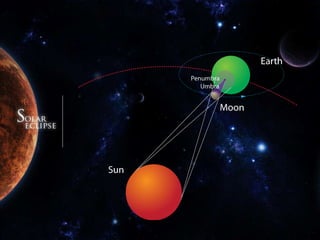
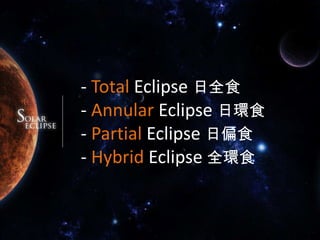
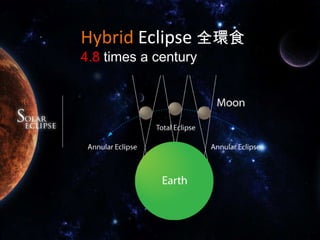
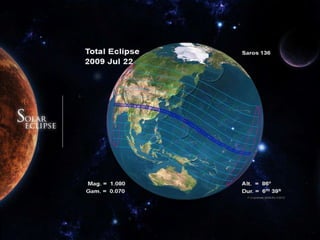
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the Earth and the sun, blocking the sun's light. There are typically 2-5 solar eclipses per year. There are four types of solar eclipses: total, annular, partial, and hybrid. A total solar eclipse, where the moon completely blocks the sun's light, occurs on average every 18 months and can only be seen from a narrow path on Earth. The longest total solar eclipse of the 21st century occurred on July 22, 2009 and lasted over 6 minutes. Special care must be taken to safely observe a solar eclipse by using eclipse glasses or other filters to view the sun.