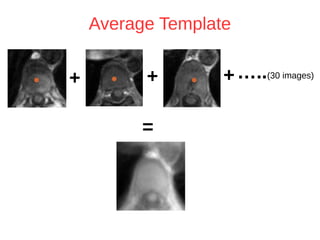
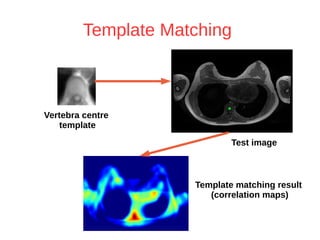
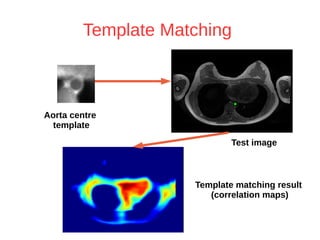
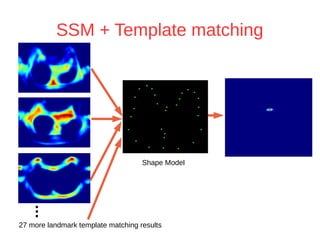
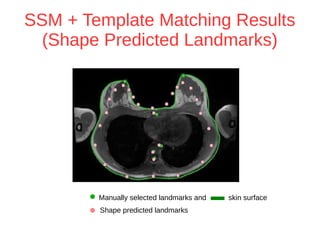
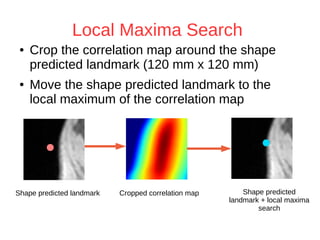
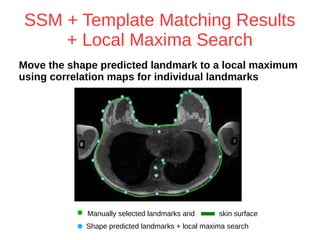
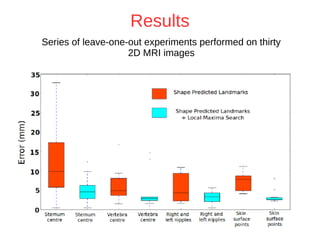
The document discusses a method for automatic landmark detection on the human breast using statistical shape modeling and template matching. It outlines the challenges in aligning and matching the mesh to new image data, noting the variability in breast and torso shapes, and describes the techniques used, including PCA and local maxima search to improve accuracy. The findings indicate that the combined method yields an average error of 3.4mm, with future work suggested to extend the algorithm to 3D and incorporate active appearance models.