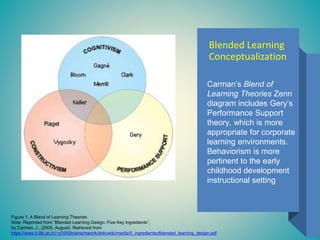
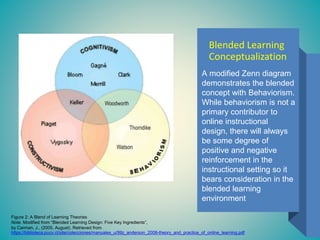
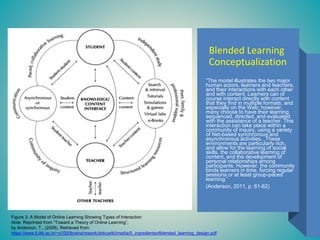
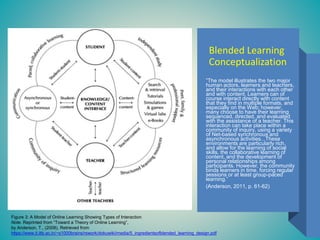
This document discusses planning for instruction using different learning theories. It summarizes a kindergarten math lesson plan on money using constructs of cognitivism, behaviorism, and a blended approach. The author determines that a blended learning approach combining elements of multiple theories is best suited for their online instructional setting. This includes using Gagne's nine events of instruction, synchronous/asynchronous learning, and models that address the unique needs of distance learning like social-emotional learning. The author conceptualizes their blended approach using diagrams integrating constructs from various theories to support online instructional design.