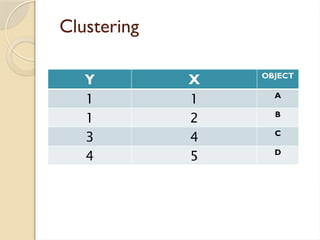
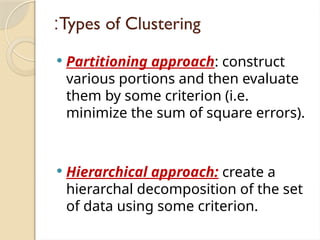
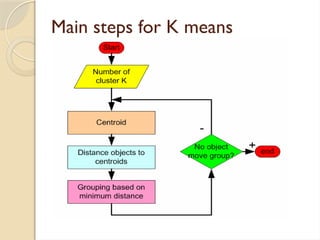
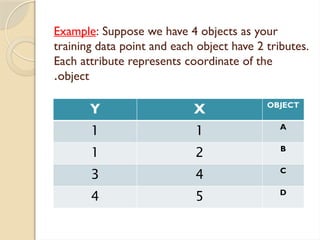
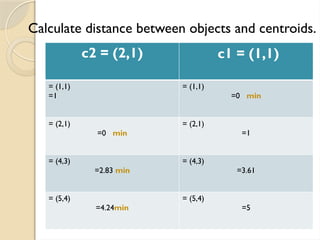
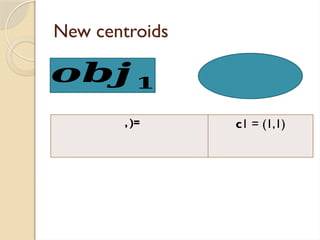
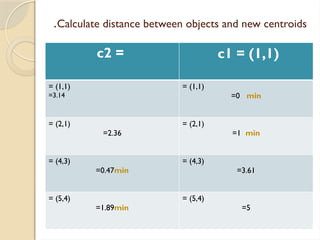
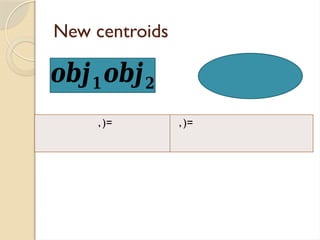
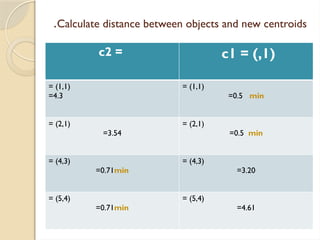
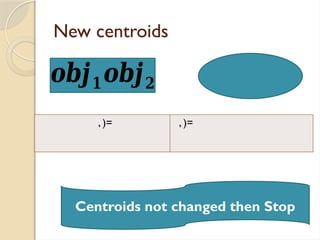
Clustering is an unsupervised learning process that partitions data into similar subsets, with methods including partitioning and hierarchical approaches. K-means clustering is a centroid-based algorithm that groups data points into k clusters by minimizing the distance within clusters, using distance metrics like Euclidean and Manhattan distances. Key steps in this process involve selecting initial centroids, assigning data points to clusters based on distance, and recalculating centroids until convergence.