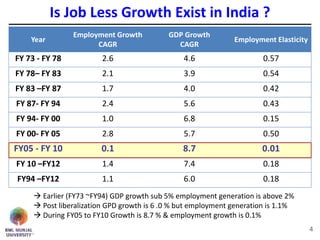
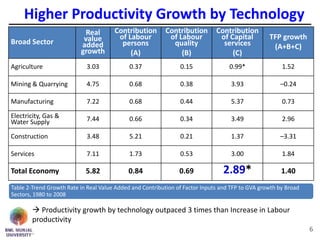
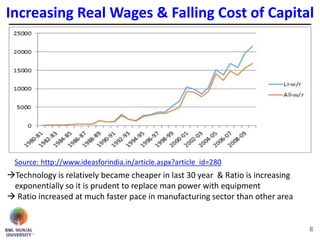
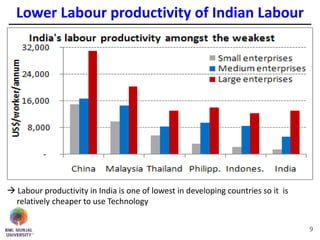
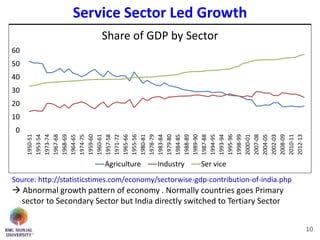
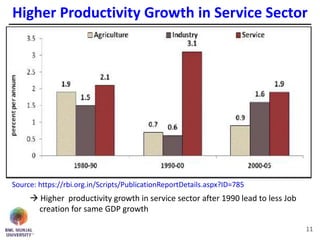
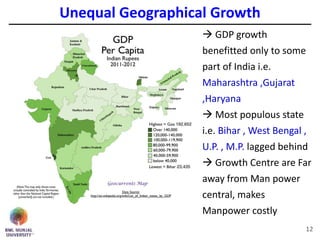
The document discusses jobless growth in India after economic liberalization. It summarizes employment growth and GDP growth from 1956 to 2012, showing that while GDP growth increased after 1994, employment growth declined. Several reasons for jobless growth are provided: higher productivity growth through technology outpacing labor productivity increases; increasing real wages and falling costs of capital making technology replacement of labor more viable; lower labor productivity in India; service sector-led growth rather than growth in manufacturing; and unequal geographical growth benefiting some states more than others. Proposed solutions to promote job creation include focusing on skill development, labor law reforms, promoting labor-intensive sectors, supporting MSMEs and free movement of labor.