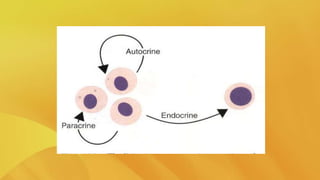
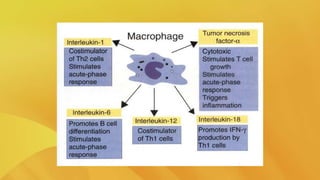
Cytokines are proteins secreted by immune cells that regulate the immune response through communication between cells. They affect a wide variety of cells and organs, and multiple cytokines may have similar effects. The main types of cytokines are interleukins, interferons, tumor necrosis factors, growth factors, and chemokines. Interleukins regulate interactions between lymphocytes and leukocytes. Interferons have antiviral properties and activate the immune system. Tumor necrosis factors destroy tumor cells and mediate inflammation. Growth factors control leukocyte production. Chemokines regulate leukocyte migration and activation during inflammation. Cytokines function through autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine patterns of activity.