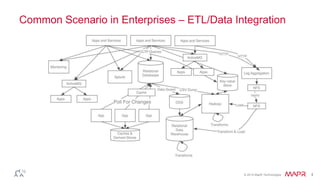
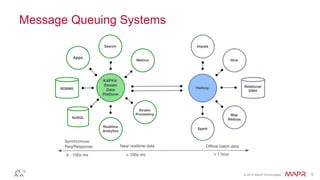
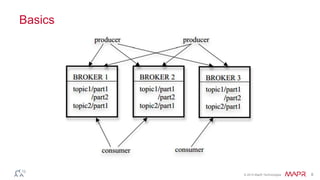
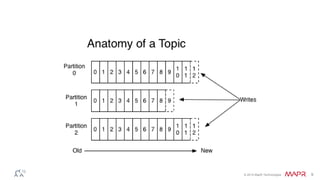
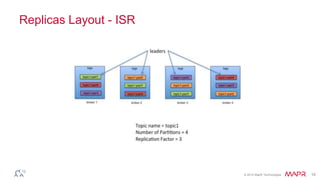
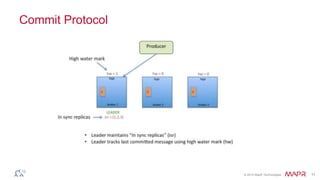
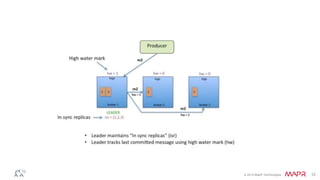
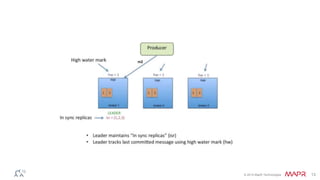
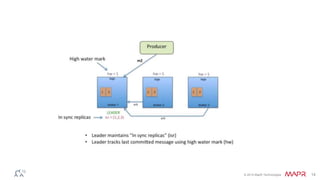
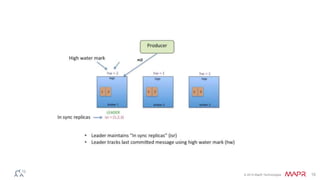
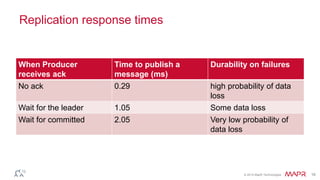
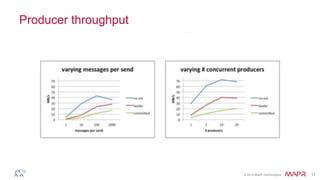
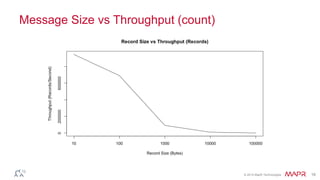
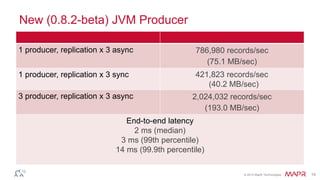
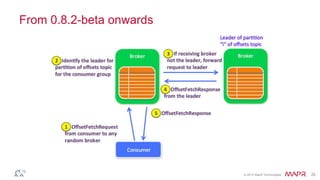
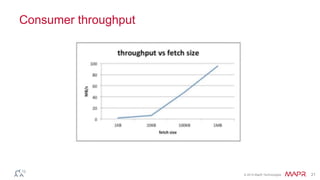
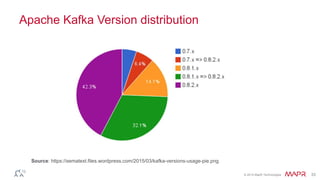
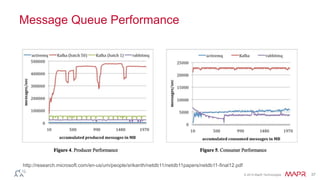
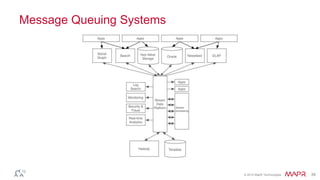
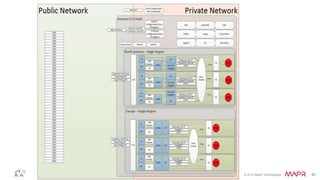
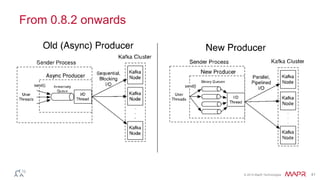
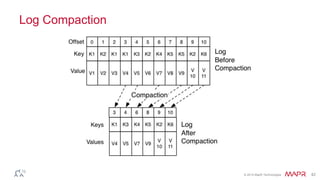
This document discusses Apache Kafka and message queuing systems. It provides an overview of Kafka, including how producers and consumers work, and details on topics, partitions, and Zookeeper. It then discusses performance, production issues, and what improvements are planned for future Kafka releases. The document also reviews the Kafka community and integrations with other technologies.