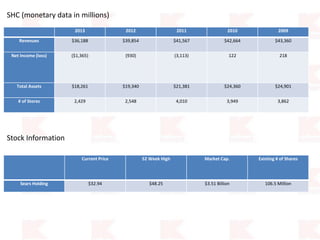
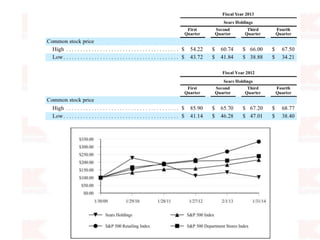
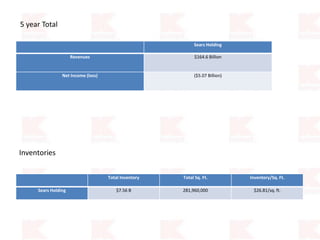
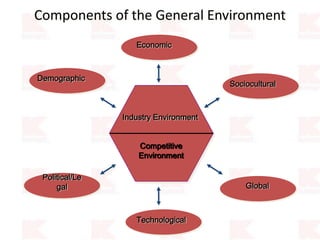
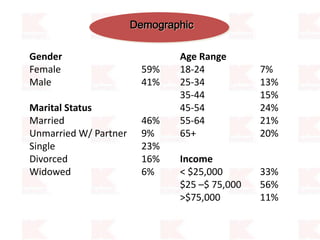
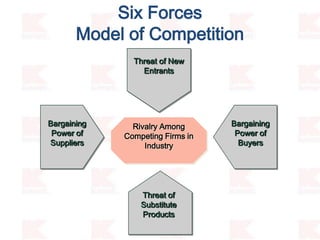
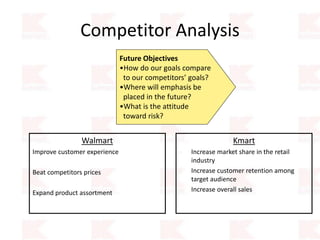
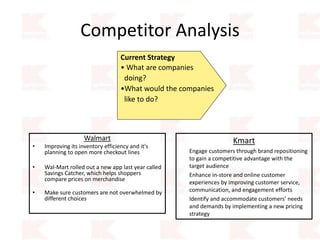
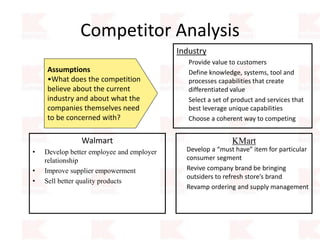
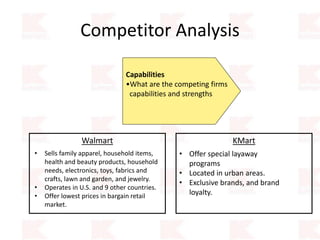
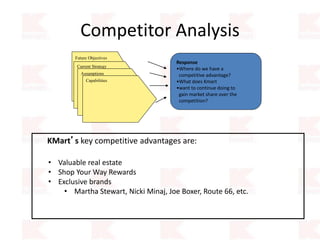
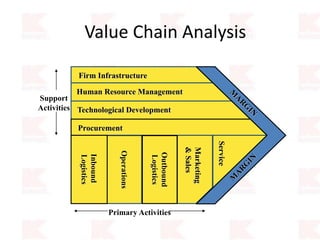
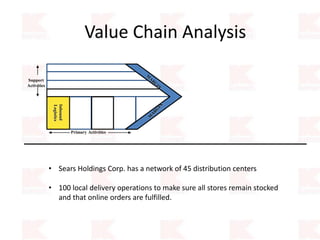
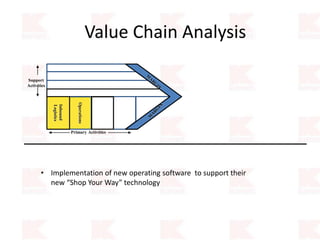
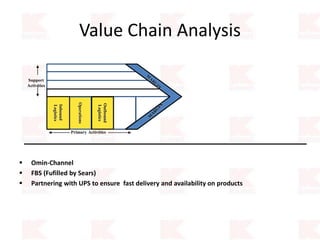
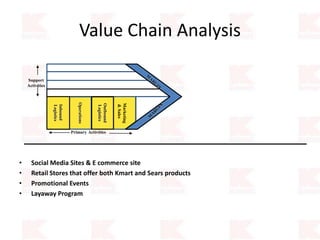
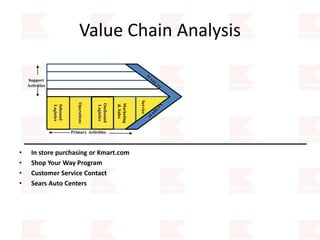
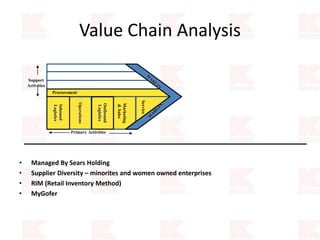
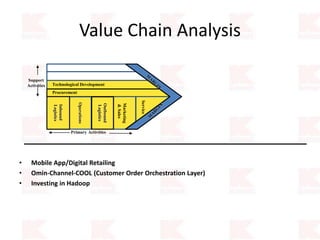
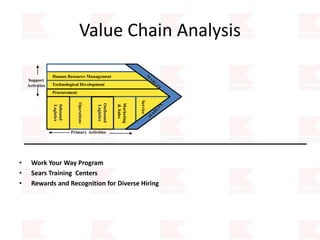
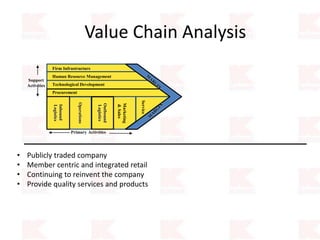
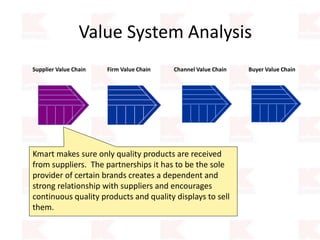
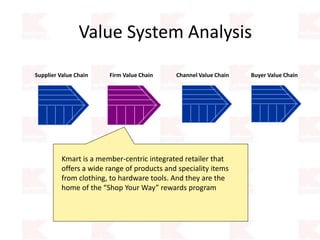
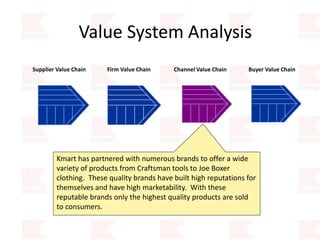
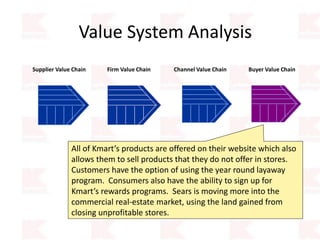
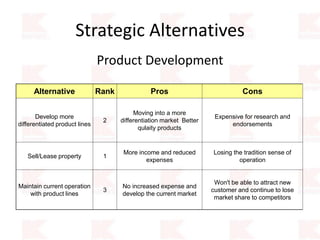
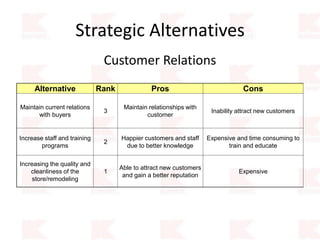
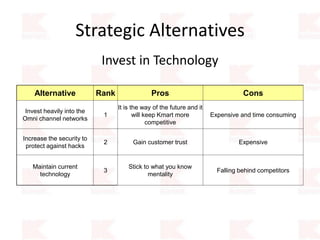
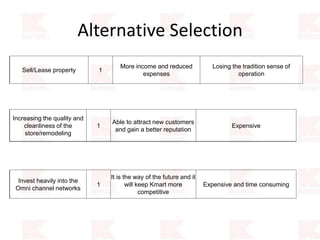
Kmart was founded in 1899 and filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2002. It was acquired by Sears in 2005. Sears Holdings Corporation's strategy is to focus on being a member-centric retailer by leveraging its Shop Your Way rewards program and integrated retail approach across Kmart and Sears stores and online. Its five strategic pillars are creating lasting customer relationships, attaining productivity and efficiency, building its brands, reinvention through technology and innovation, and living its values. The plan is to transform by focusing on Shop Your Way, business realignment, and enhancing financial flexibility. However, its financial performance from 2009-2013 shows declining revenues and increasing losses. It faces high competition from retailers like Walmart.