This document discusses principles of brain-based learning and summarizes key points from a conference on brain research. It covers the following main topics:
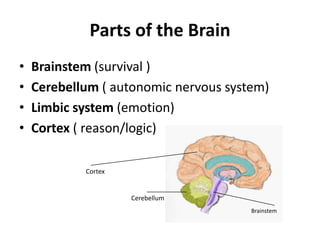
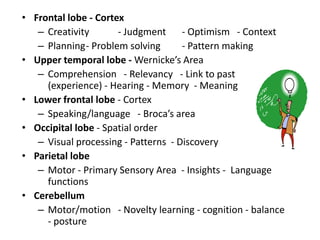
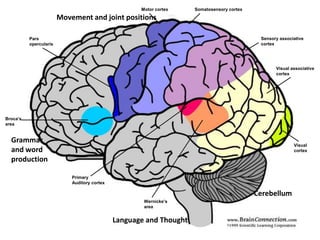
1. An overview of brain anatomy and the different parts of the brain including the cortex, cerebellum, and brainstem.
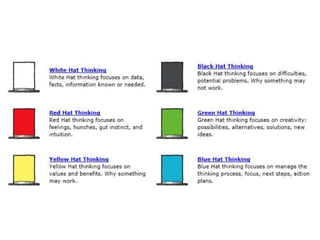
2. Principles of how the brain learns including that learning engages the whole body, each brain is unique, emotions are important for learning, and learning occurs through meaning and patterning.
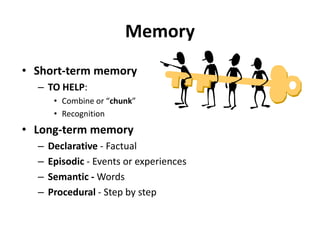
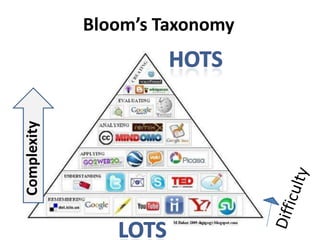
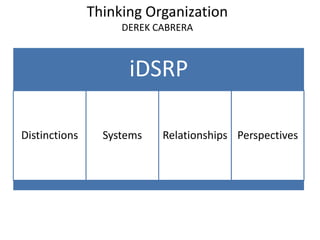
3. A discussion of 12 principles of brain-based learning including that the brain is a parallel and social processor, learning involves conscious and unconscious processes, and memory is organized in different ways including short and long-term.