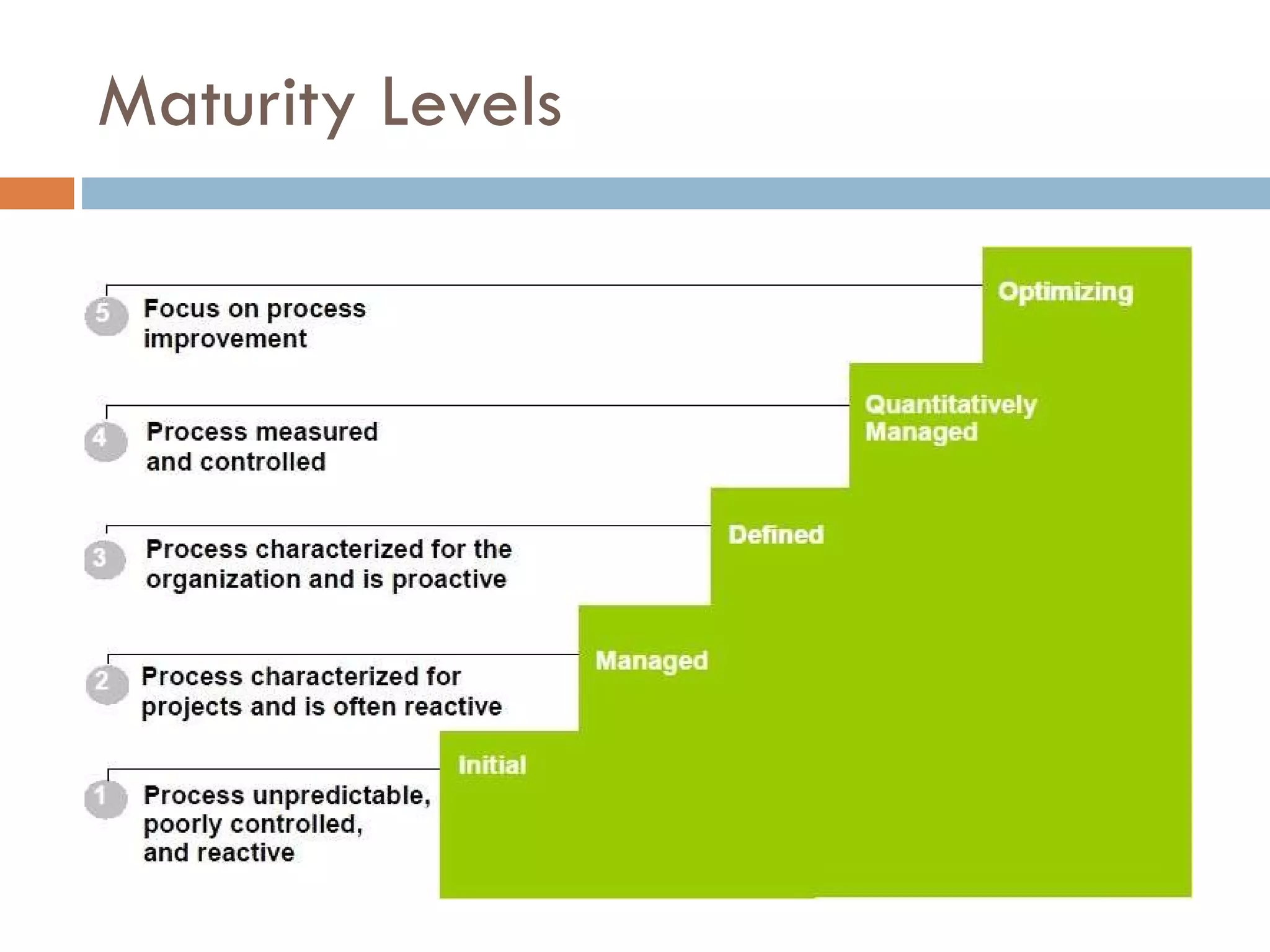
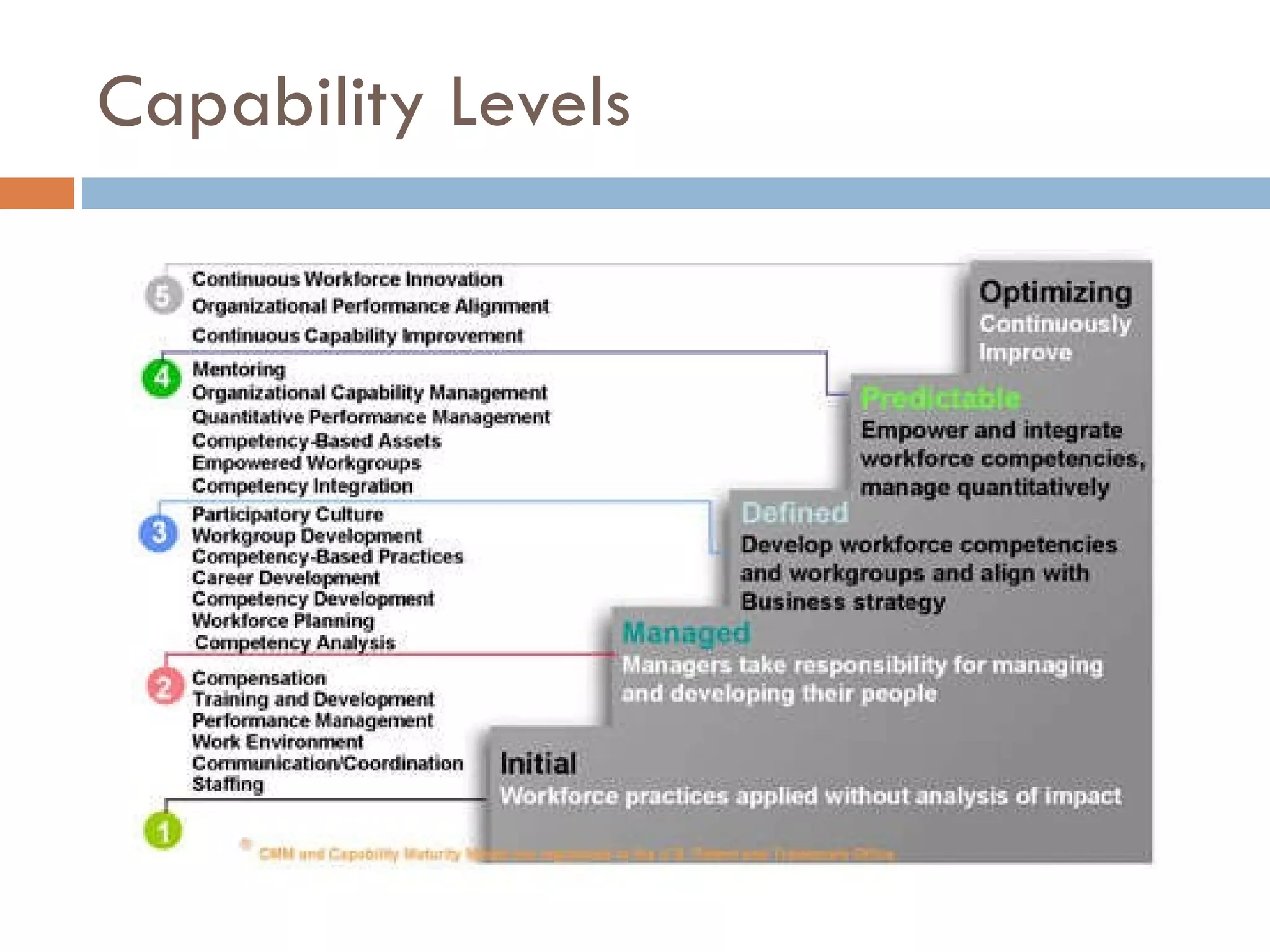
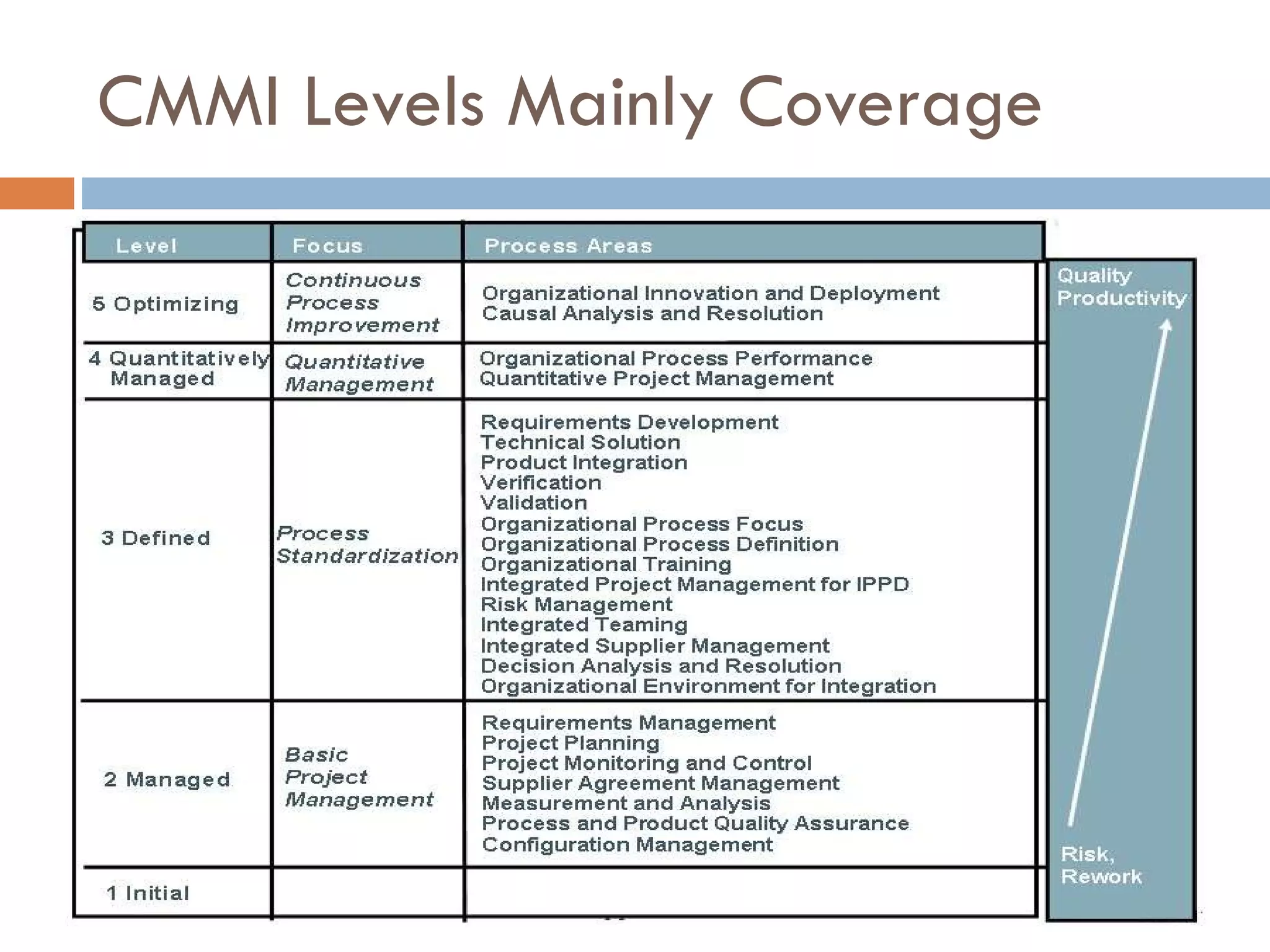
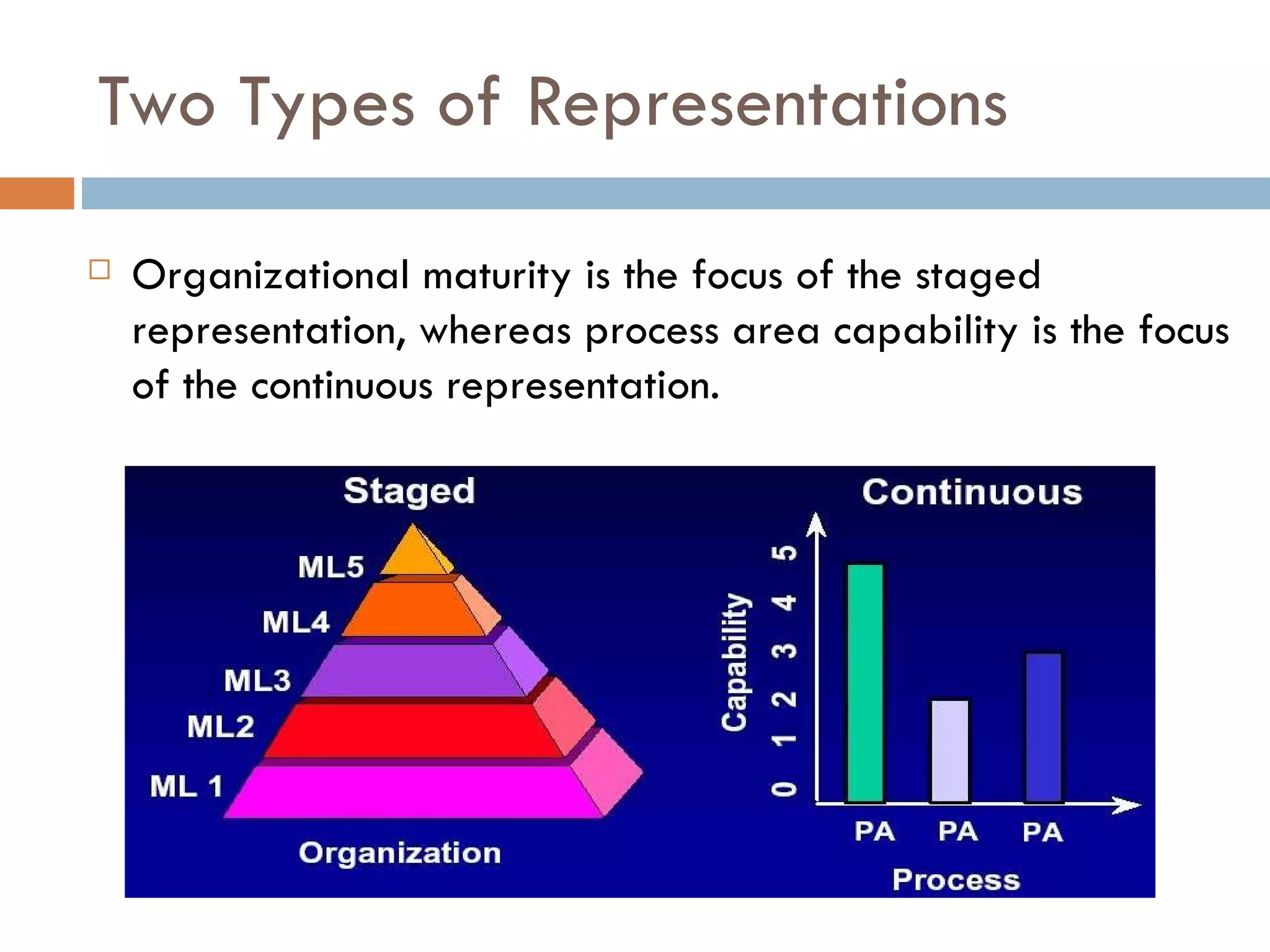
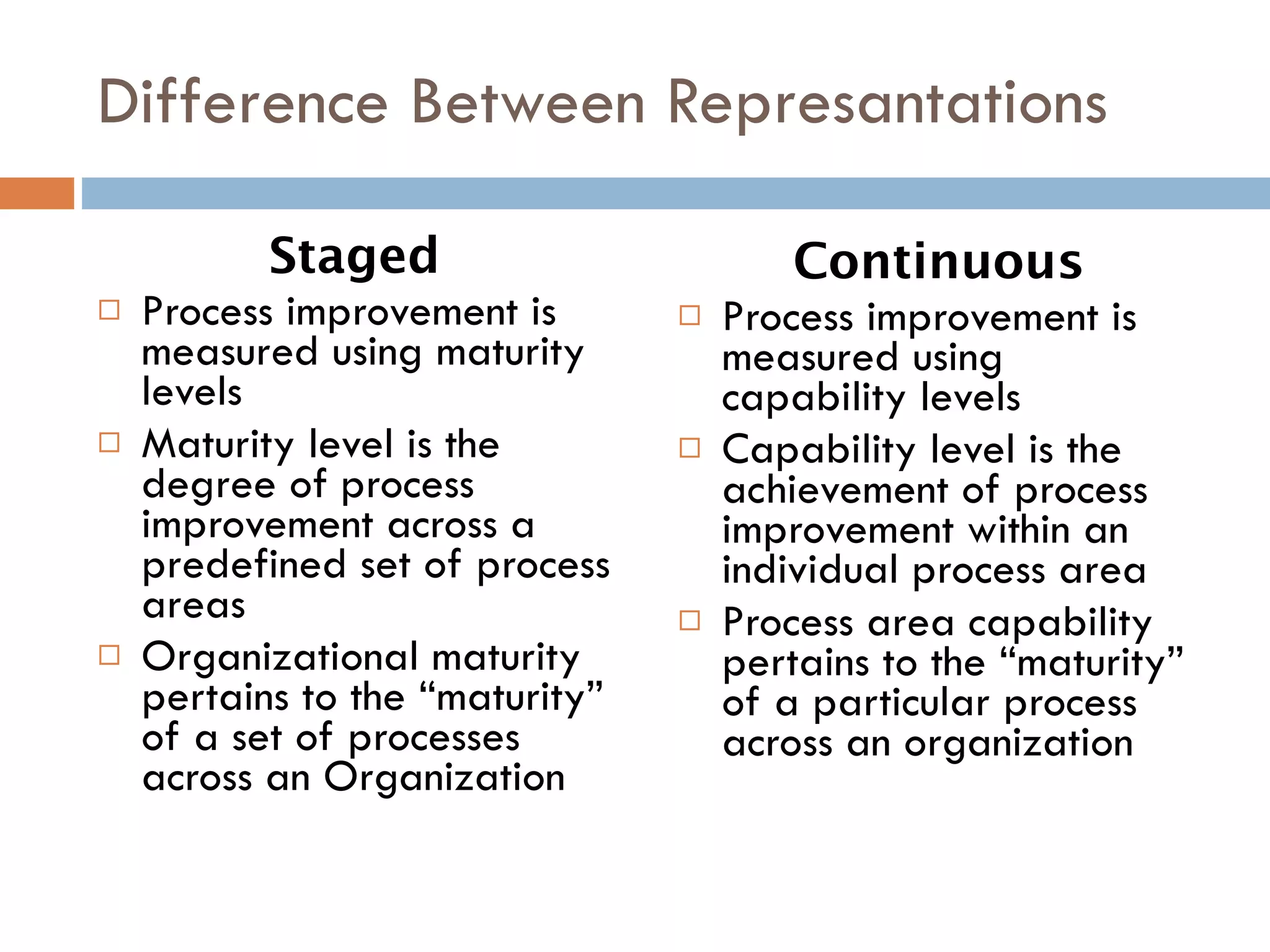
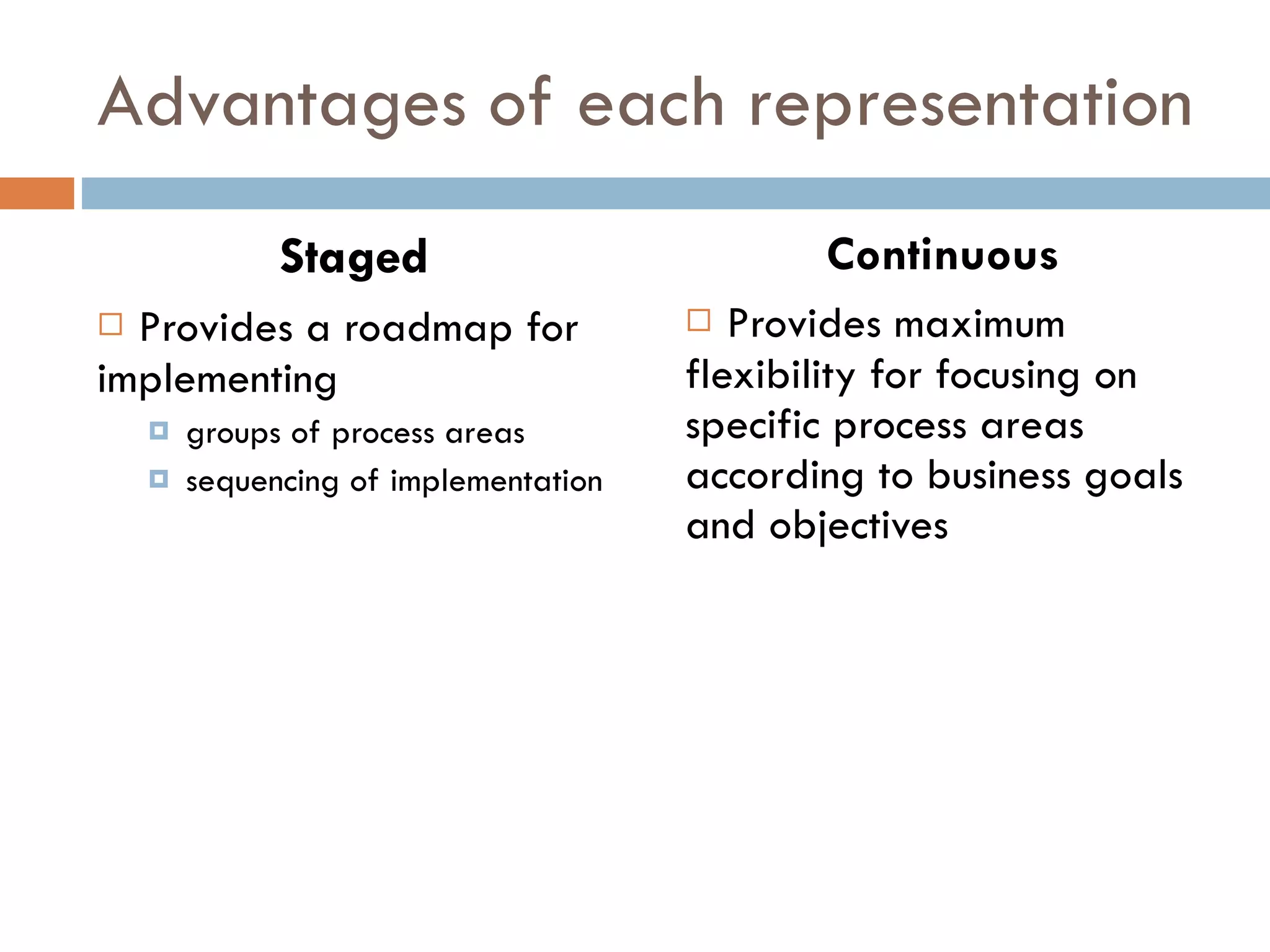
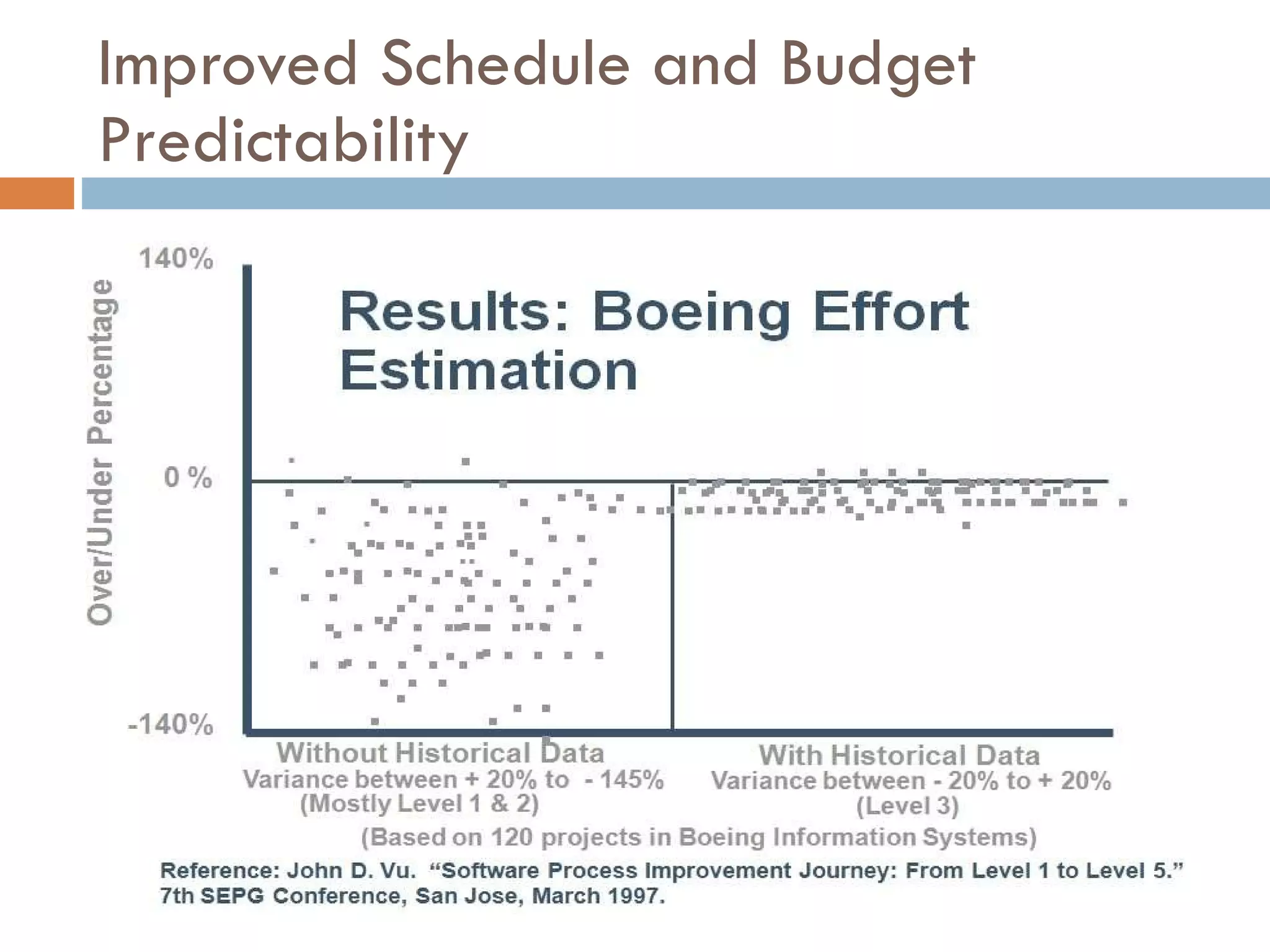
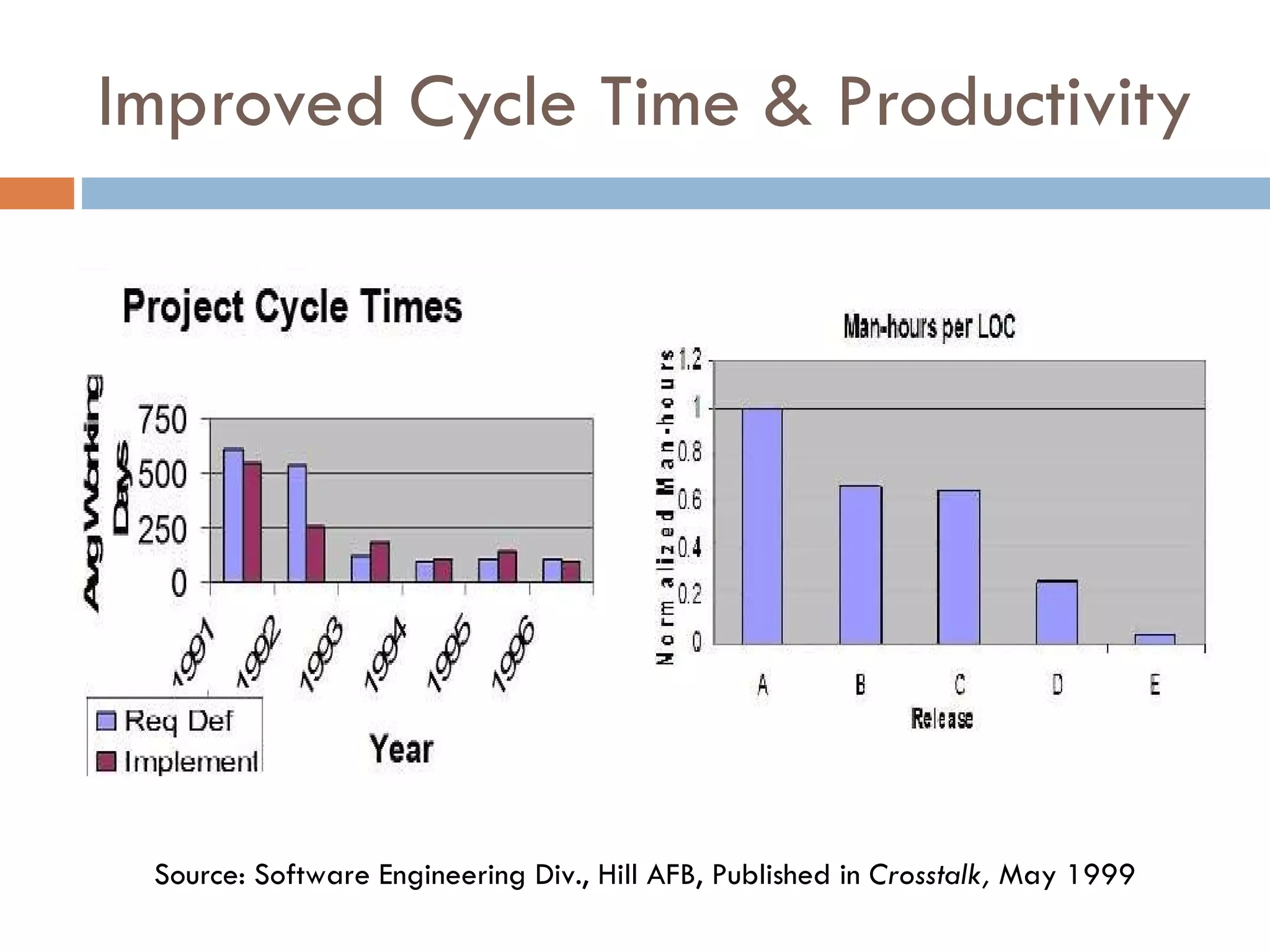
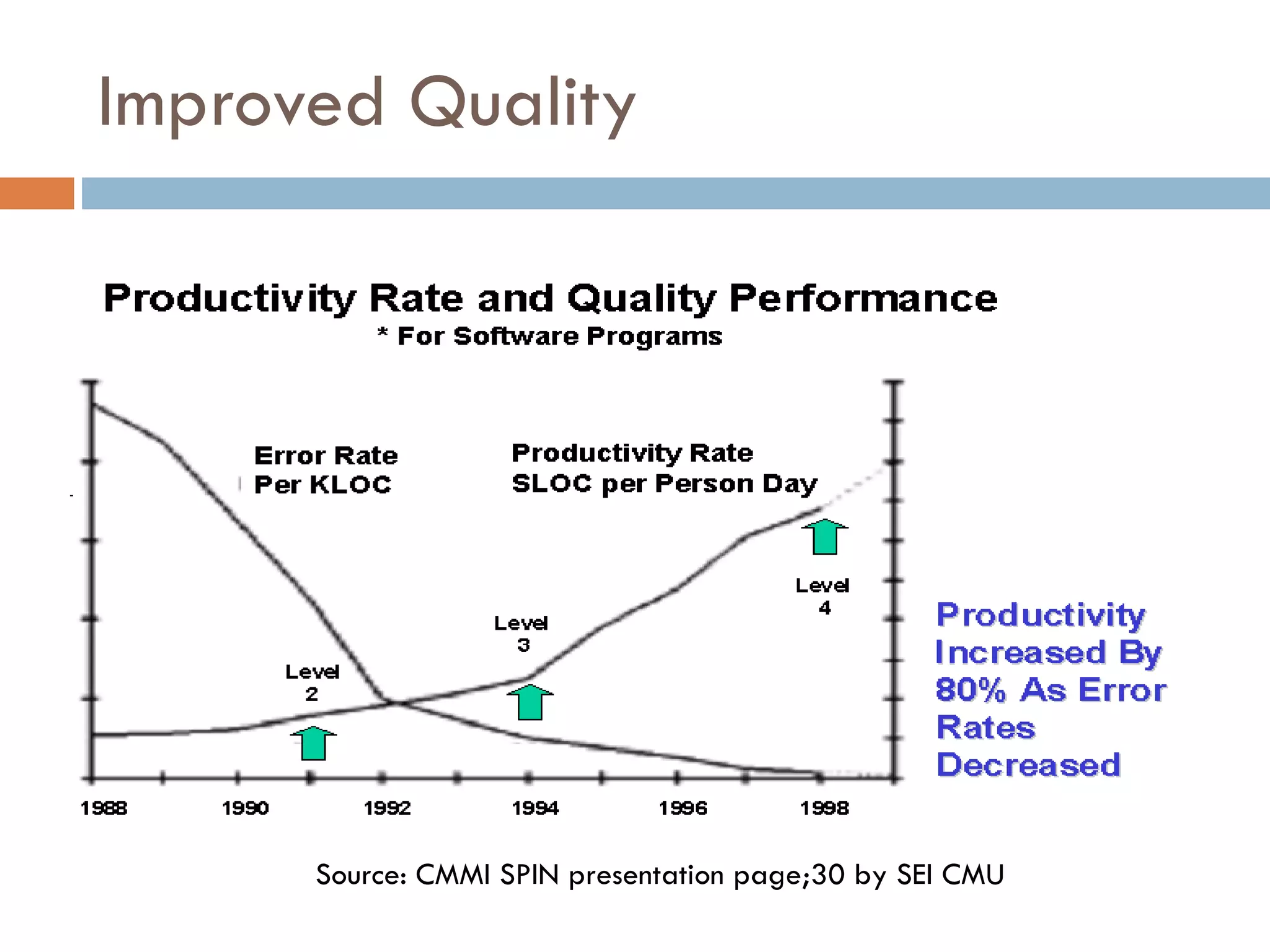
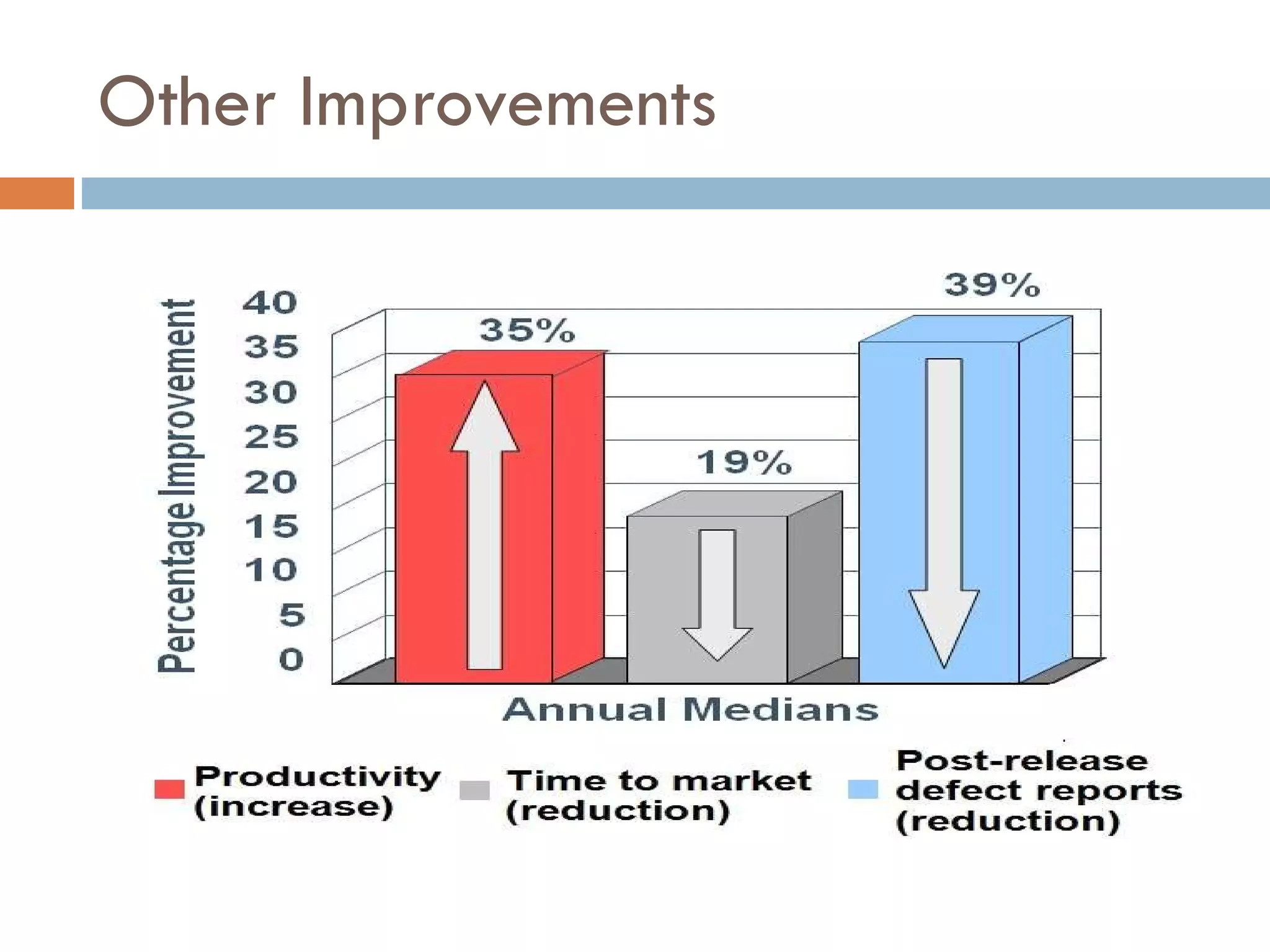
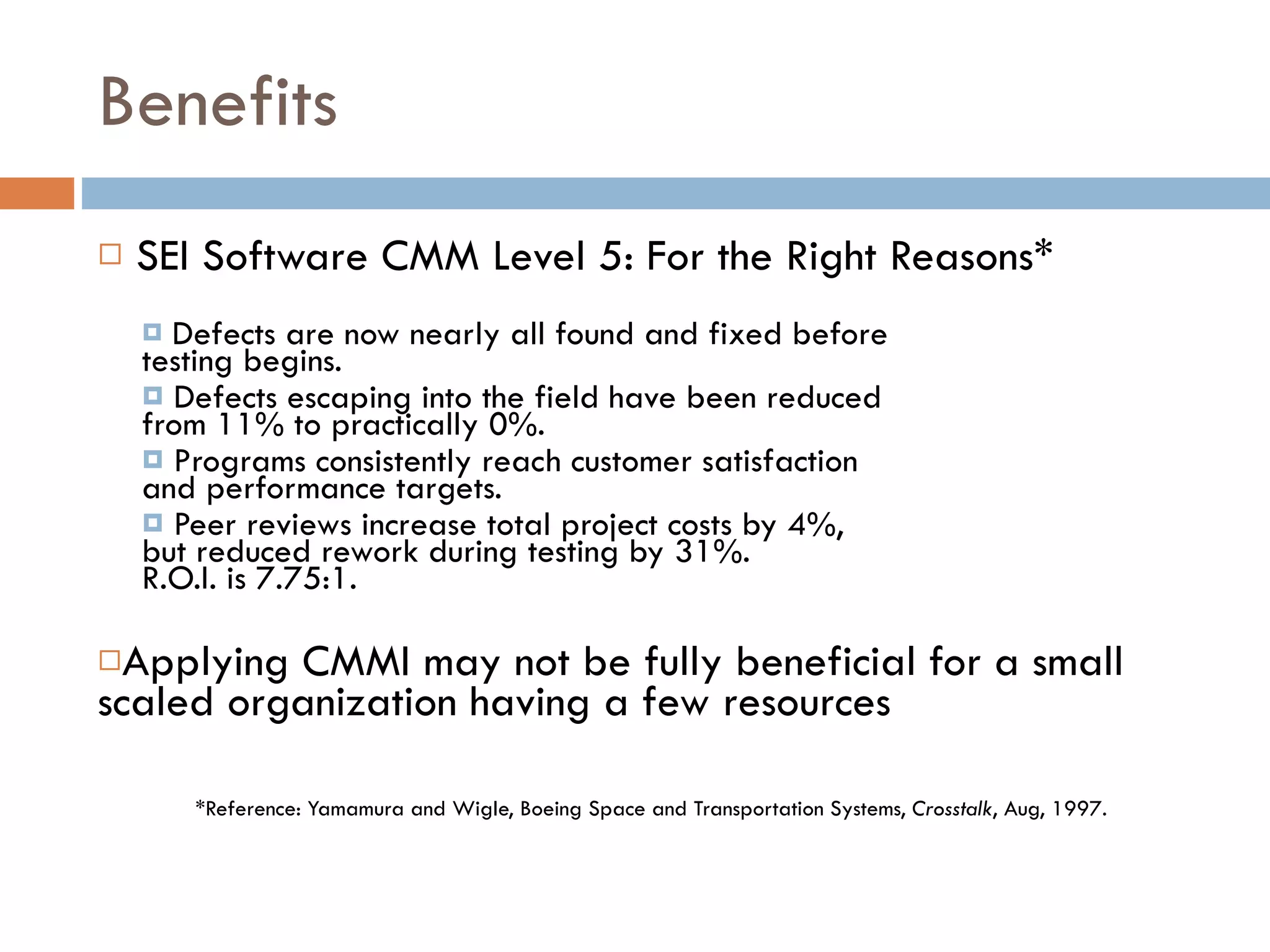
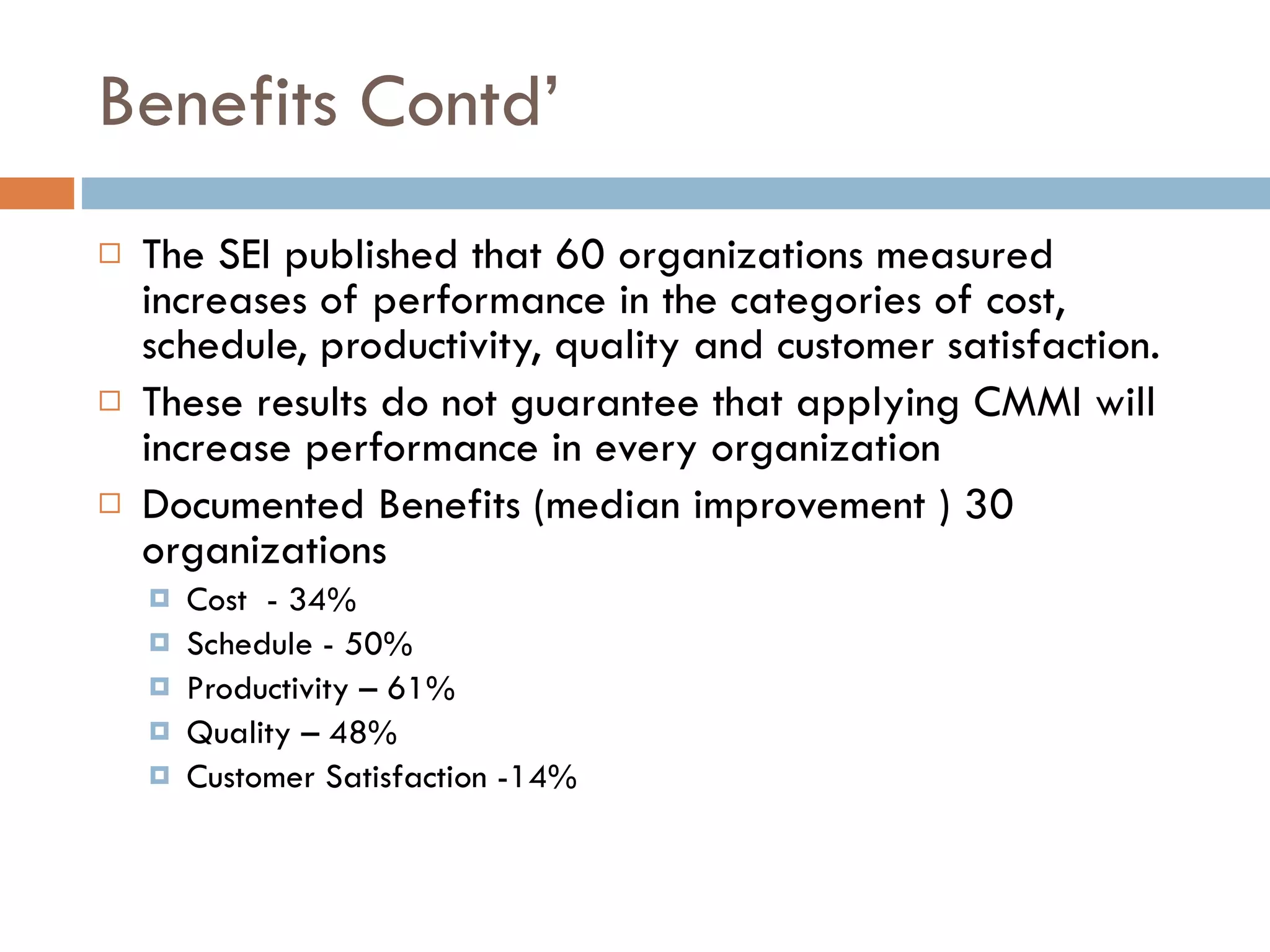
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) provides a framework for improving processes in organizations. It includes two types of levels - maturity levels and capability levels - to measure process improvement. There are two representations, staged and continuous, that allow organizations to measure improvement across predefined process areas or within individual process areas. Implementing CMMI best practices has proven benefits like improved schedule and budget predictability, increased productivity and quality, and reduced costs.