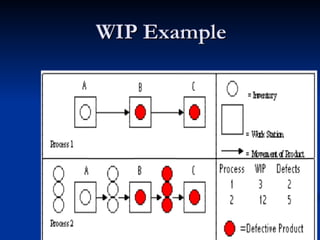
The document summarizes Kanban signals and the Kanban system. As a customer pulls an order, signals are sent through the production process to replenish parts. Signals move from finished goods to final assembly and then to suppliers. Advantages include providing precise information with low costs and quick response to changes while avoiding overproduction and waste.