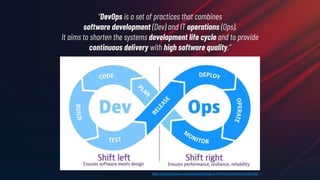
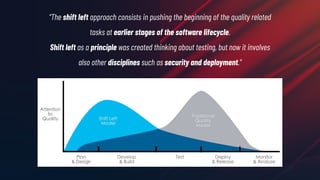
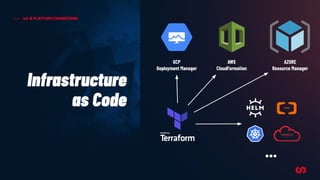
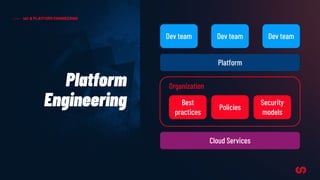
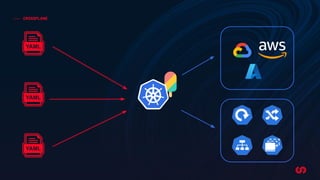
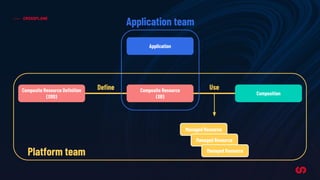
The document discusses the concept of application-driven infrastructure using Crossplane, emphasizing the importance of DevOps practices such as shift-left and shift-right methodologies in the software lifecycle. It explains how Crossplane allows platform teams to create higher-level self-service APIs for developers, improving automation, consistency, and collaboration across infrastructure management. Additionally, it highlights Crossplane's ability to manage resources as part of the Kubernetes ecosystem, although it notes the complexity and development stage of its providers.