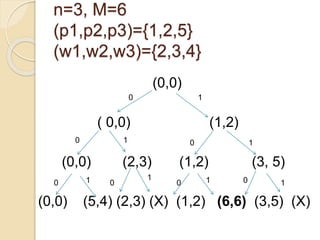
The document discusses the 0/1 knapsack problem and the greedy algorithm approach. It describes the knapsack problem as selecting a subset of items with weights and values that fit within a knapsack capacity while maximizing the total value. The greedy algorithm works by selecting the highest value item at each step that fits within remaining capacity. The document provides an example problem of selecting boxes to fill a knapsack of 15kg capacity to maximize profit. It outlines the recurrence relation and time/space complexity of the greedy knapsack algorithm.

![Greedy Method
It is a design technique applied to those
problems having n inputs and requires us
to obtain a subset that satisfies some
constraints.
Any subset that satisfies these constraints
is called a feasible solution.
Ultimate goal is to find a feasible solution
that minimizes [or maximizes] an
objective function; this solution is known
as optimal solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knapsack-140923125527-phpapp01/85/Knapsack-2-320.jpg)