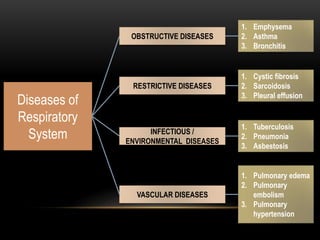
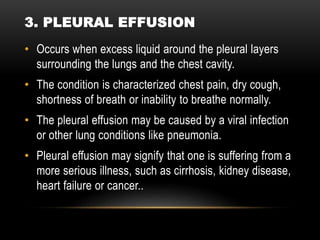
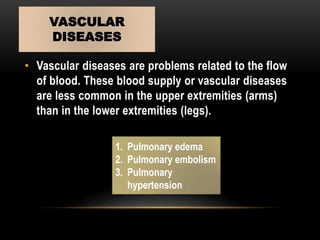
This document discusses diseases that affect the respiratory and circulatory systems. It describes various obstructive, restrictive, infectious/environmental, and vascular diseases. Obstructive diseases like emphysema, asthma, and bronchitis cause airflow blockages. Restrictive diseases such as cystic fibrosis limit lung expansion. Infectious diseases including tuberculosis, pneumonia, and asbestosis are caused by pathogens. Vascular conditions such as pulmonary edema, embolism, and hypertension involve issues with blood flow in the lungs. Each disease is defined and its symptoms are outlined.