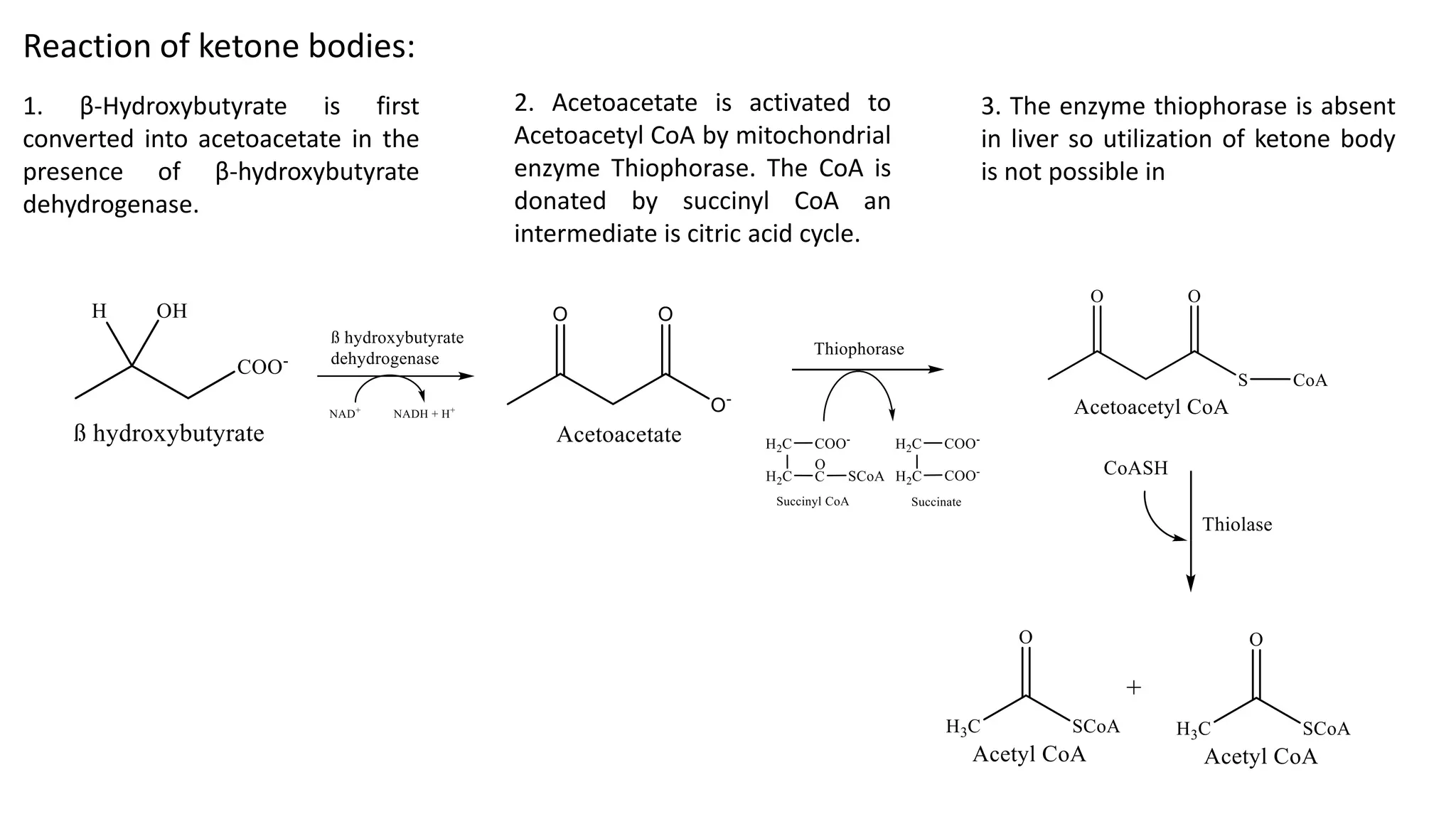
Ketone bodies (acetone, acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate) are produced in the liver through a process called ketogenesis when fatty acids are broken down. They can be used by tissues like muscle and heart as an energy source, especially during periods of low glucose such as fasting or diabetes. Ketone bodies are converted back to acetyl-CoA in tissues through a series of reactions. High levels of ketone bodies can cause ketoacidosis, lowering the pH of the blood, which is dangerous and requires treatment with insulin.