Embed presentation
Downloaded 17 times











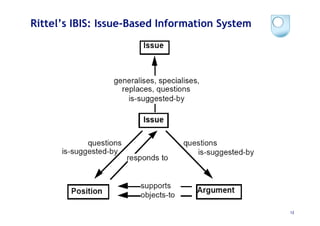
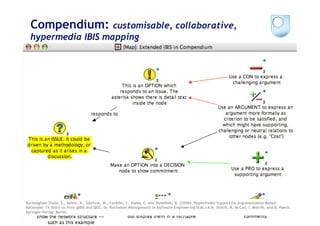
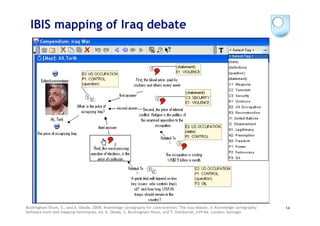

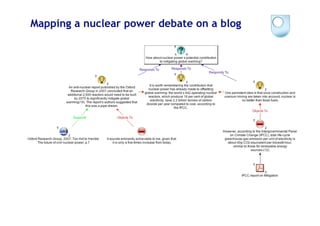
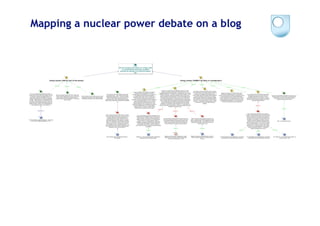

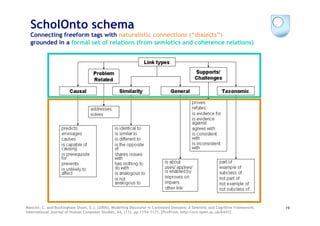
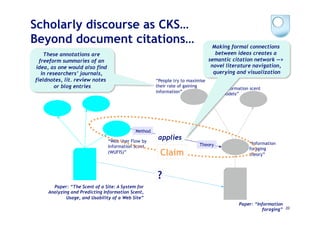

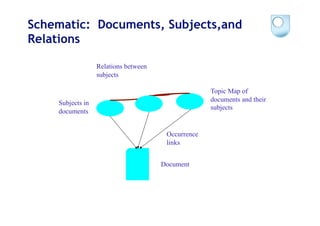


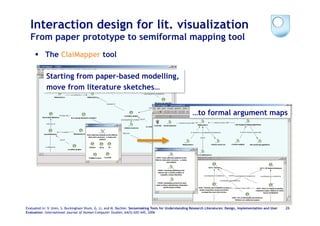



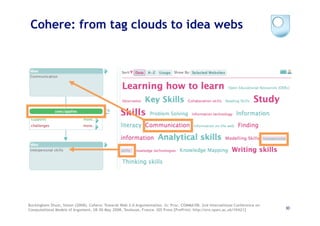
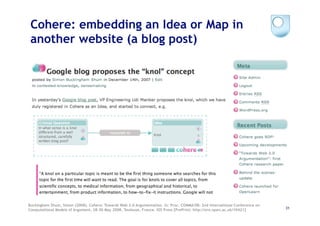
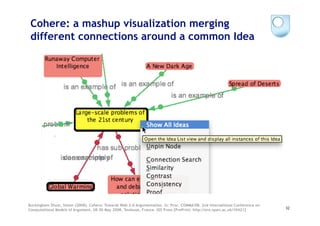
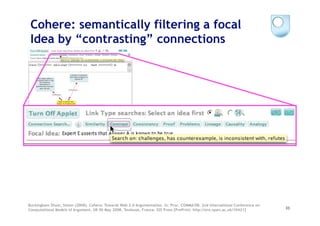
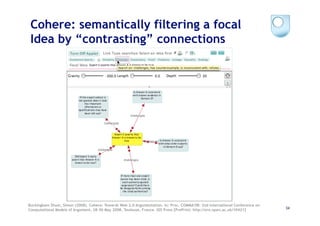

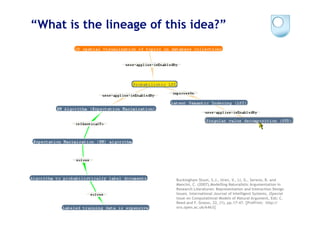






The document discusses the evolution of scientific publishing and the potential transition from traditional prose papers to a new infrastructure that utilizes the social and semantic web to create a network of claims and arguments. It emphasizes the importance of tools for annotating, visualizing, and navigating scientific literature and identifies key questions the next generation scientific infrastructure should address, like evidence and consistency of claims. Several modeling schemes and user interaction design strategies, including user studies, are also outlined as part of developing a collaborative discourse around scientific knowledge.









































