Embed presentation
Download to read offline




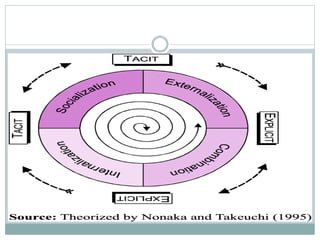
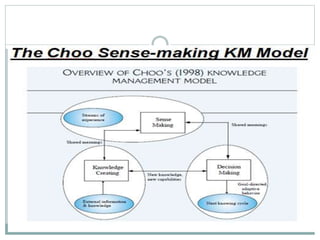
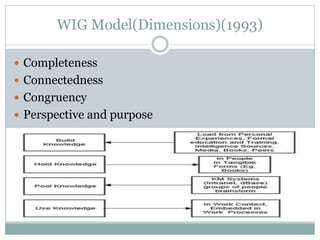




The document discusses key aspects of knowledge management, including defining knowledge management as the systematic management of an organization's knowledge assets to create value and meet goals. It outlines areas like globalization, leaner organizations, and technological advances that impact knowledge management and presents models for knowledge management including the Nonaka and Takeuchi model and WIG model. The document stresses that a good knowledge management strategy aligns with business objectives and strategies, identifies knowledge resources, and recommends how to apply knowledge.










