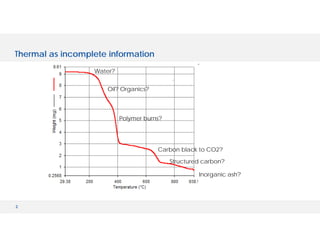
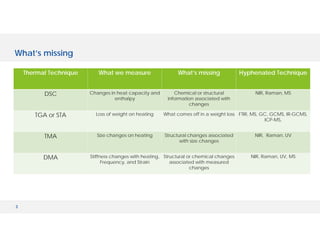
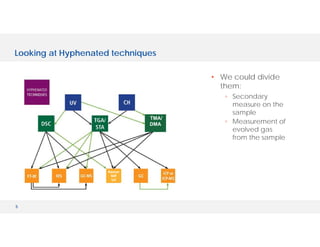
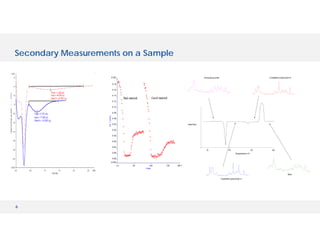
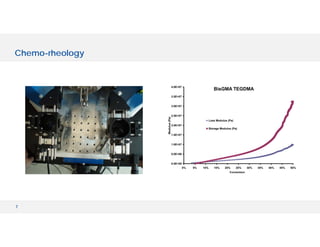
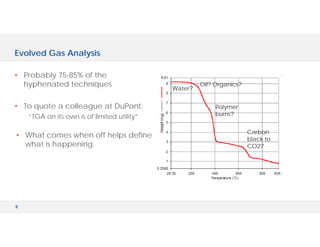
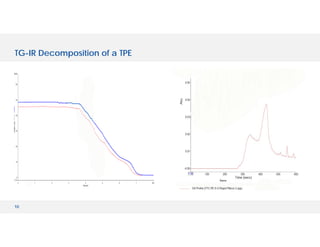
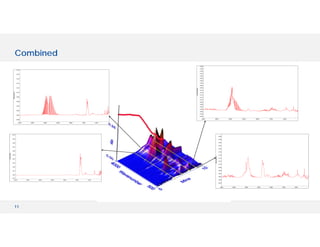
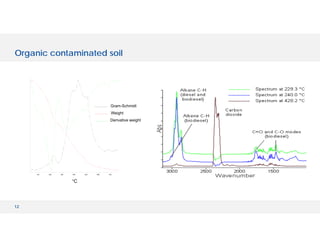
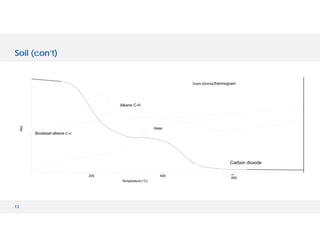
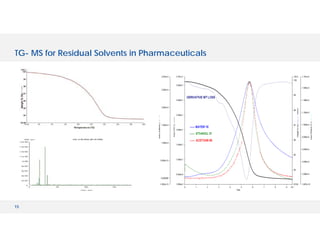
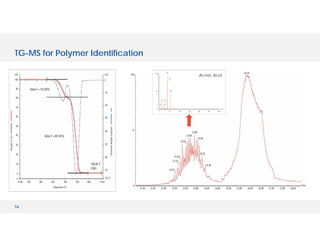
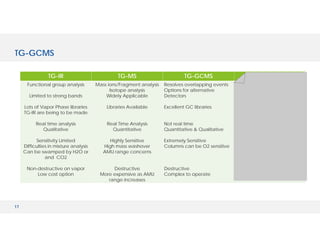
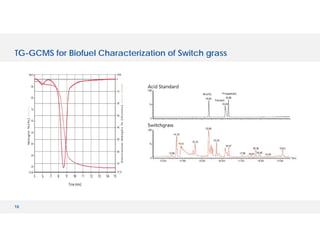
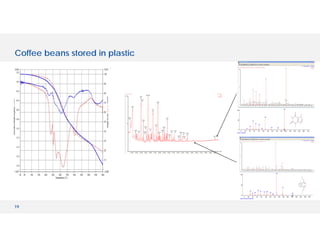
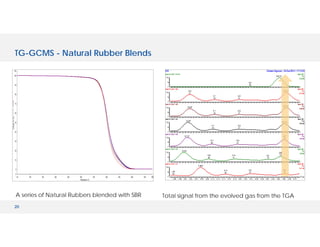
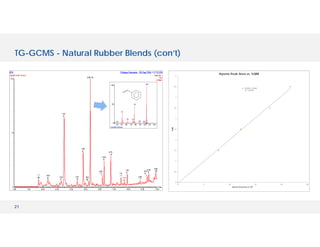
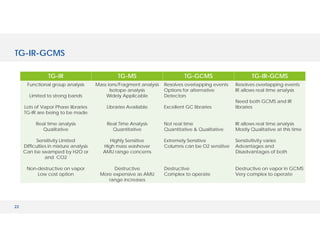
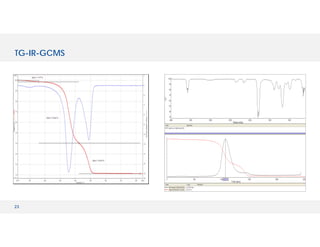
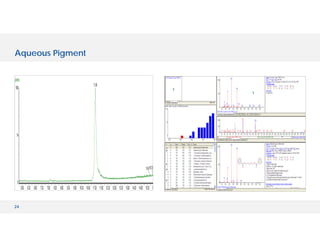
The document discusses various hyphenated thermal analysis techniques and their applications in material characterization. It outlines historical developments in these techniques, detailing the strengths and limitations of methods such as TG-MS, TG-IR, and TG-GCMS. Additionally, it highlights the importance of evolved gas analysis and the significance of secondary measurements in understanding material properties.