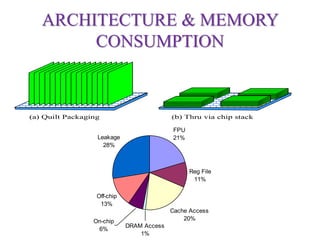
Exascale computing refers to systems capable of performing 1 quintillion (1018) calculations per second, which is 1000 times more powerful than the first petascale computers. The goals of exascale are to develop systems by 2018 that can perform simulations with greater precision and speed. Such systems will require new architectures and memory designs to handle the power and reliability challenges at this scale. GPUs and new low-power processors will be important for exascale computing.