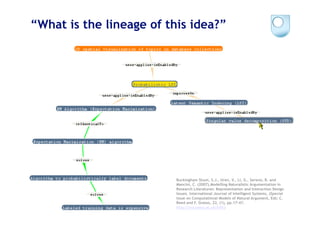
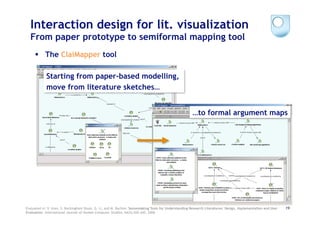
The document discusses various models and tools for enhancing scientific discourse through semantic web technologies, focusing on argumentation and collaboration. It highlights the evolution of discourse modeling, including the use of IBIS and Scholonto frameworks, and describes tools for annotation and visualization of research literature. Additionally, it touches on recent developments and projects aimed at integrating these tools into scholarly communications.







![ScholOnto schema
Connecting freeform tags with naturalistic connections (“dialects”)
grounded in a formal set of relations (from semiotics and coherence relations)
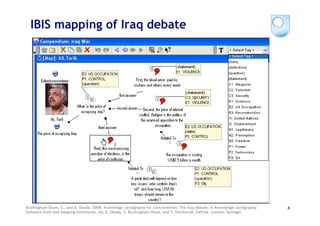
Mancini, C. and Buckingham Shum, S.J. (2006). Modelling Discourse in Contested Domains: A Semiotic and Cognitive Framework. 15
International Journal of Human Computer Studies, 64, (11), pp.1154-1171. [PrePrint: http://oro.open.ac.uk/6441]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kmi-w3c-hcls-july2009-090710095207-phpapp01/85/Supporting-Sensemaking-by-Modelling-Discourse-as-Hypermedia-Networks-15-320.jpg)
![polarity
source type comparativeness
Cognitive Coherence Relations
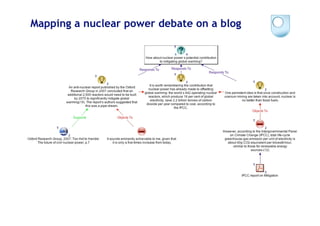
Mancini, C. and Buckingham Shum, S.J. (2006). Modelling Discourse in Contested Domains: A Semiotic and Cognitive Framework. 16
International Journal of Human Computer Studies, 64, (11), pp.1154-1171. [PrePrint: http://oro.open.ac.uk/6441]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kmi-w3c-hcls-july2009-090710095207-phpapp01/85/Supporting-Sensemaking-by-Modelling-Discourse-as-Hypermedia-Networks-16-320.jpg)



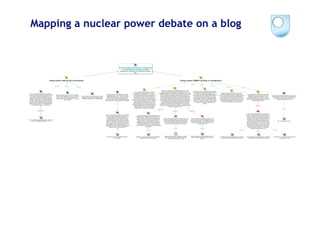
![Cohere: semantically filtering a focal
Idea by “contrasting” connections
Buckingham Shum, Simon (2008). Cohere: Towards Web 2.0 Argumentation. In: Proc. COMMA'08: 2nd International Conference on
Computational Models of Argument, 28-30 May 2008, Toulouse, France. IOS Press [PrePrint: http://oro.open.ac.uk/10421] 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kmi-w3c-hcls-july2009-090710095207-phpapp01/85/Supporting-Sensemaking-by-Modelling-Discourse-as-Hypermedia-Networks-21-320.jpg)
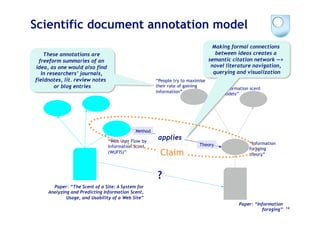
![Cohere: semantically filtering a focal
Idea by “contrasting” connections
Buckingham Shum, Simon (2008). Cohere: Towards Web 2.0 Argumentation. In: Proc. COMMA'08: 2nd International Conference on
Computational Models of Argument, 28-30 May 2008, Toulouse, France. IOS Press [PrePrint: http://oro.open.ac.uk/10421] 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kmi-w3c-hcls-july2009-090710095207-phpapp01/85/Supporting-Sensemaking-by-Modelling-Discourse-as-Hypermedia-Networks-22-320.jpg)