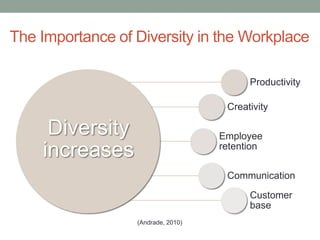
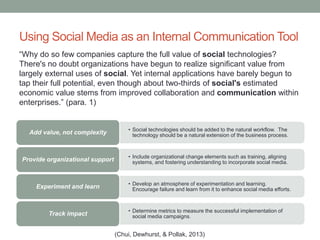
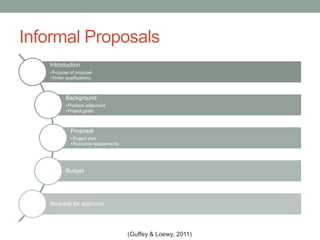
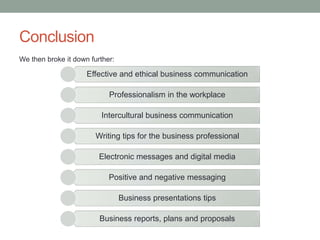
This document provides an overview of best practices in business writing and communication. It discusses enhancing the workplace through effective communication, communicating effectively, and various communication tools. Specific topics covered include the definition of business communication, elements of effective communication, ethical communication principles, active listening, intercultural communication, diversity in the workplace, writing tips, using electronic messages and social media, delivering presentations, and writing reports and proposals.