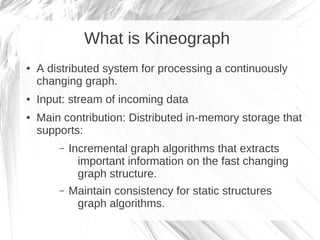
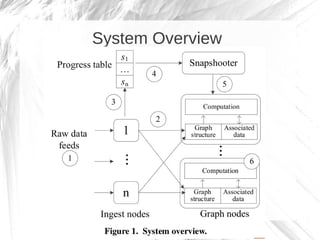
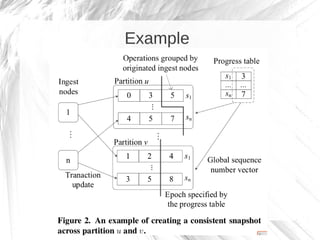
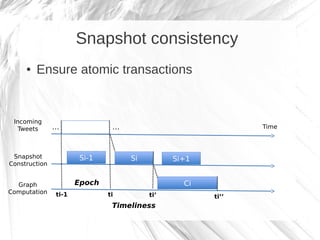
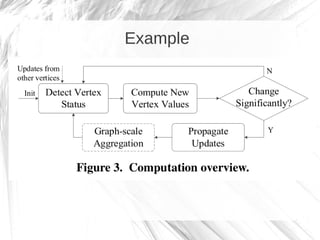
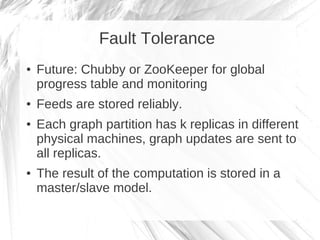
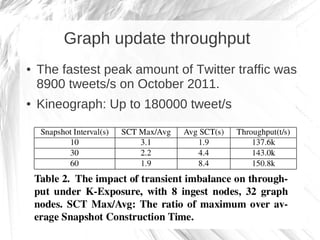
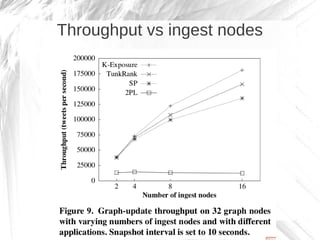
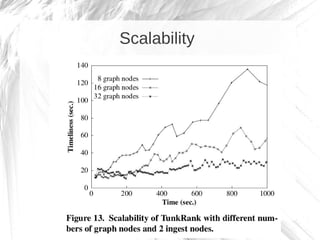
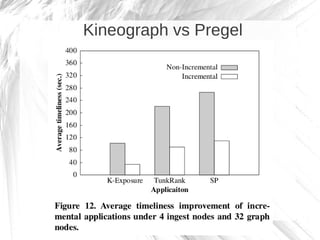
Kineograph is a distributed system for processing large and continuously changing graph structures in memory. It can ingest Twitter data at a rate of up to 100,000 tweets per second on a 40 machine cluster. Kineograph separates graph processing from graph updates to provide consistent snapshots of the graph for analysis. It uses a log-structured approach to distribute graph updates across partitions and sequence them to ensure consistency. Initial results show it can process over 100,000 tweets per second and scales linearly by adding more ingestion nodes.