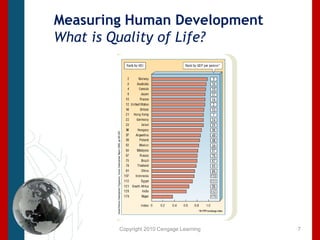
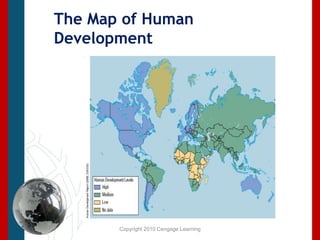
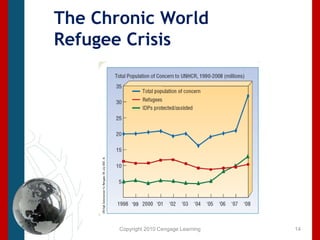
This document discusses concepts related to human rights such as ethics, morality, civil society, and sanctions. It then examines the human condition globally, particularly in the global south, using metrics like poverty rates, life expectancy, and access to resources. It also discusses measures of human development through indices that evaluate factors like income, education, and health. Overall, it provides an overview of the status of human rights internationally, challenges faced in different regions, and approaches to protecting human rights globally.